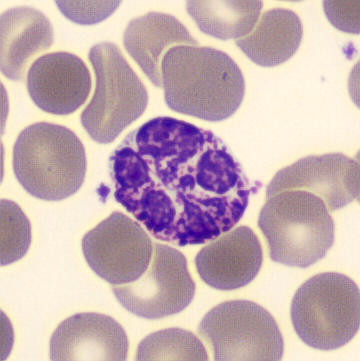
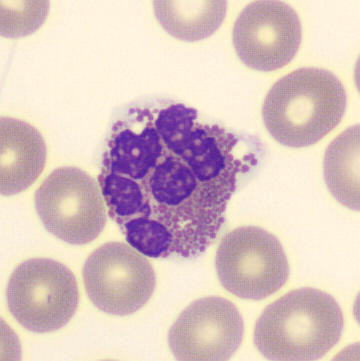
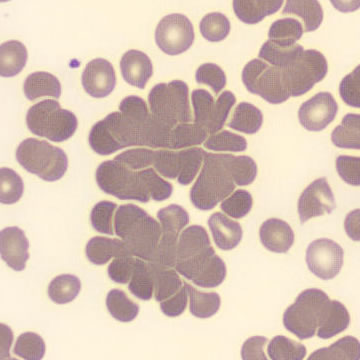
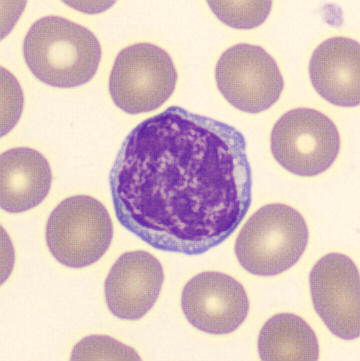
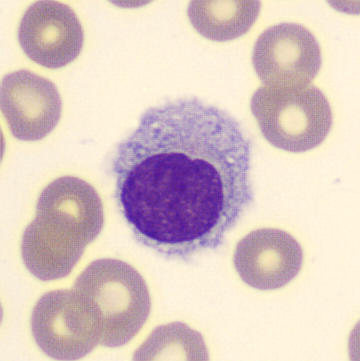
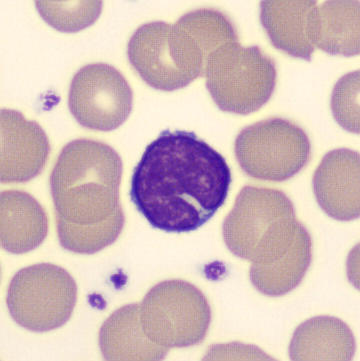
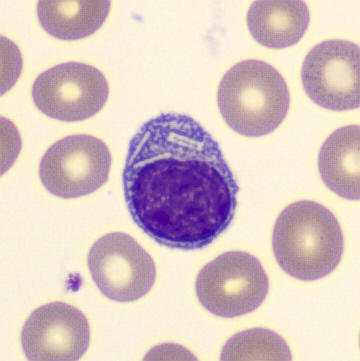
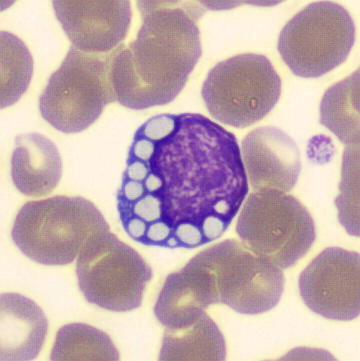
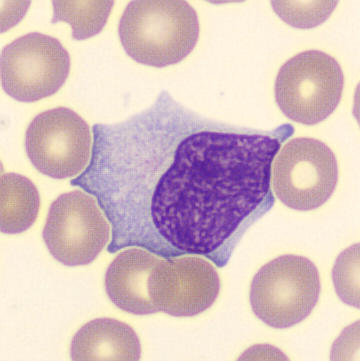
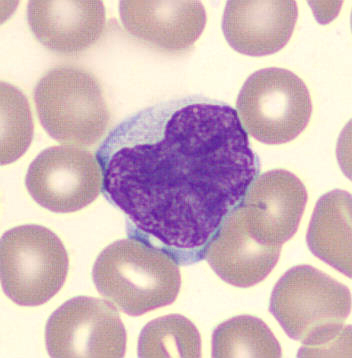
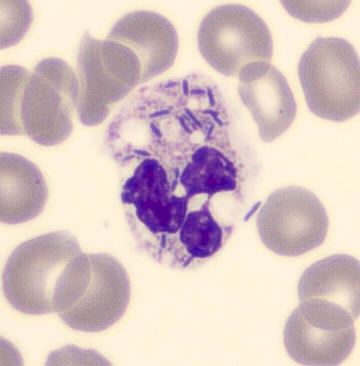
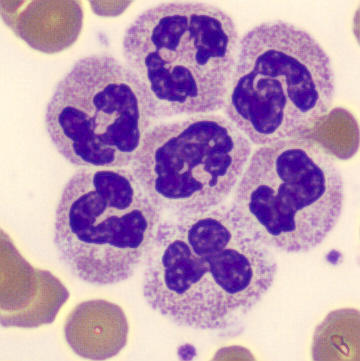
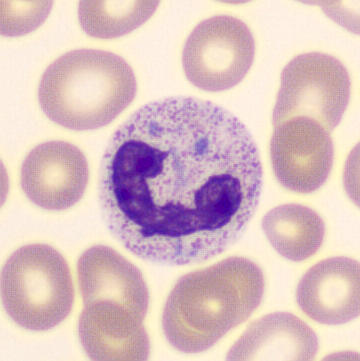
