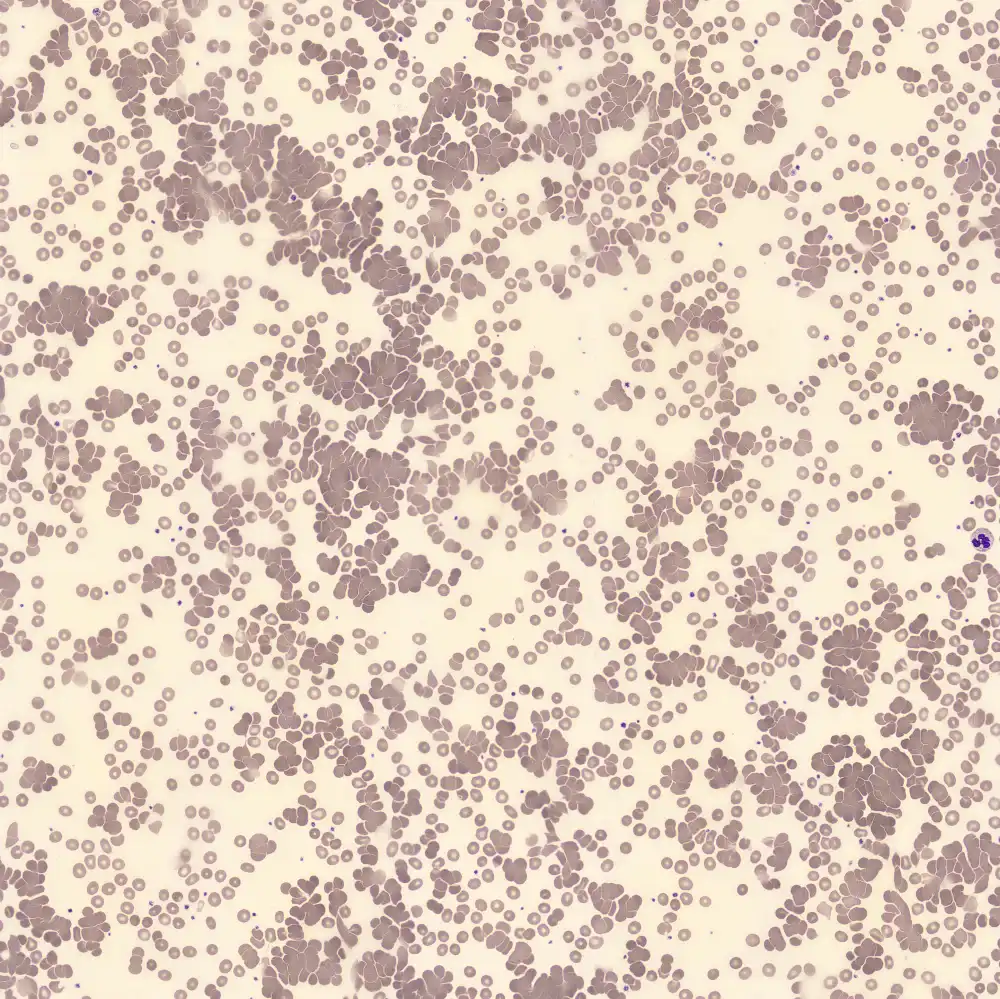
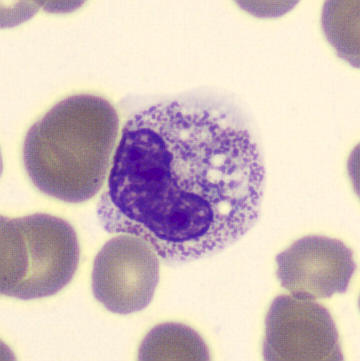
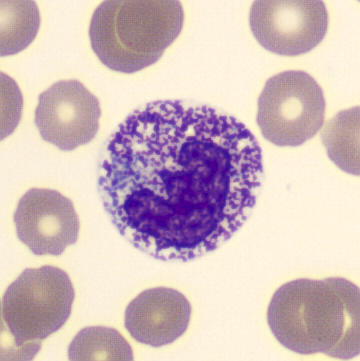
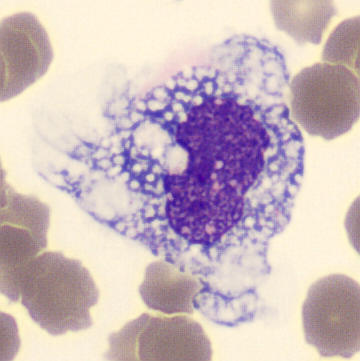
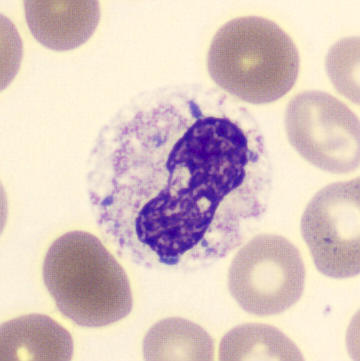
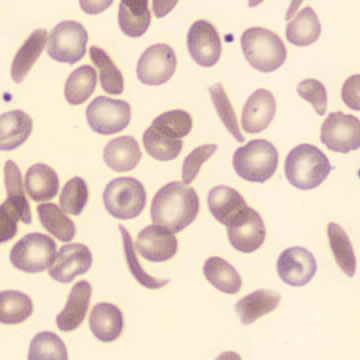
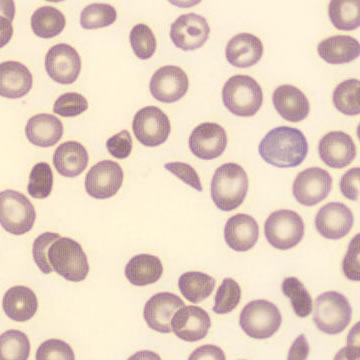
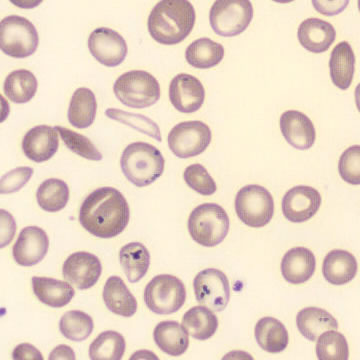
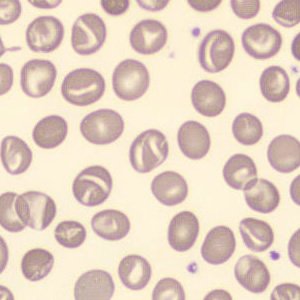
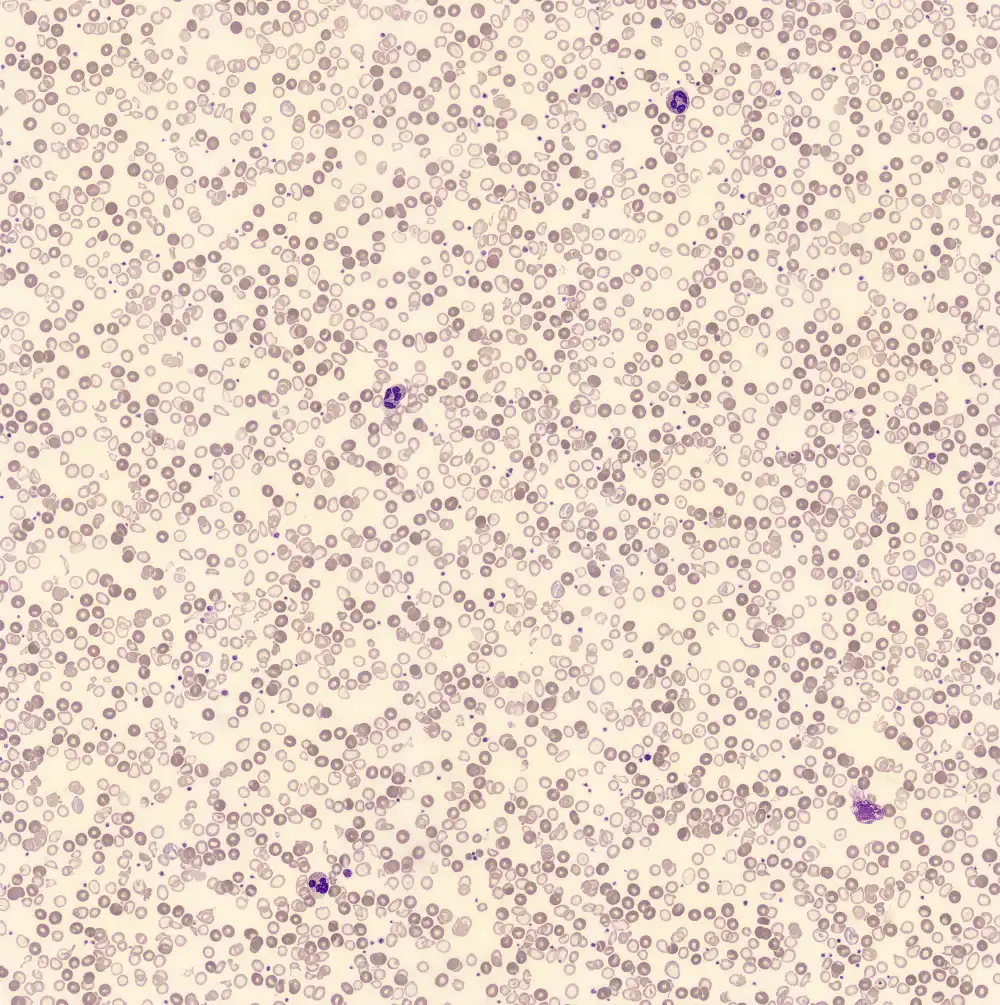
Perfringens - Slide 1
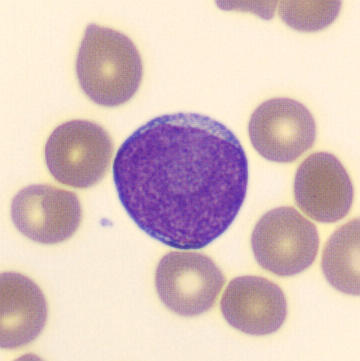
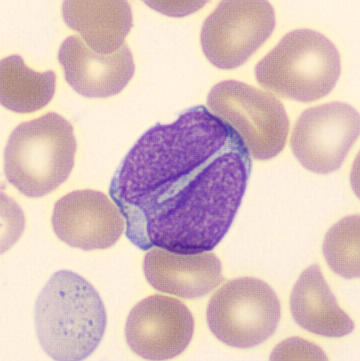
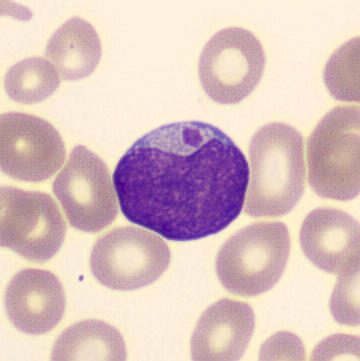
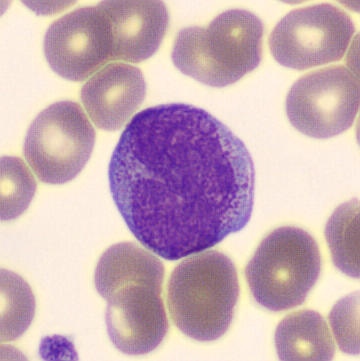
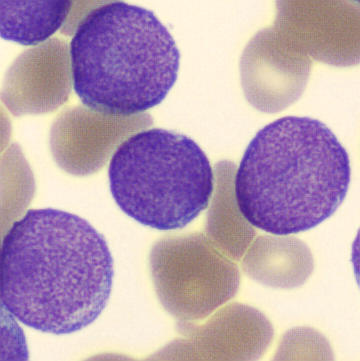
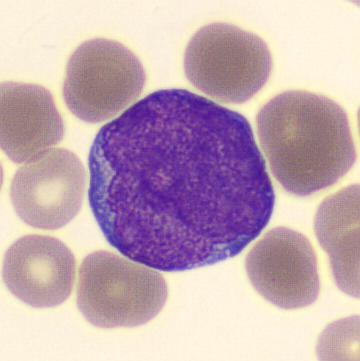
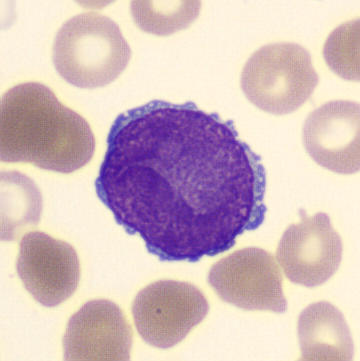
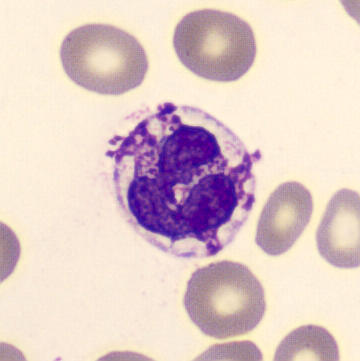
