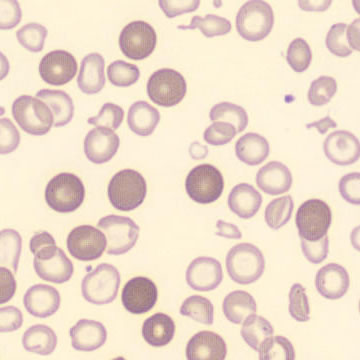
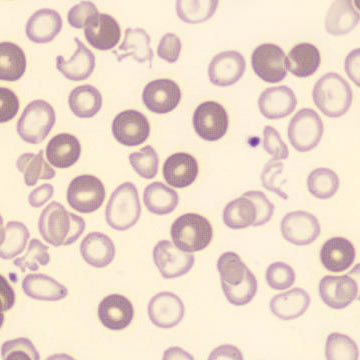
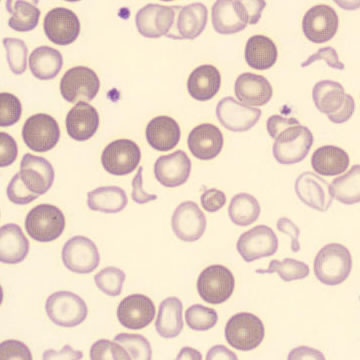
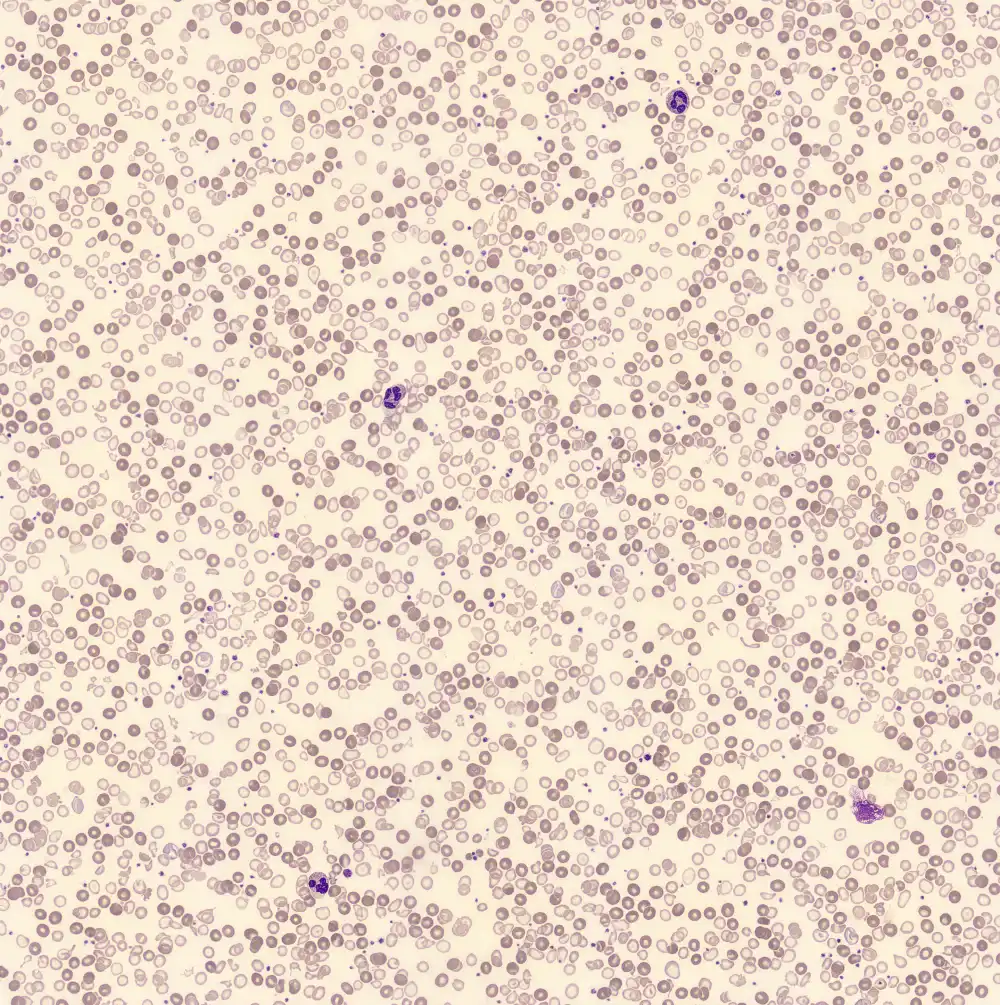
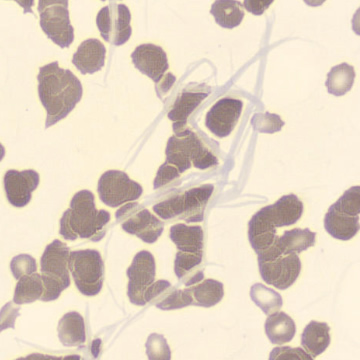
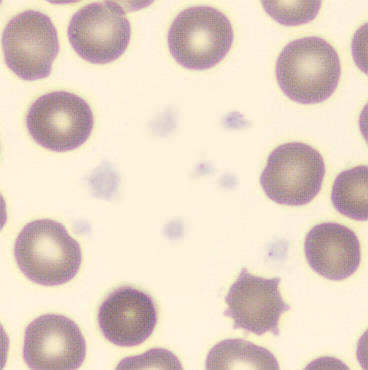
Dimorphism
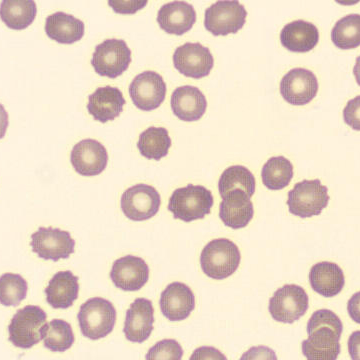
