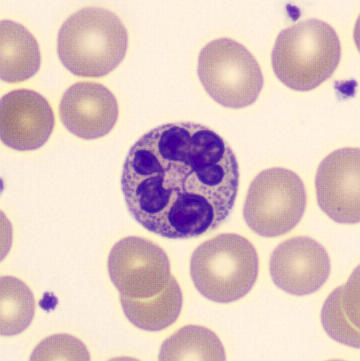
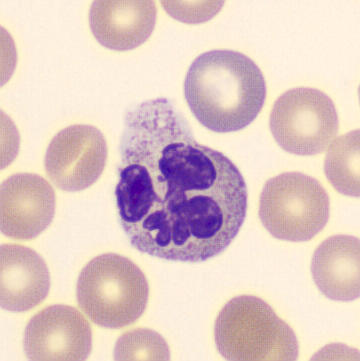
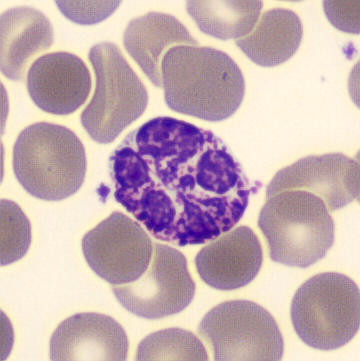
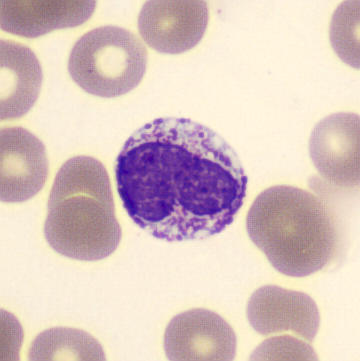
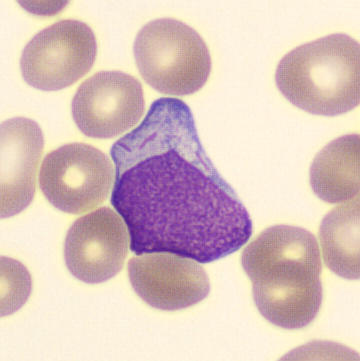
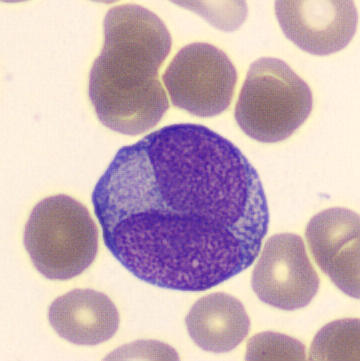
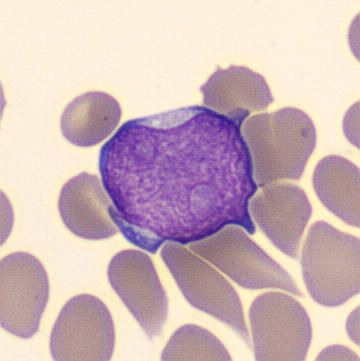
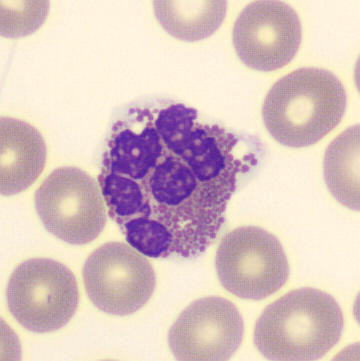
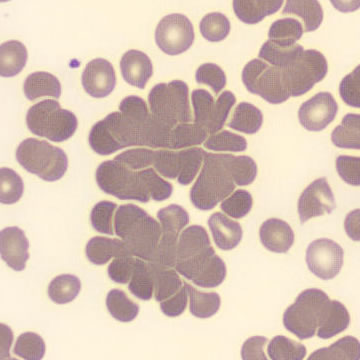
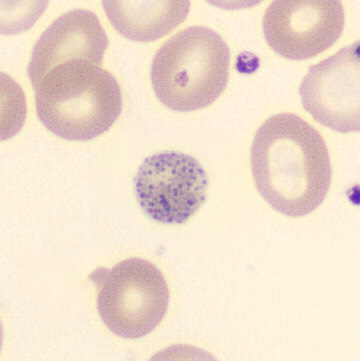
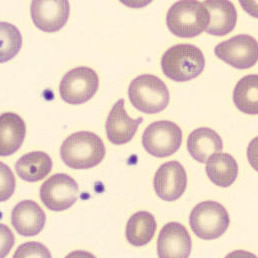