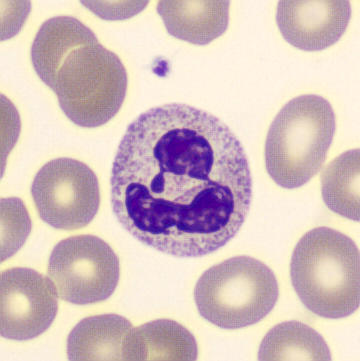
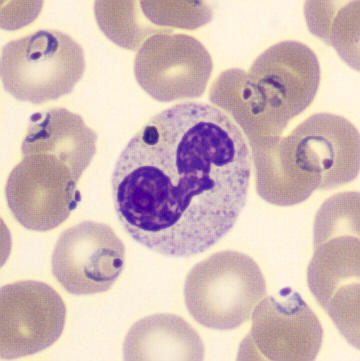
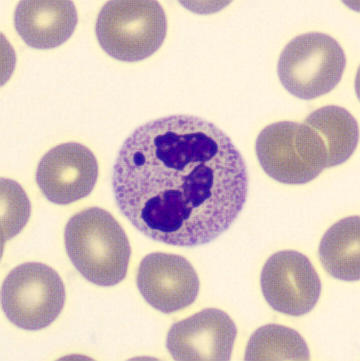
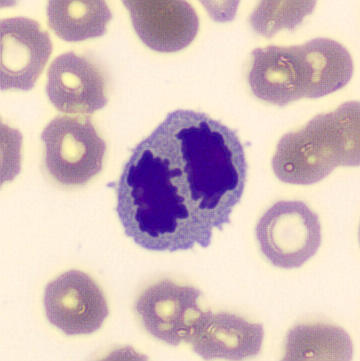
May Hegglin
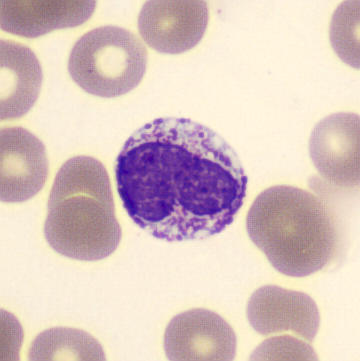
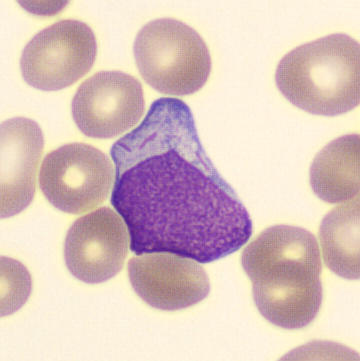
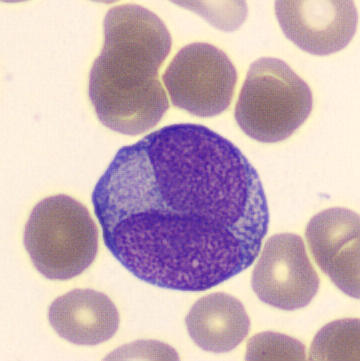
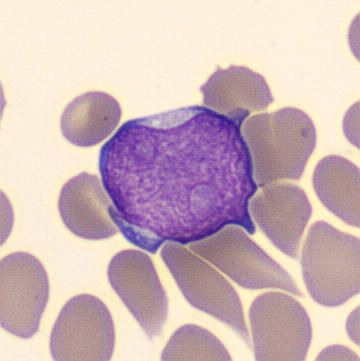
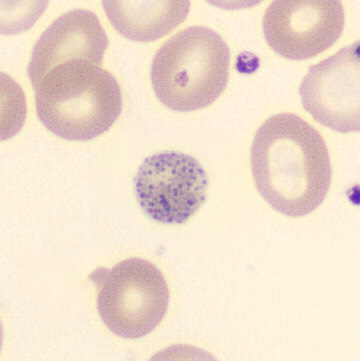
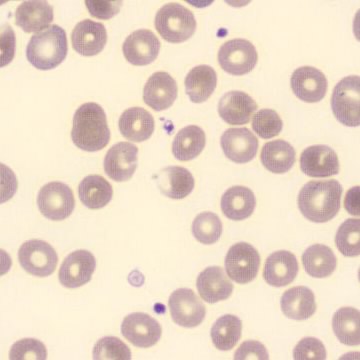
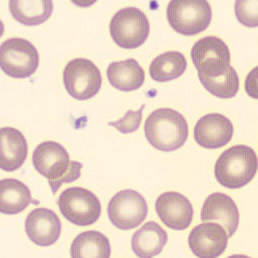
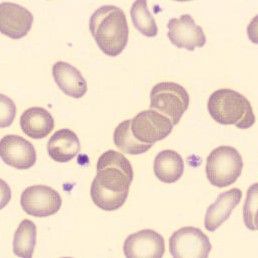
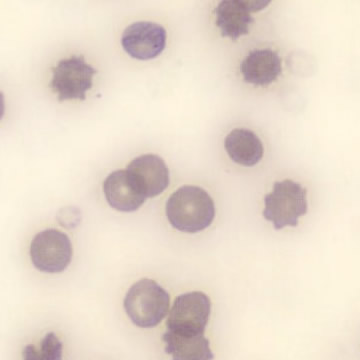