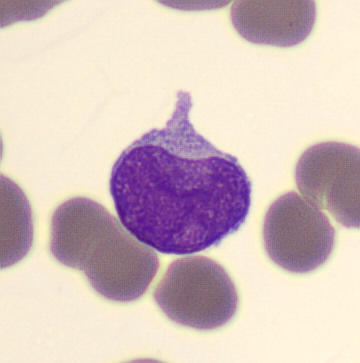
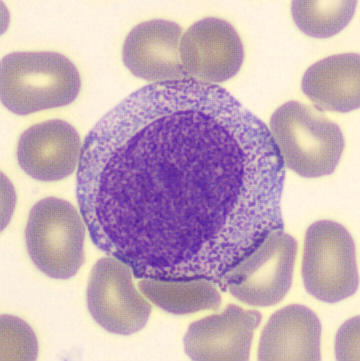
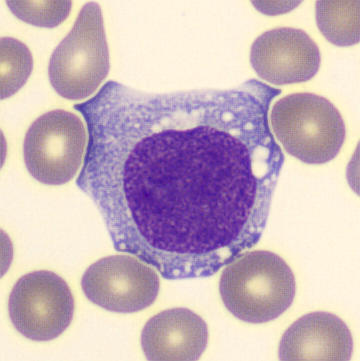
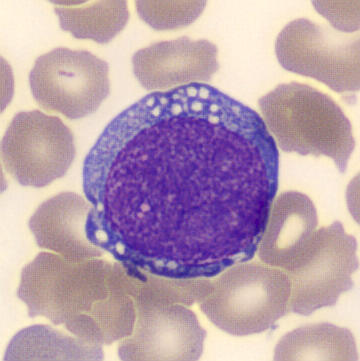
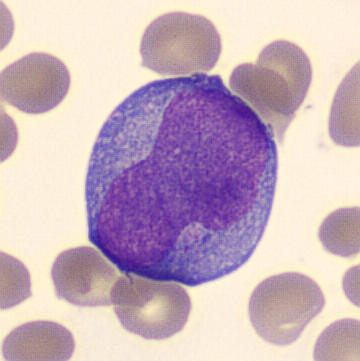
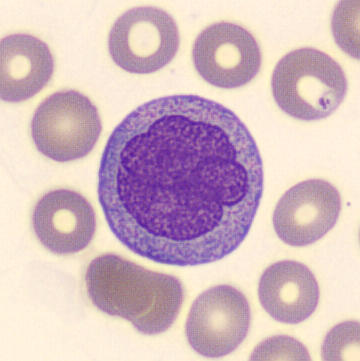
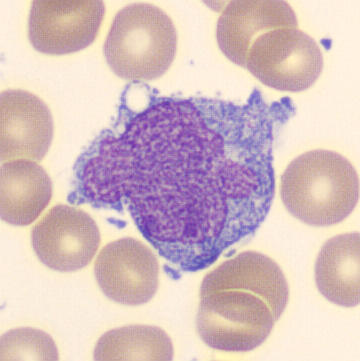
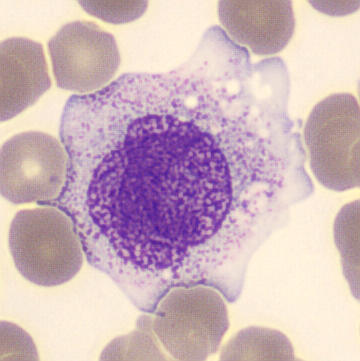
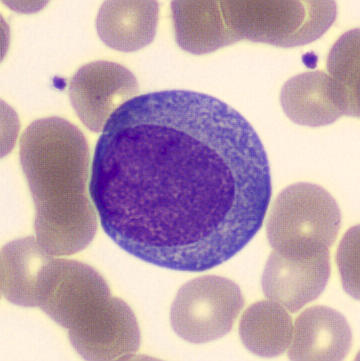
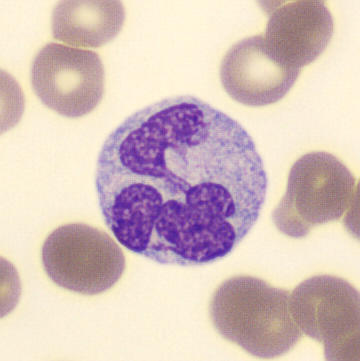
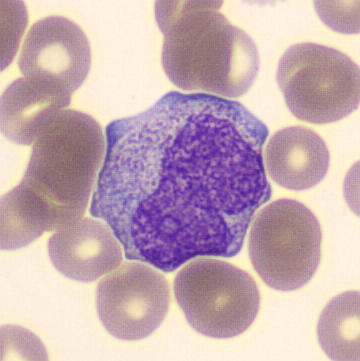
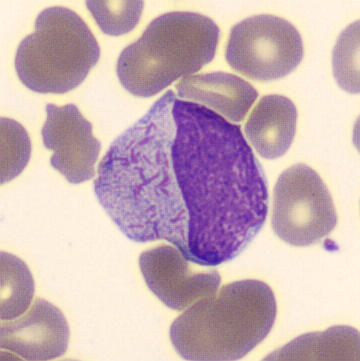
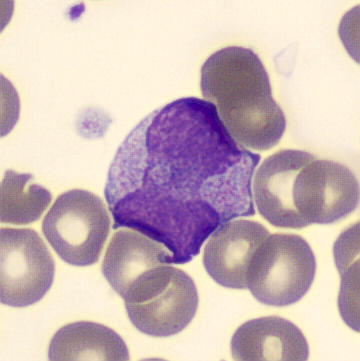
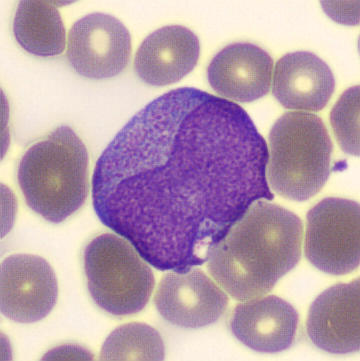
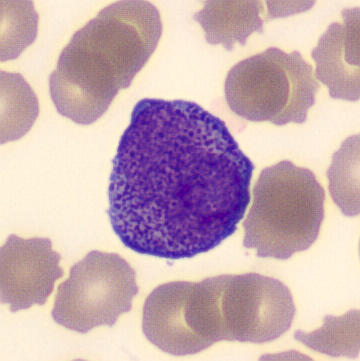
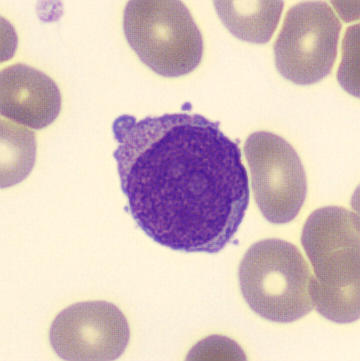
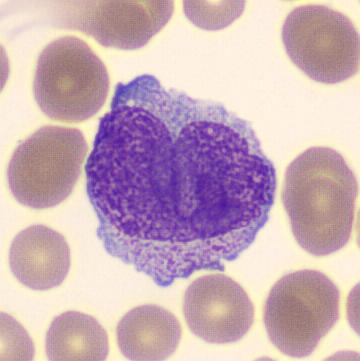
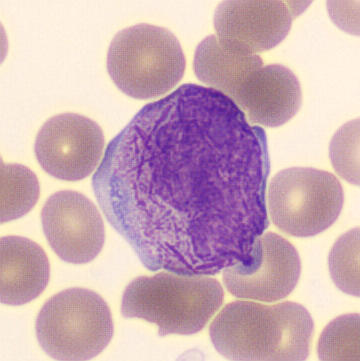
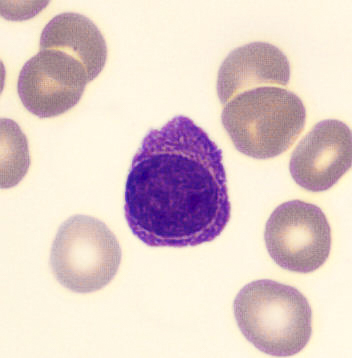