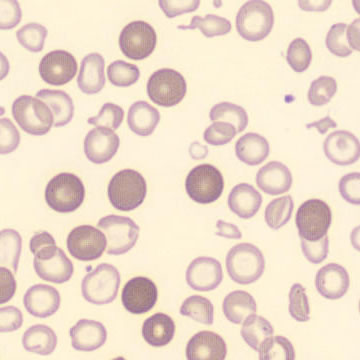
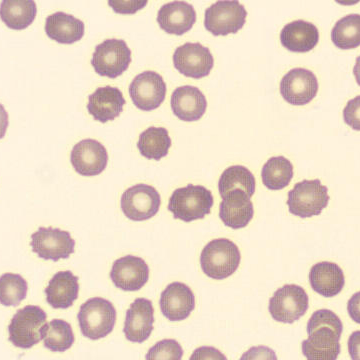
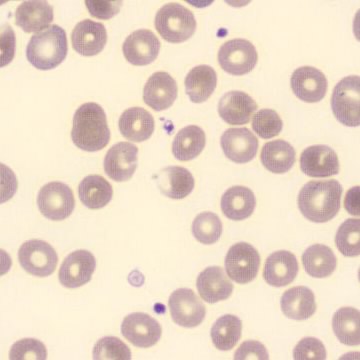
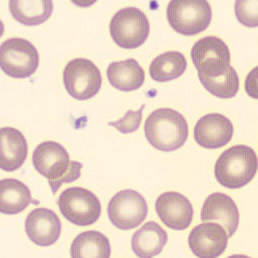
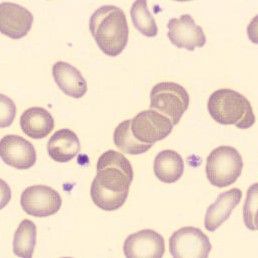
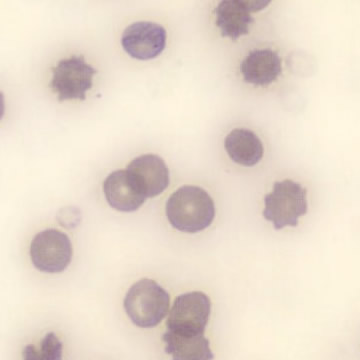
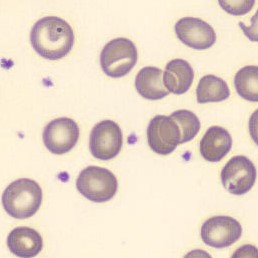
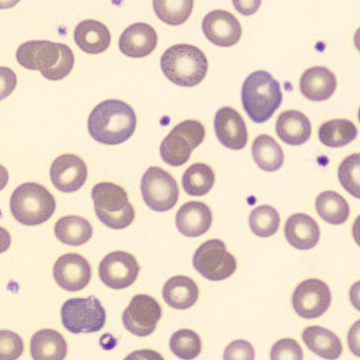
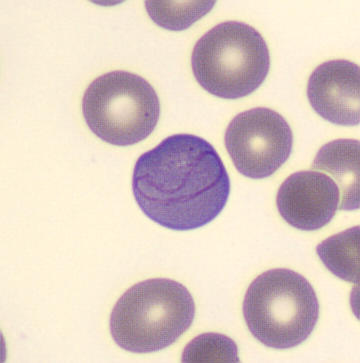
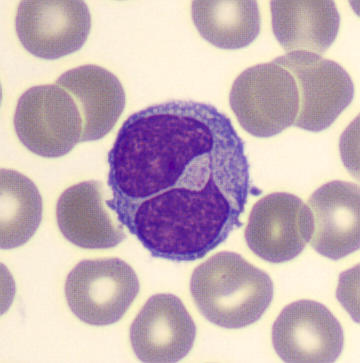
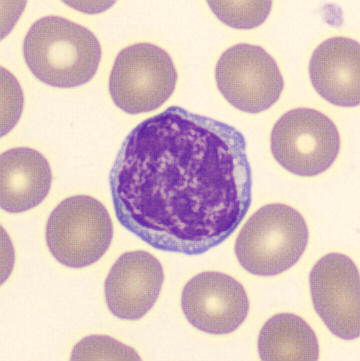
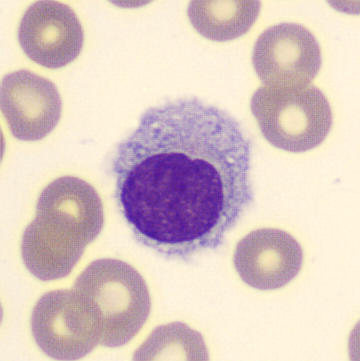