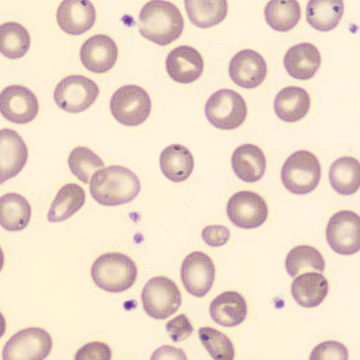
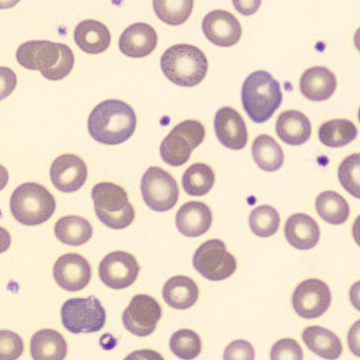
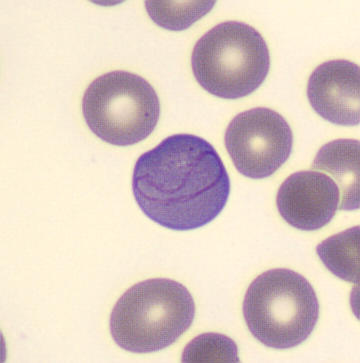
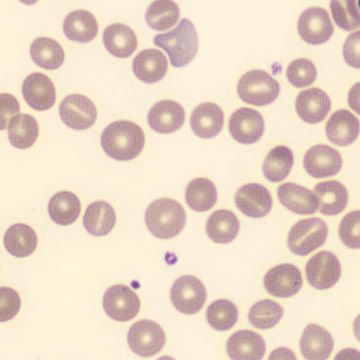
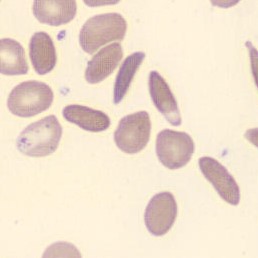
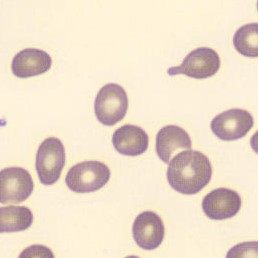
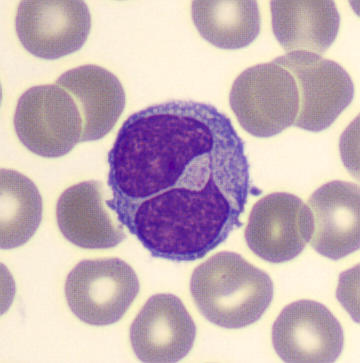
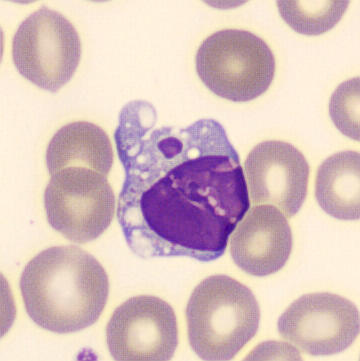
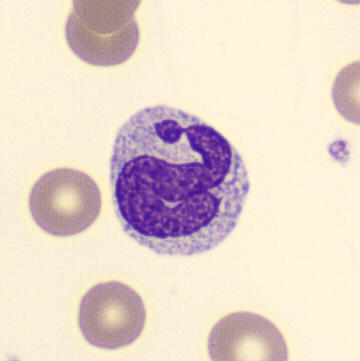
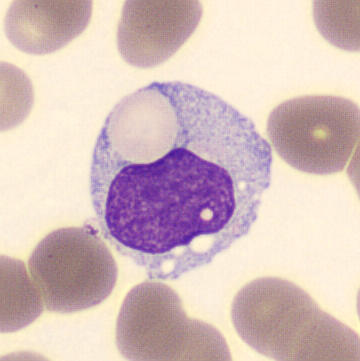
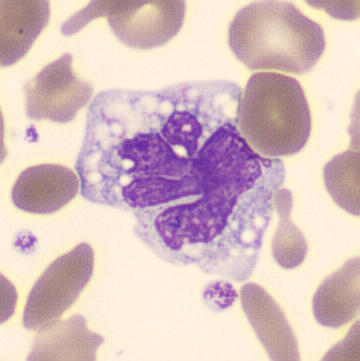
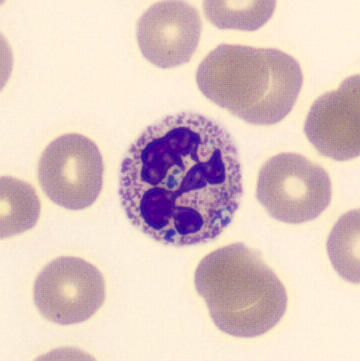
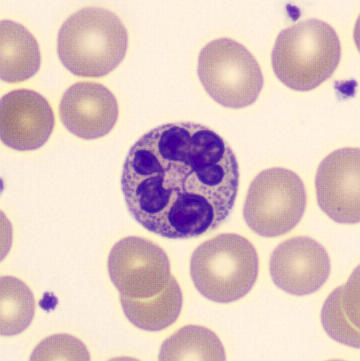