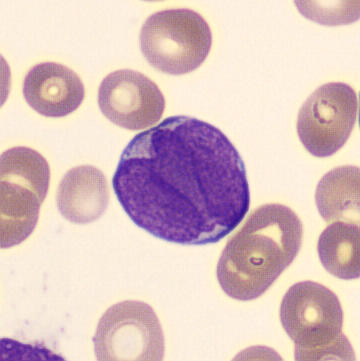
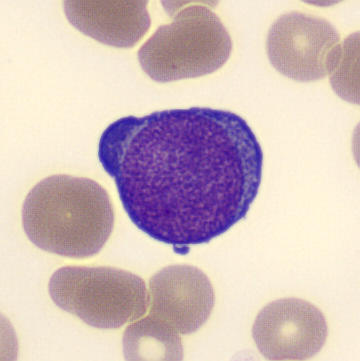
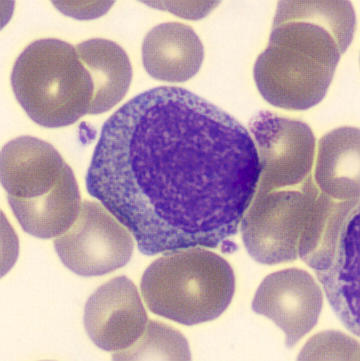
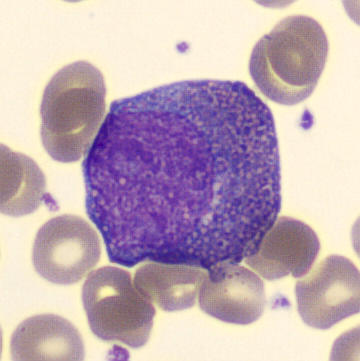
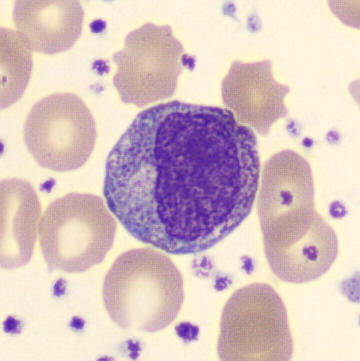
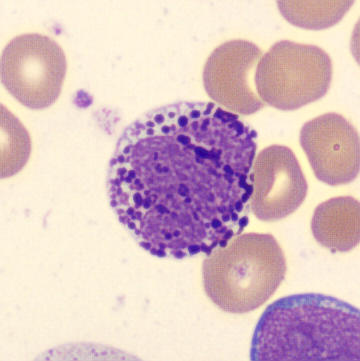
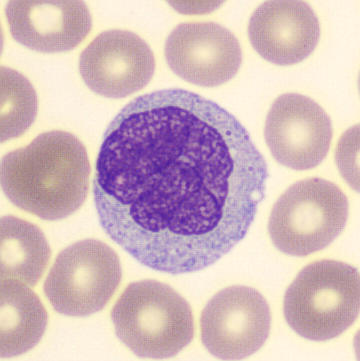
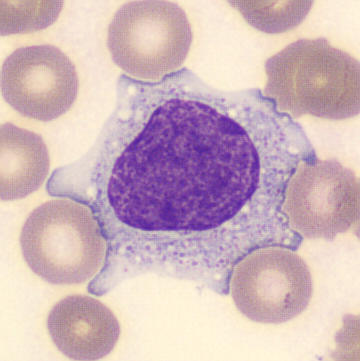
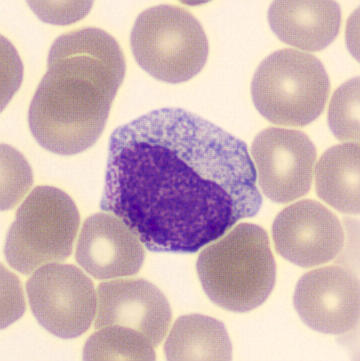
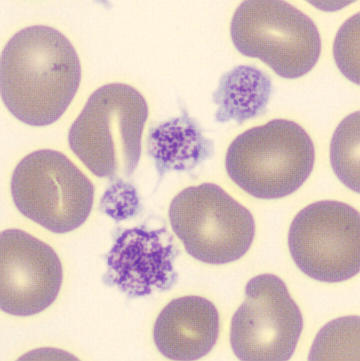
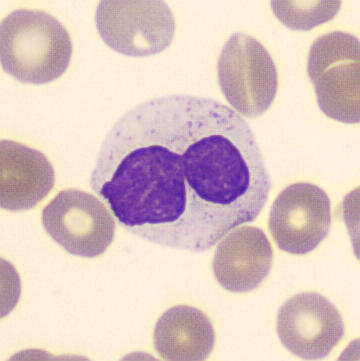
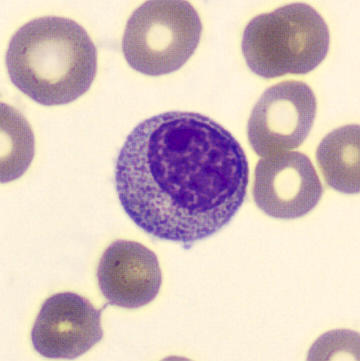
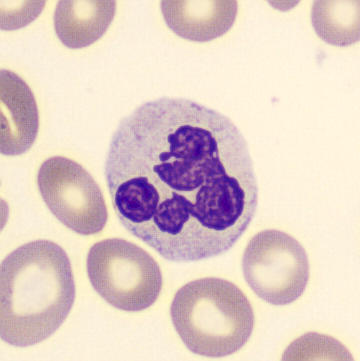
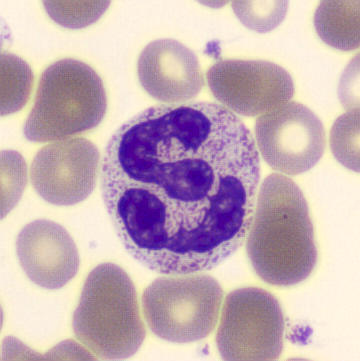
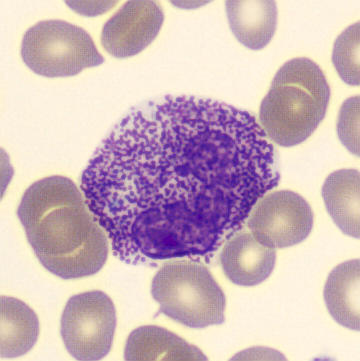
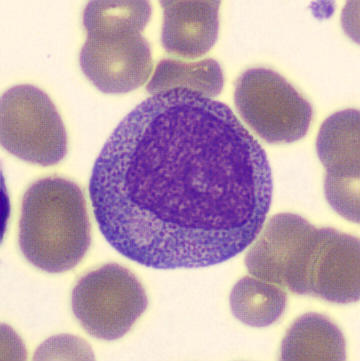
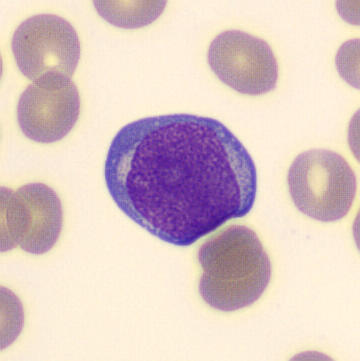
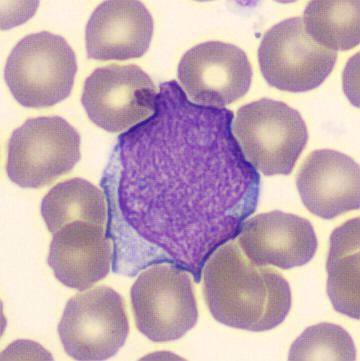
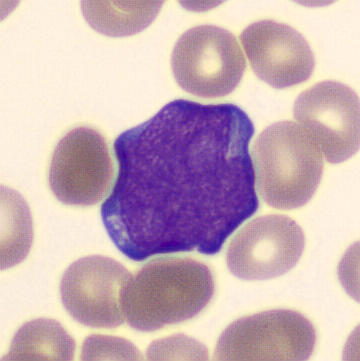
