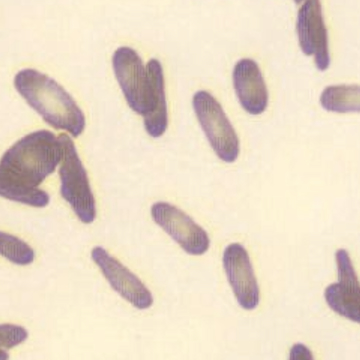
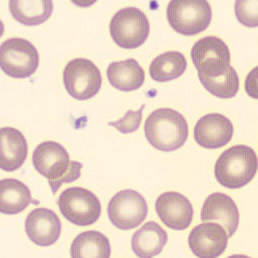
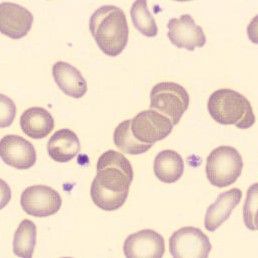
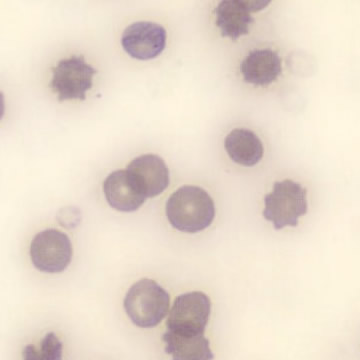
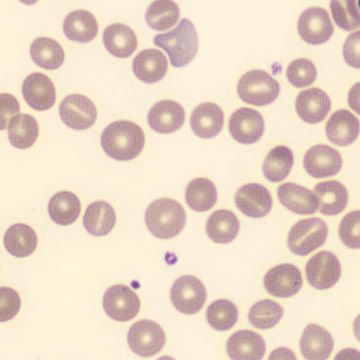
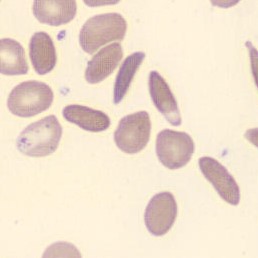
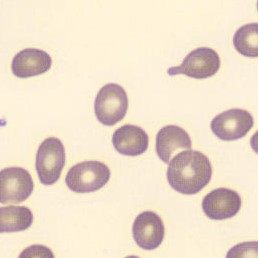
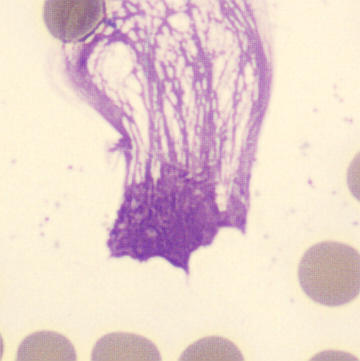
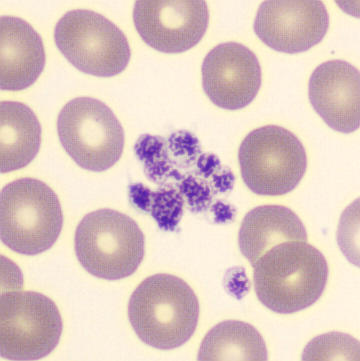
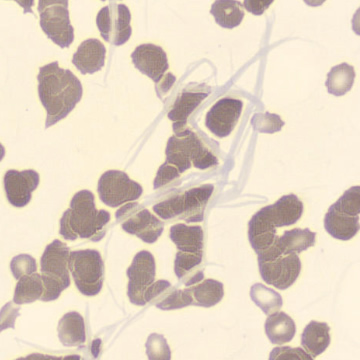
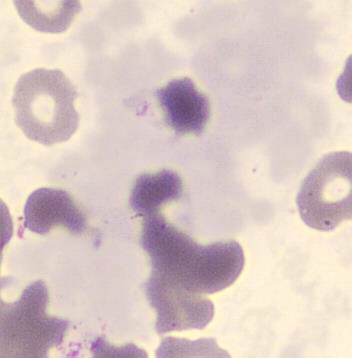
Agglutination
Clumping of erythrocytes results from the presence of IgM antibodies that (cross) react with one's own erythrocytes. Usually these are so-called cold antibodies because they react at temperatures below 37°C. These antibodies may arise during the response to viral or bacterial infections (e.g., EBV or Mycoplasma pneumoniae) or in lymphoproliferative disorders. These antibodies can cause intravascular hemolysis. In this case, we speak of Cold Agglutinin Disease (CAD).
Agglutination causes a falsely decreased erythrocyte count and increased MCV (because multiple erythrocytes are counted as one cell). Agglutination has no effect on the measured hemoglobin (because erythrocytes are lysed in this measurement). Because the MCH and MCHC are calculated from these parameters, they will be falsely elevated. One solution to this interference is to ensure that the material does not cool down until measured.