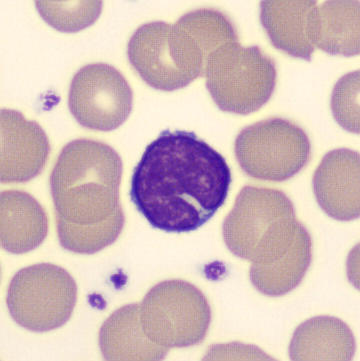
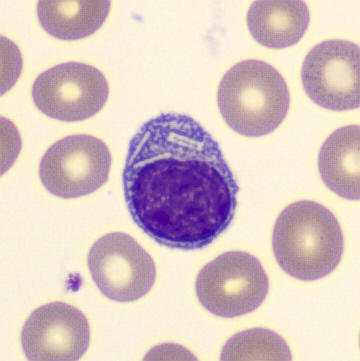
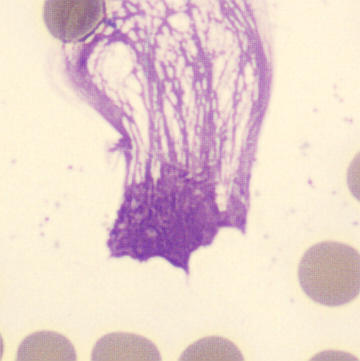
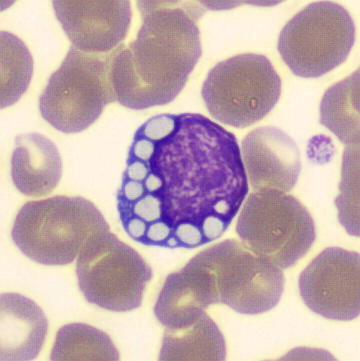
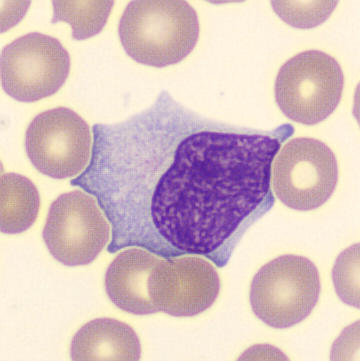
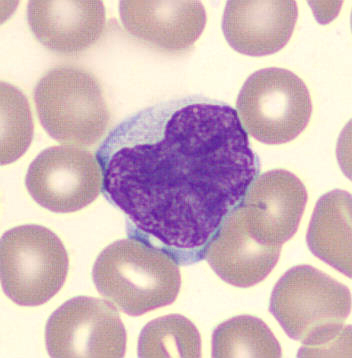
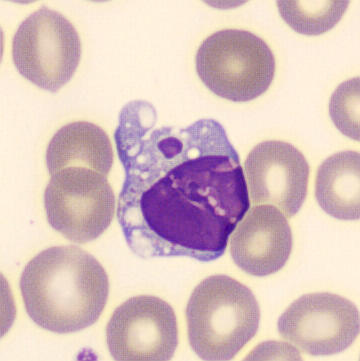
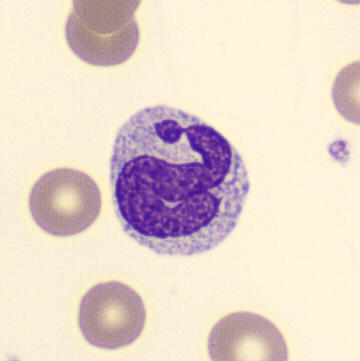
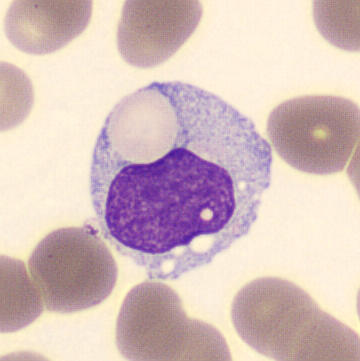
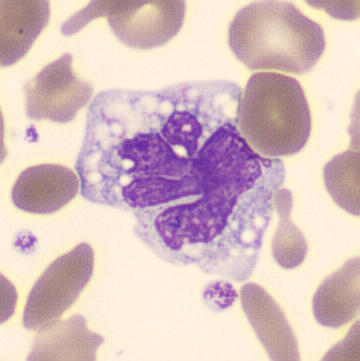
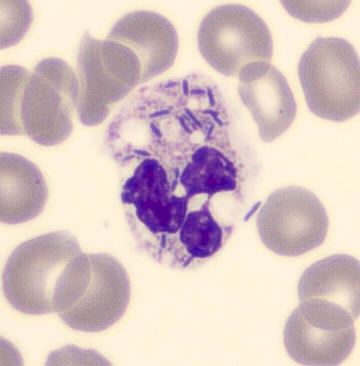