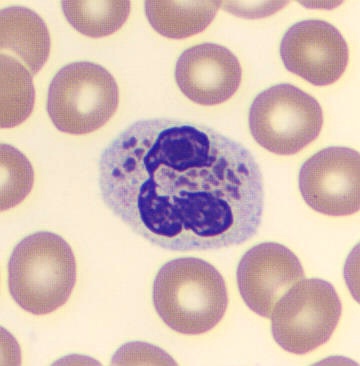
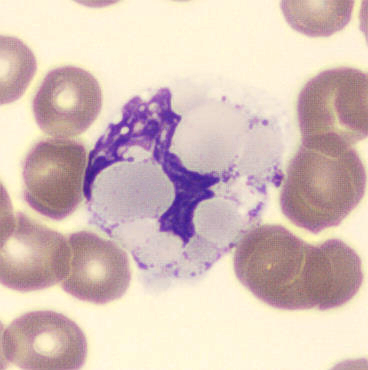
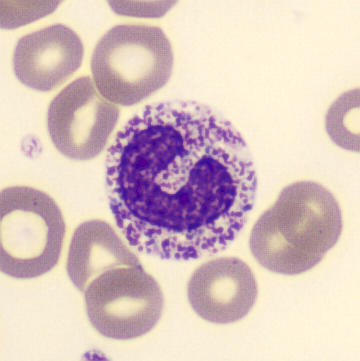
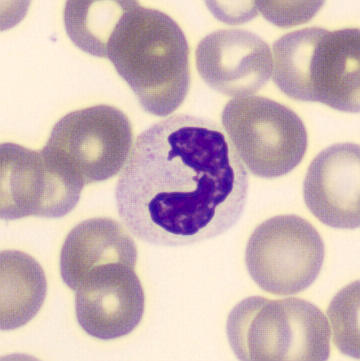
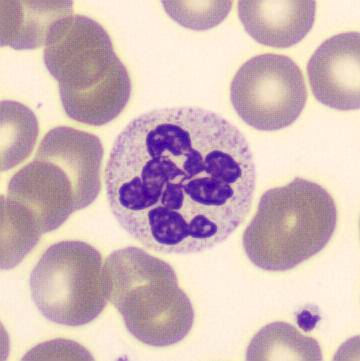
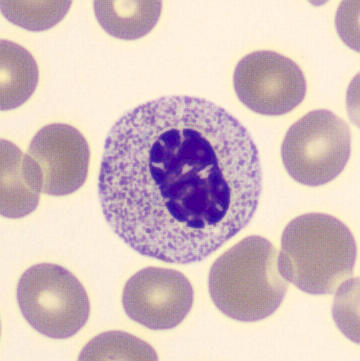
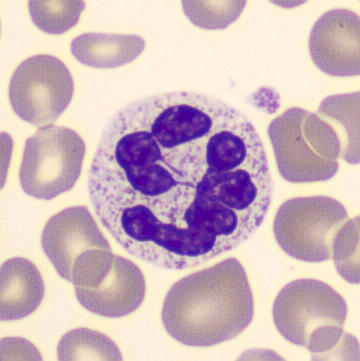
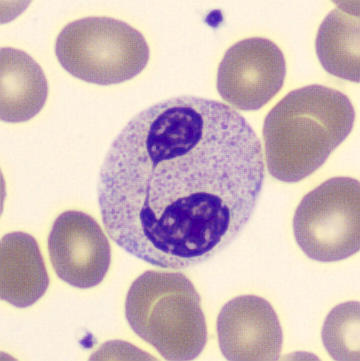
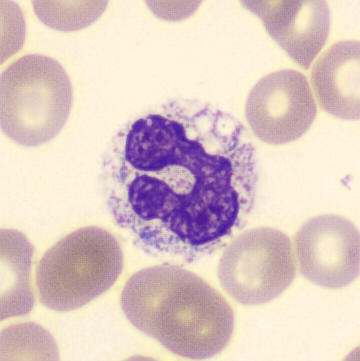
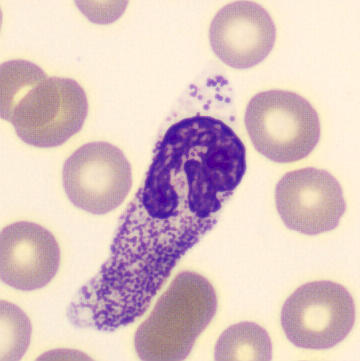
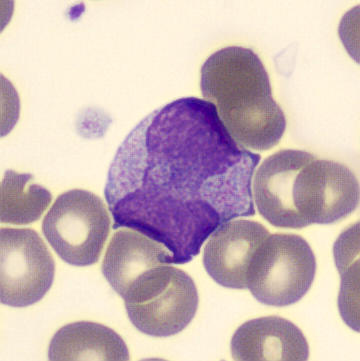
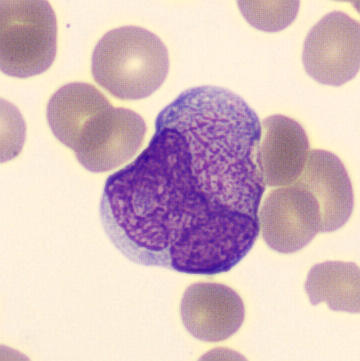
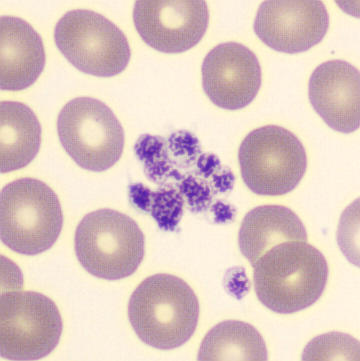
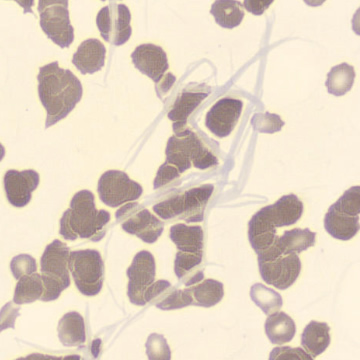