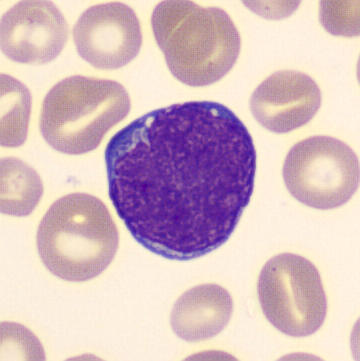
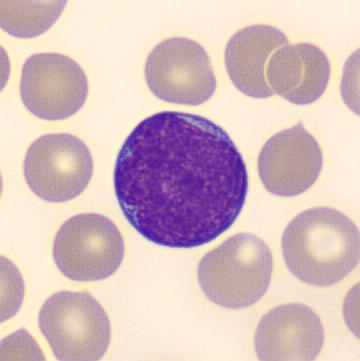
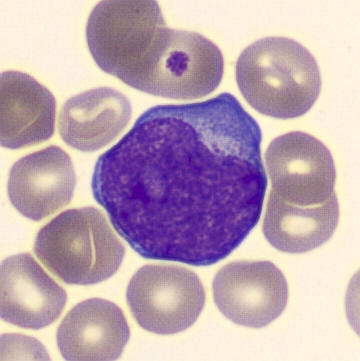
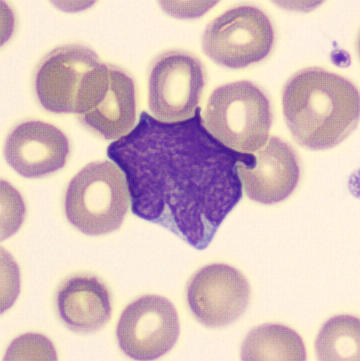
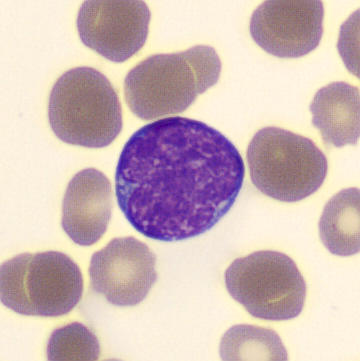
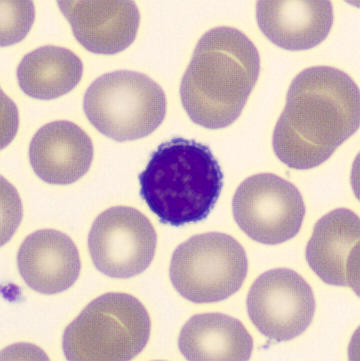
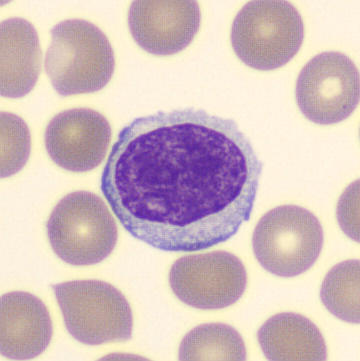
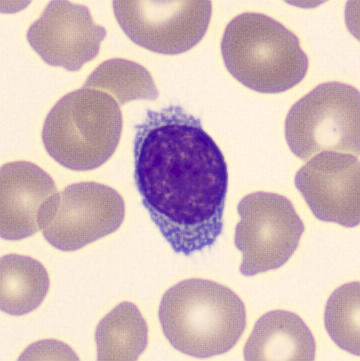
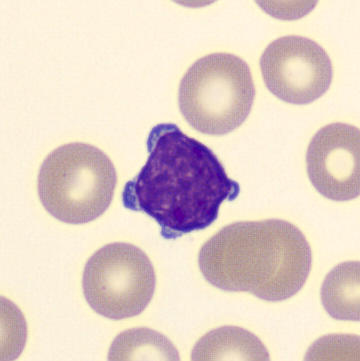
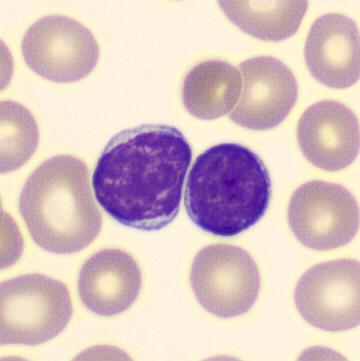
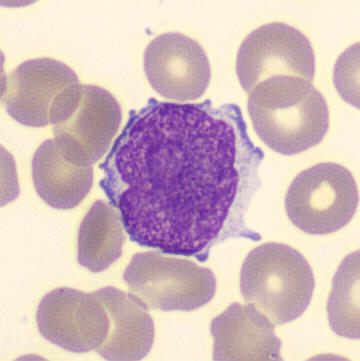
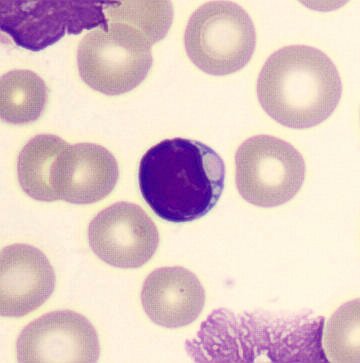
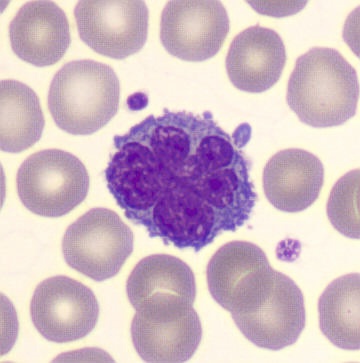
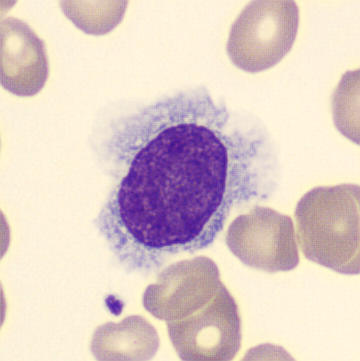
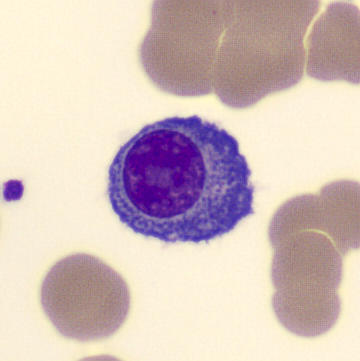
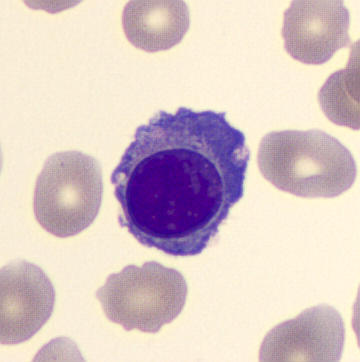
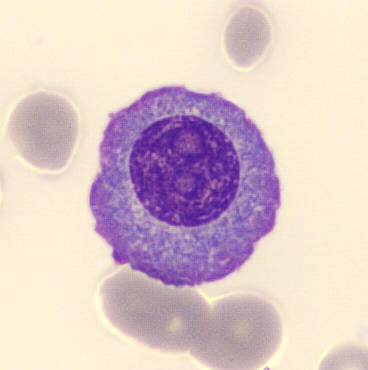
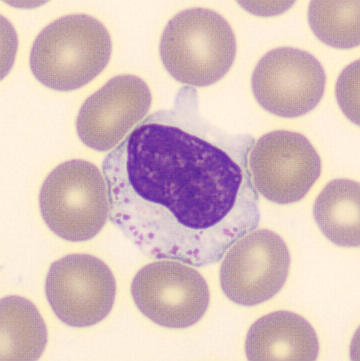
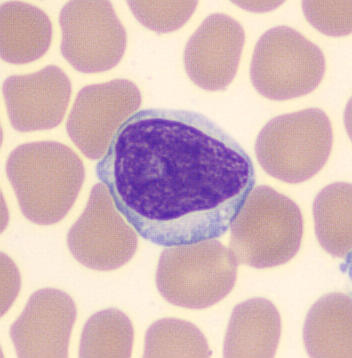