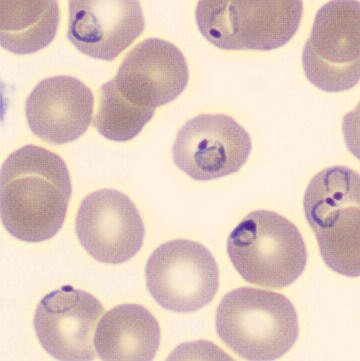
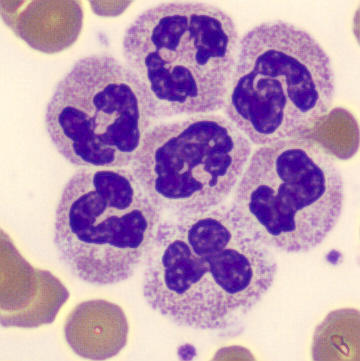
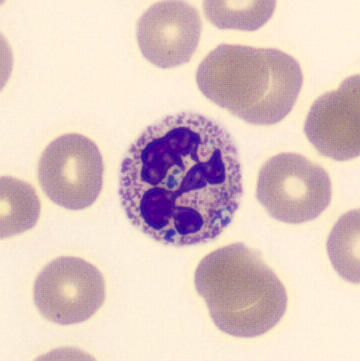
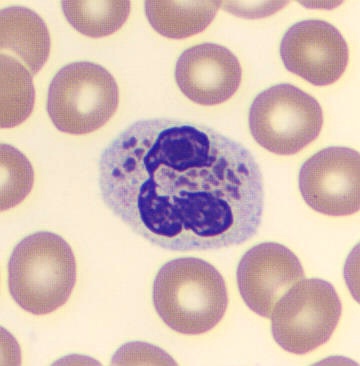
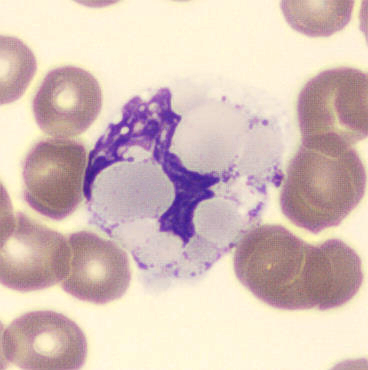
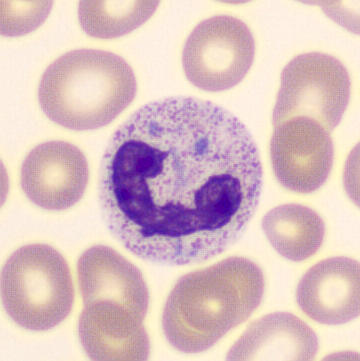
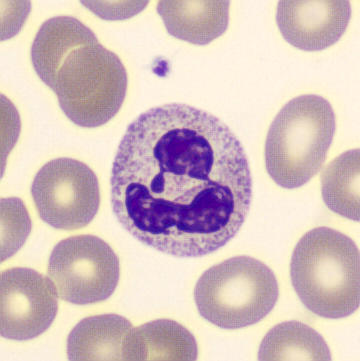
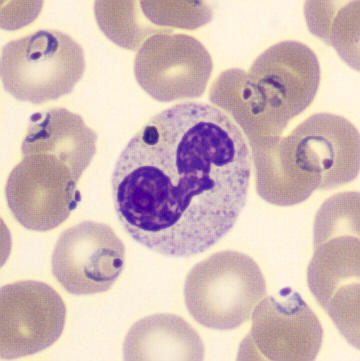
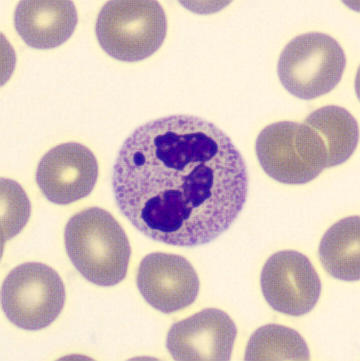
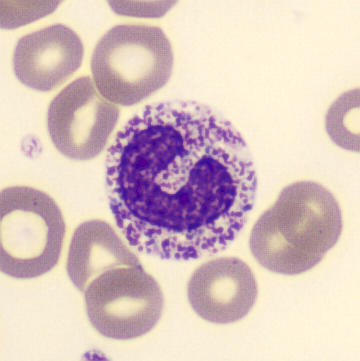
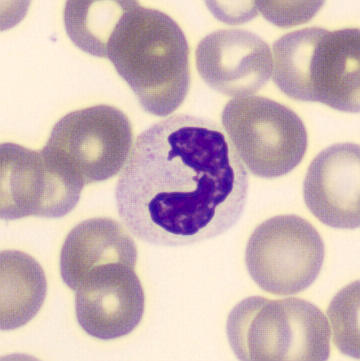