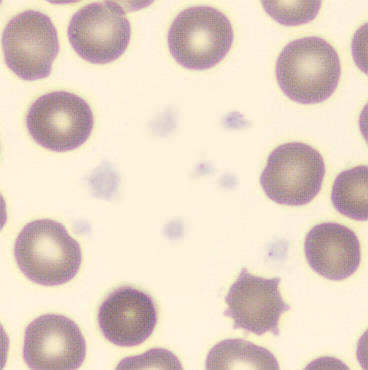
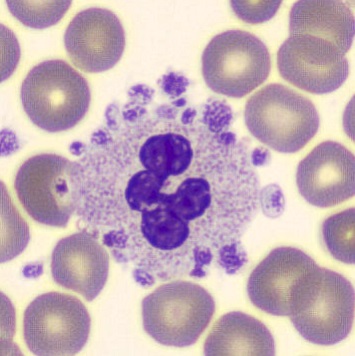
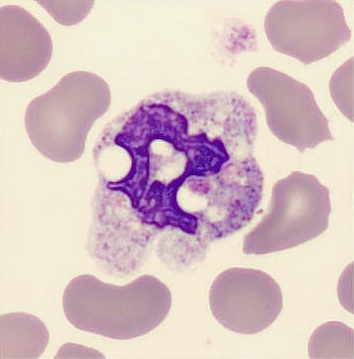
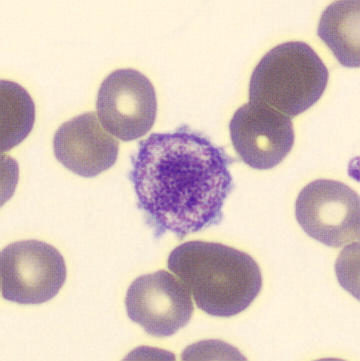
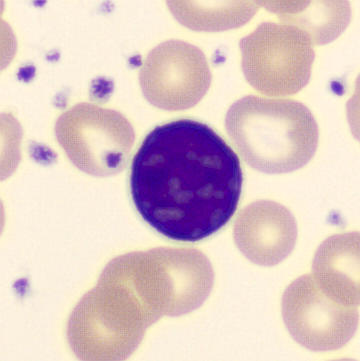
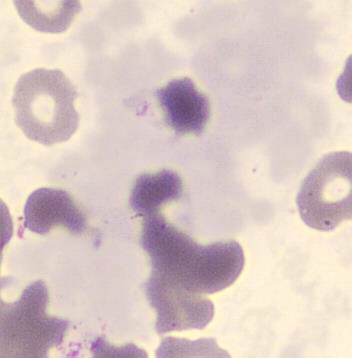
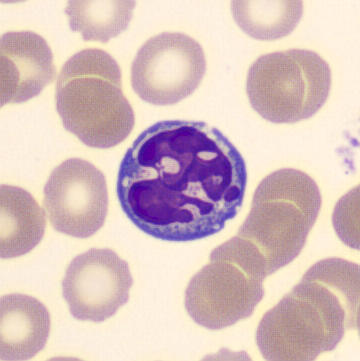
May-Hegglin anomaly is caused by a mutation in the MYH9 gene, leading to abnormal platelet and Döhle-like inclusions in leukocytes. The gene encodes for NMMHC-IIA (non-muscle myosin heavy chain), a contractile protein present in the cytoskeleton of megakaryocytes. NMMHC-IIA is also found in leukocytes, and aggregate to form cytoplasmic Döhle-like inclusions. Although these patients may have a slight bleeding tendency, this abnormality has no effect on leukocyte function.
Although reminiscent of corpuscles of Döhle, these inclusions are larger and also occur in eosinophils, basophils and monocytes. Whereas corpuscles of Döhle in particular are usually accompanied by toxic granulation or other signs of activation, May-Hegglin inclusions are also present without stimulation.