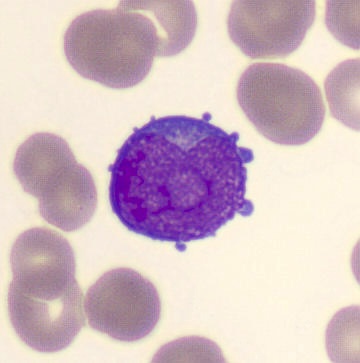
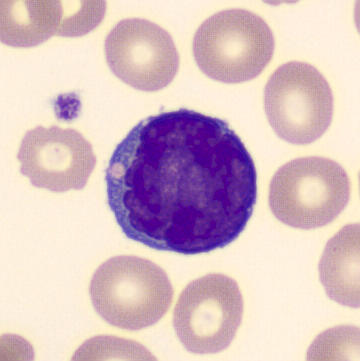
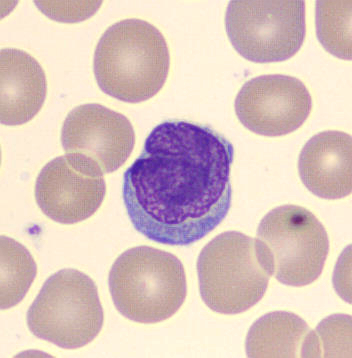
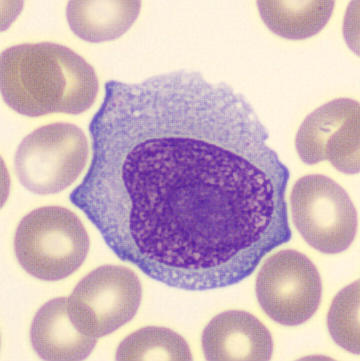
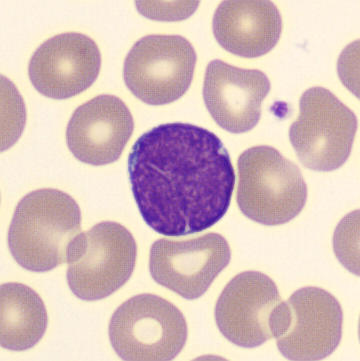
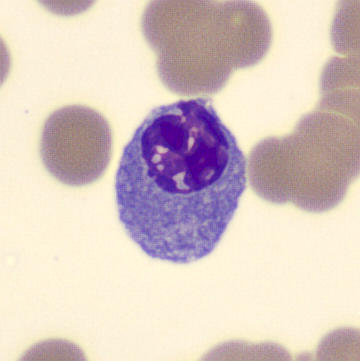
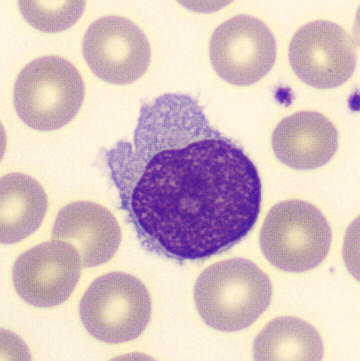
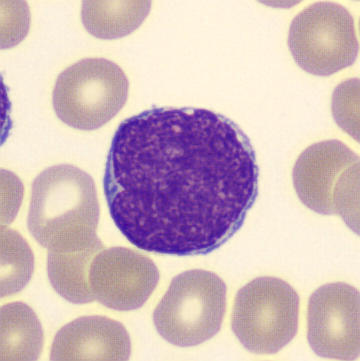
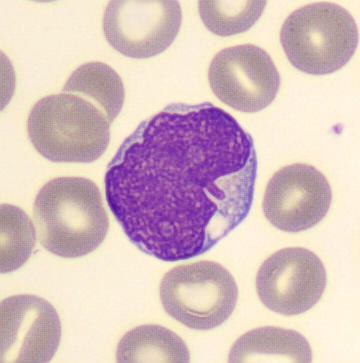
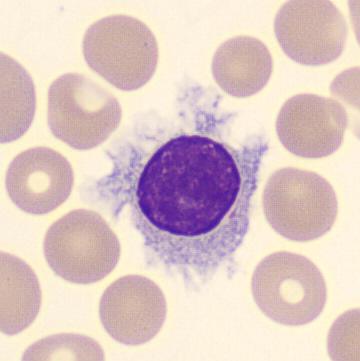
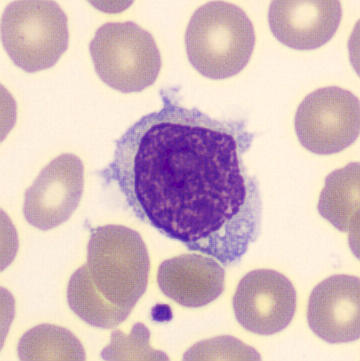
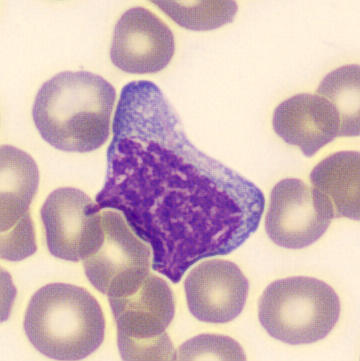
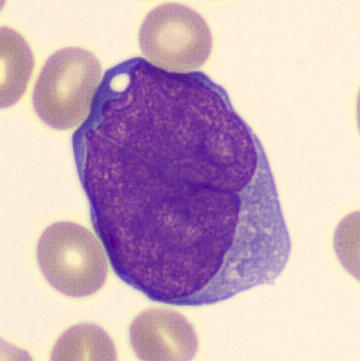
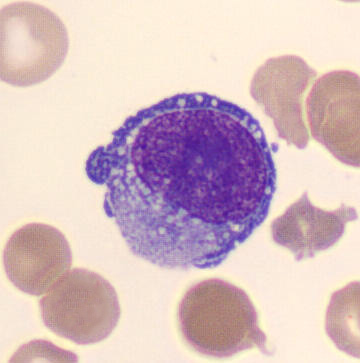
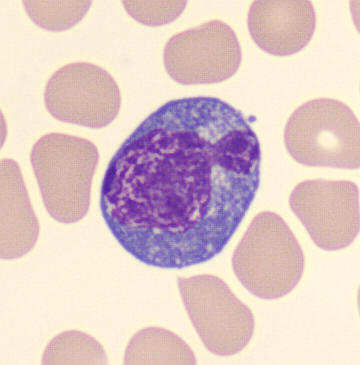
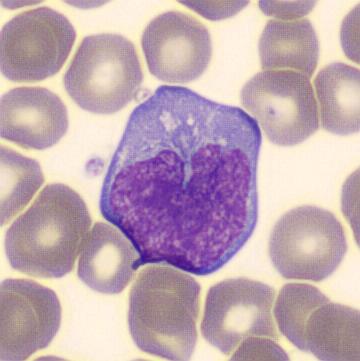
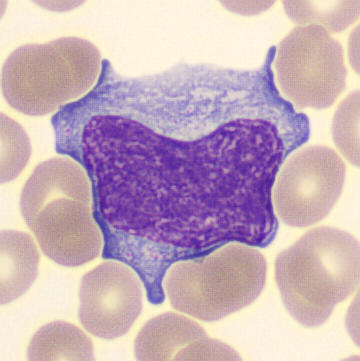
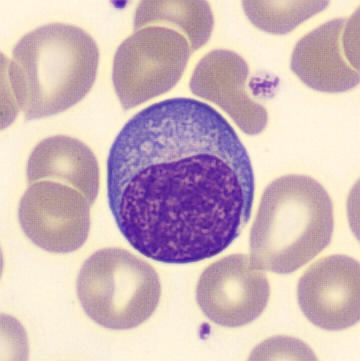
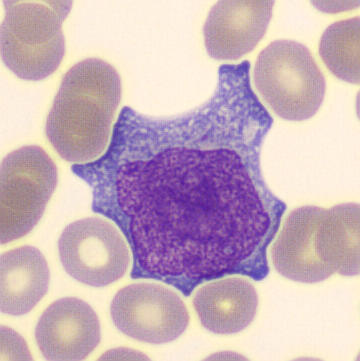