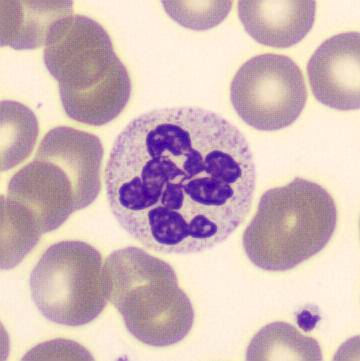
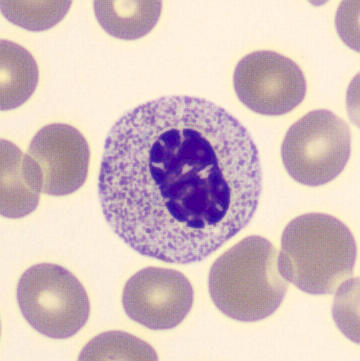
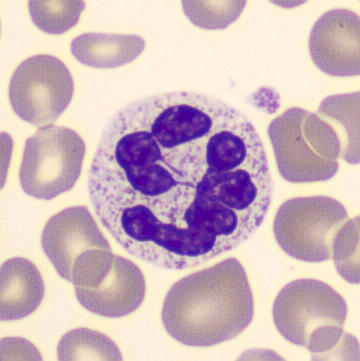
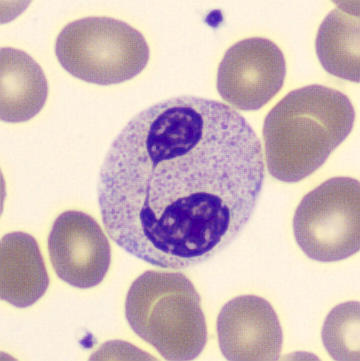
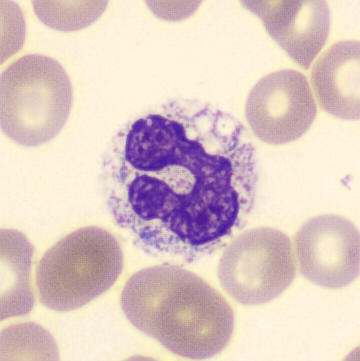
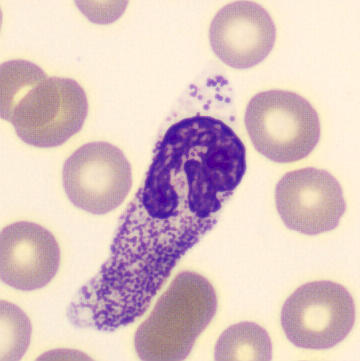
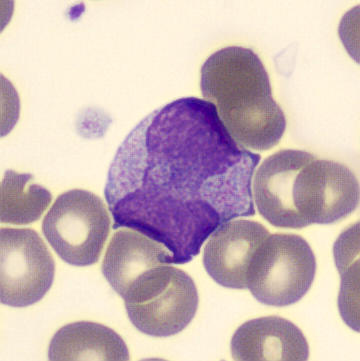
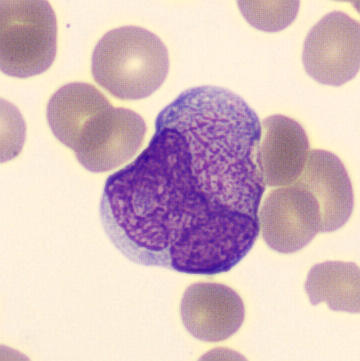
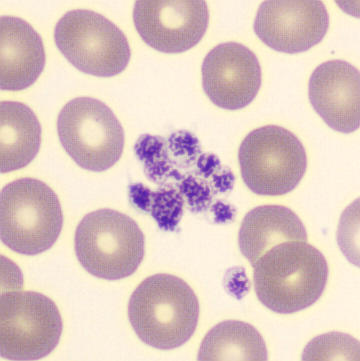
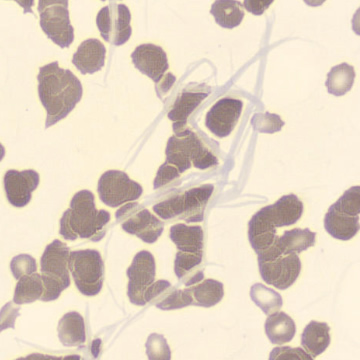
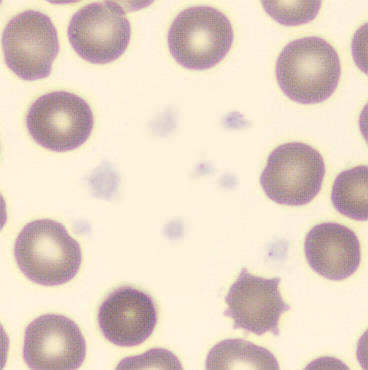
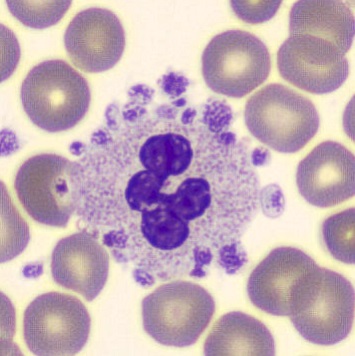