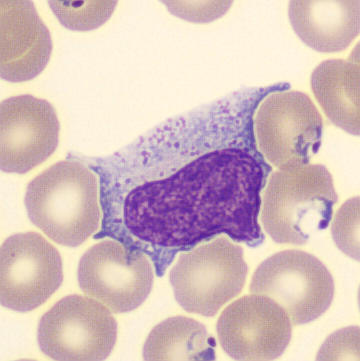
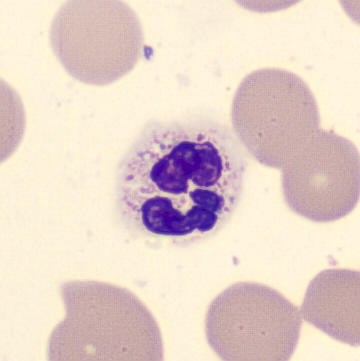
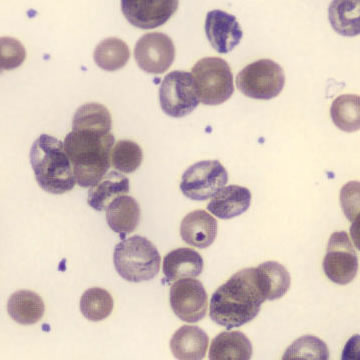
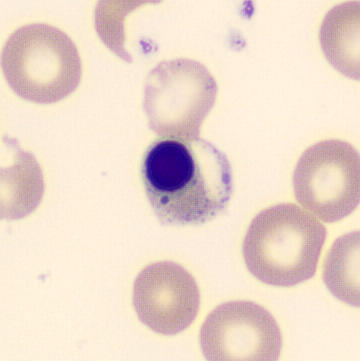
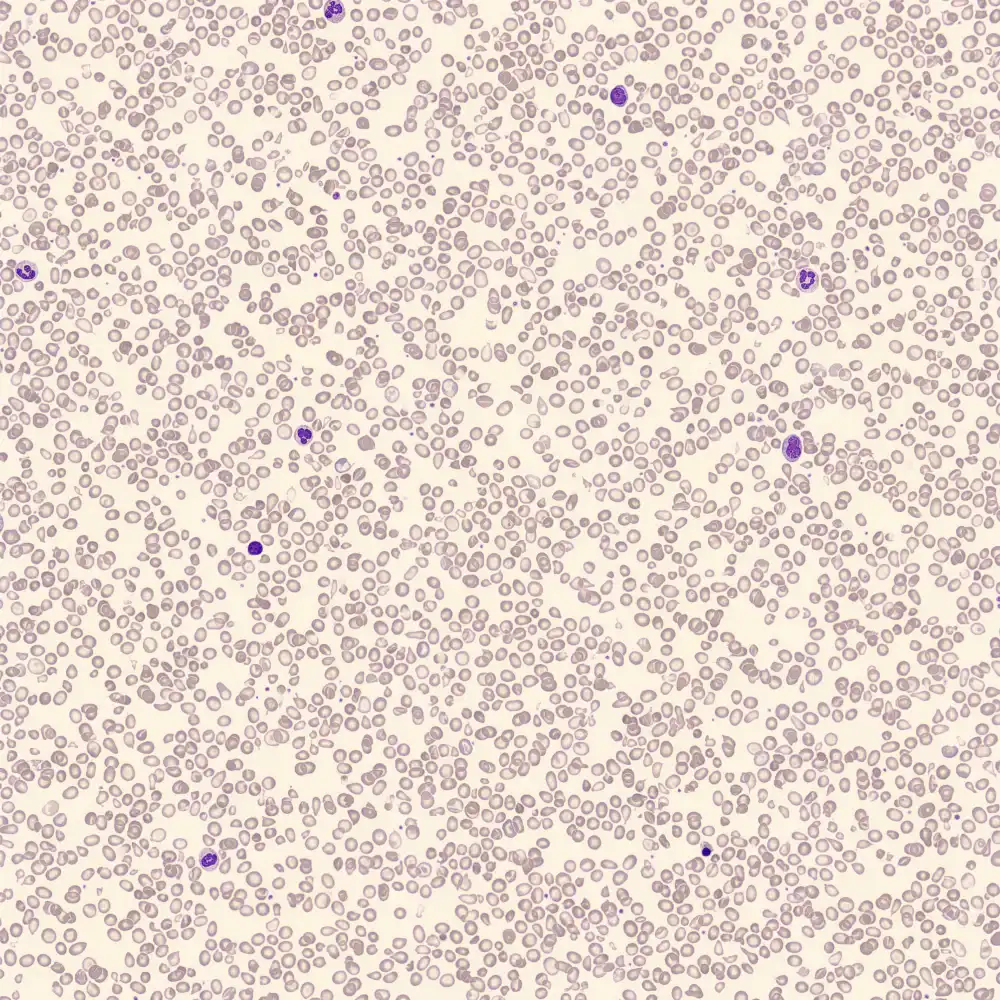
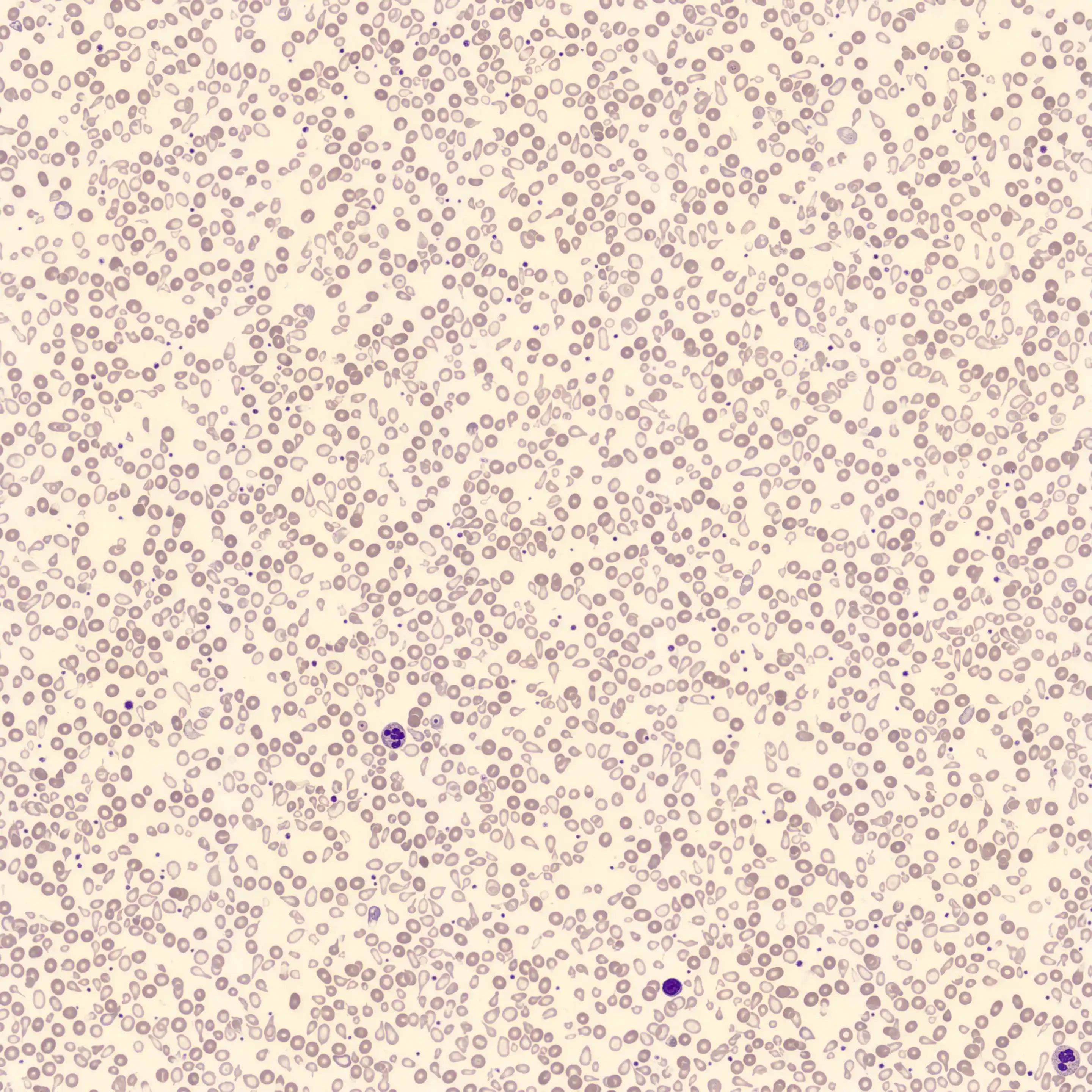
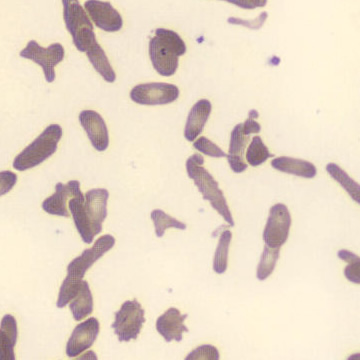
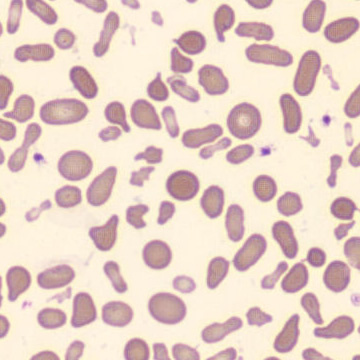
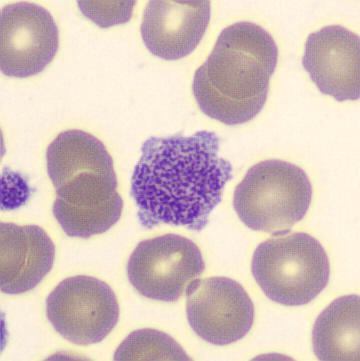
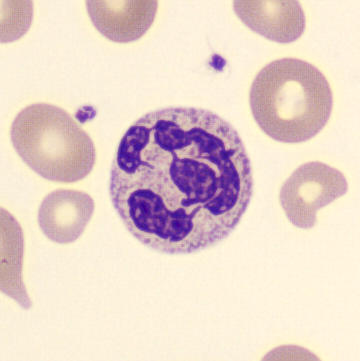
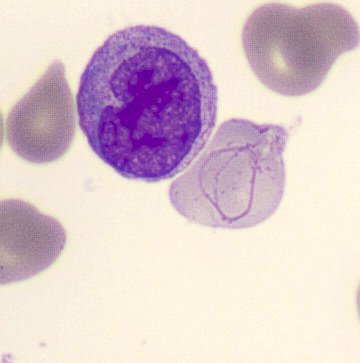
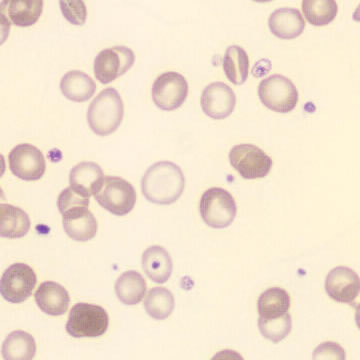
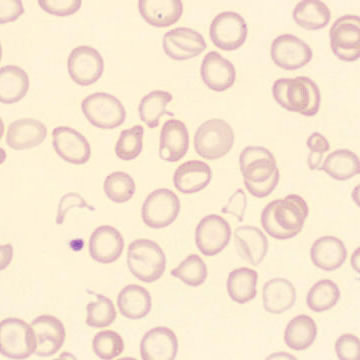
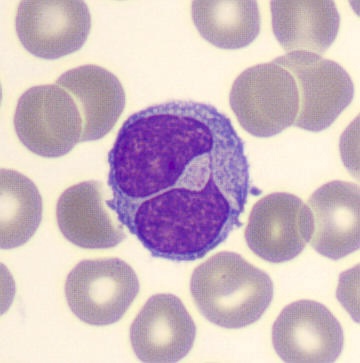
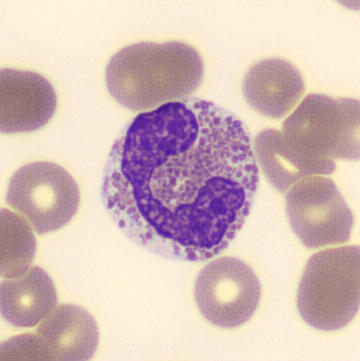
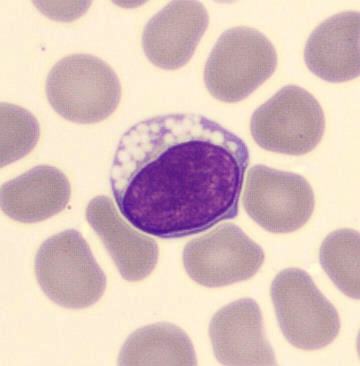
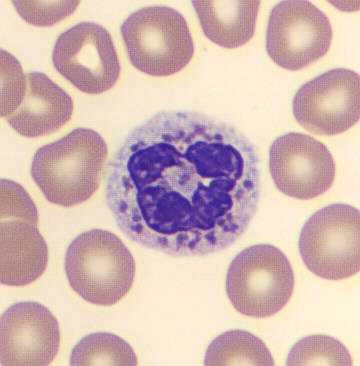
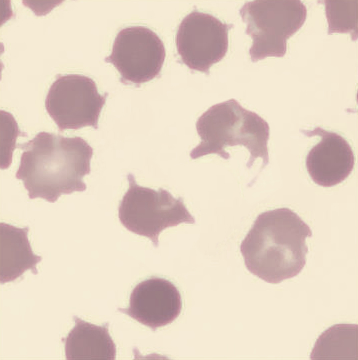