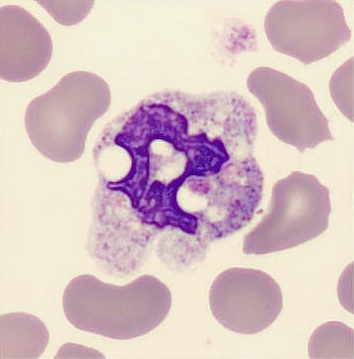
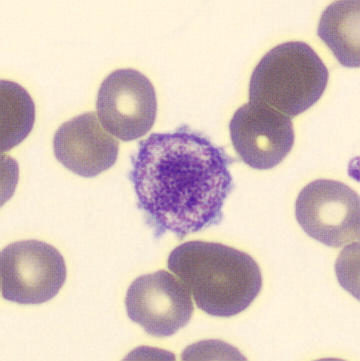
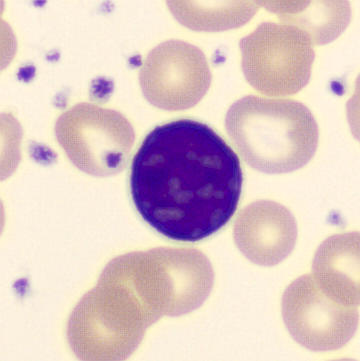
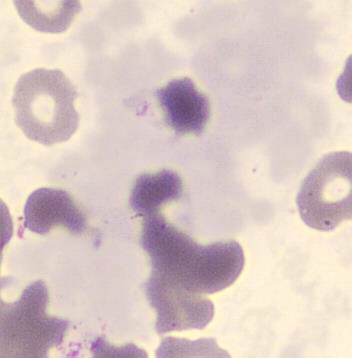
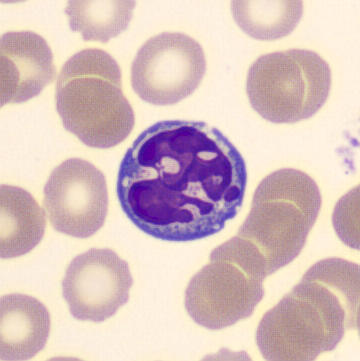
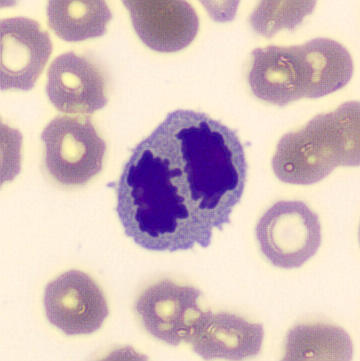
Botryoid nucleus
This abnormal core segmentation in the neutrophil is seen in severe hyperthermia (~40°C). The segments are connected by a very thin filament and fan out from a central point. Some examples of clinical causes of hyperthermia are sunstroke, sepsis, encephalitis, drug abuse (cocaine and methamphetamine),
This abnormality can be very similar to hypersegmentation caused by vitamin B12 or folic acid deficiency, but has a different basis; deficiency really involves an irreversible synthesis defect, whereas this abnormality is inducible with heat and reversible to some extent; when the sample cools, the nuclei are usually back to normal after a few hours.