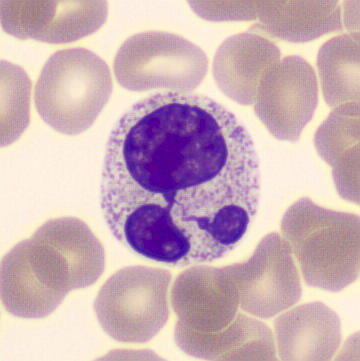
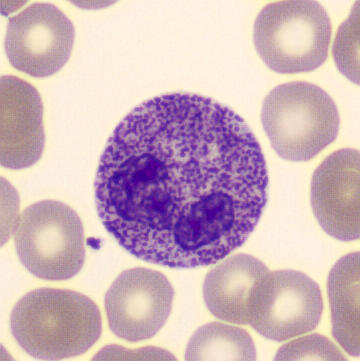
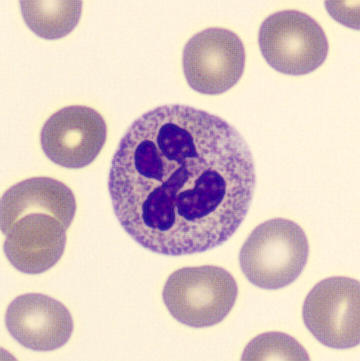
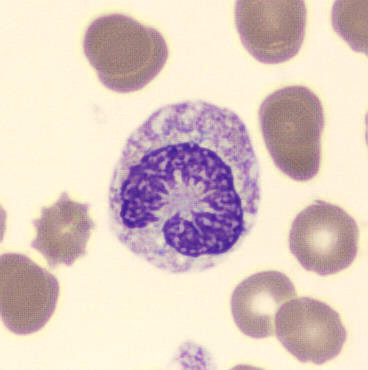
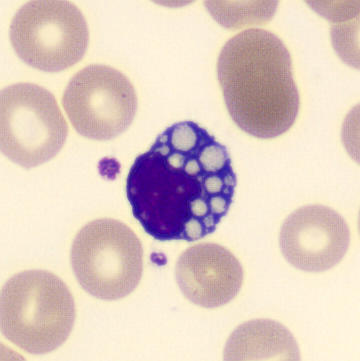
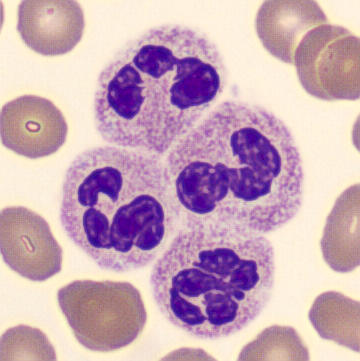
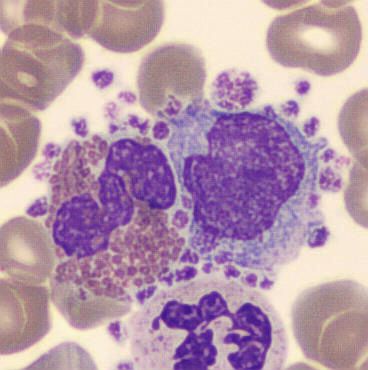
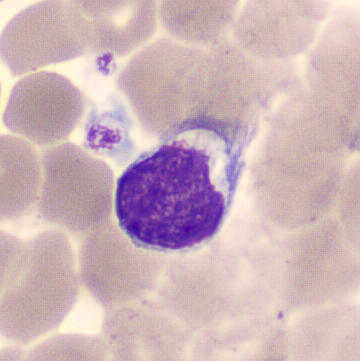
Preparation of a patient with Clostridium Perfringens sepsis. Typical of this bacterial infection are the deflated erythrocytes, also called ghost cells. These are caused by the toxin produced by the bacteria. This toxin breaks down cell walls leading to tissue destruction and massive hemolysis. In addition to the atypical erythrocytes, a highly reactive left shift is seen in which almost every neutrophil has vacuoles. See the case report for more background.
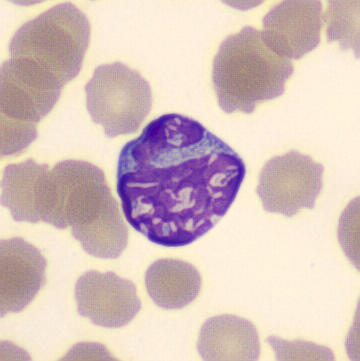
Promyelocytes
Myelocytes
Metamyelocytes
Segments
Bands
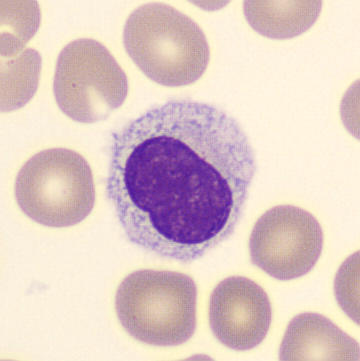
Lymphocytes
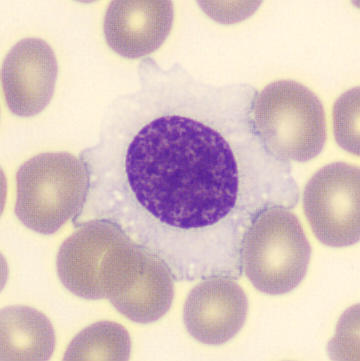
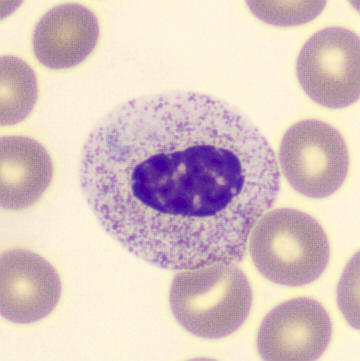
Monocytes
XN Scatterplots
Peripheral blood
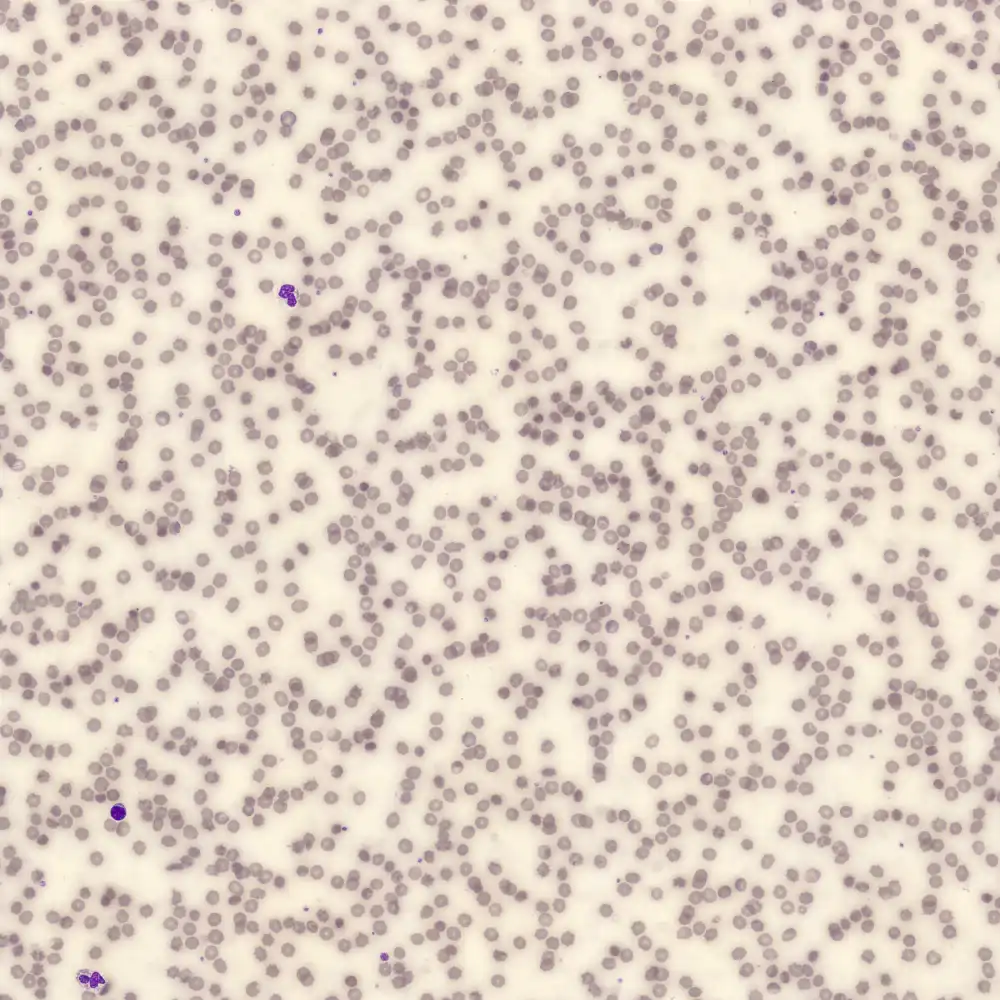
Ghostcells
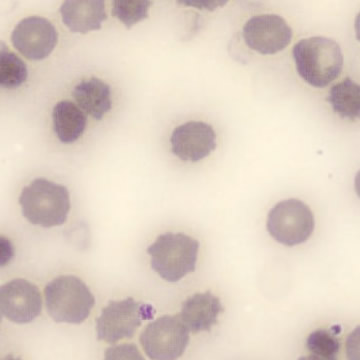

Promyelocytes

Myelocytes

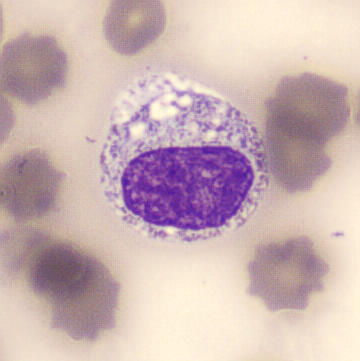

Metamyelocyte
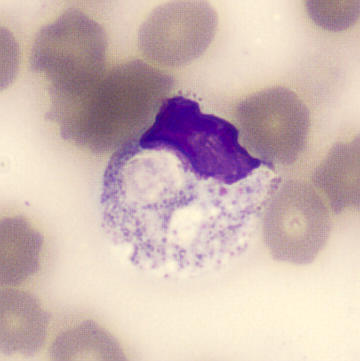


Bands

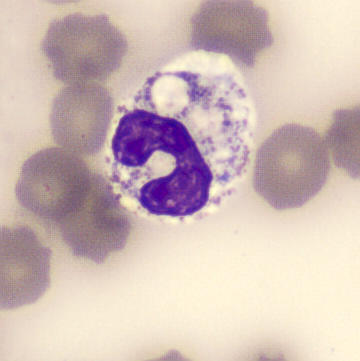
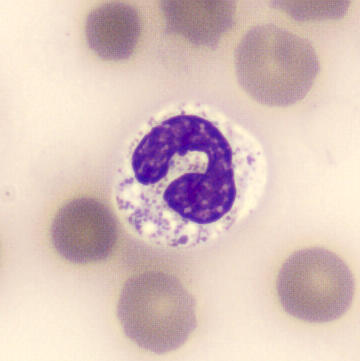
Segments