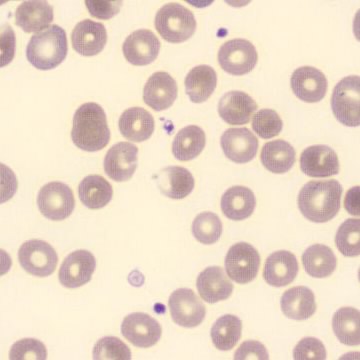
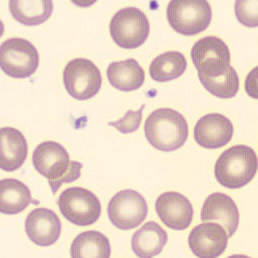
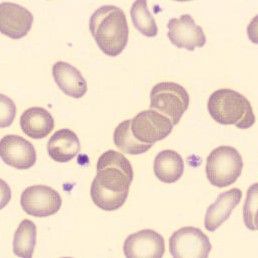
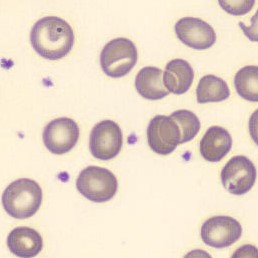
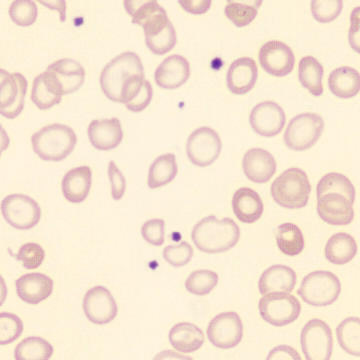
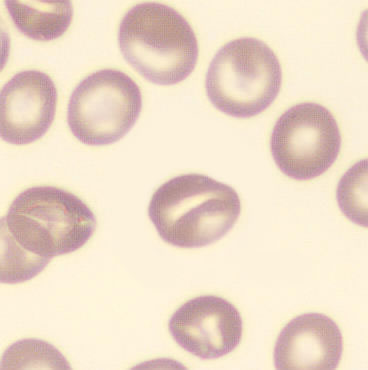
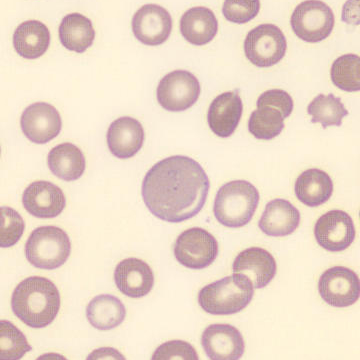
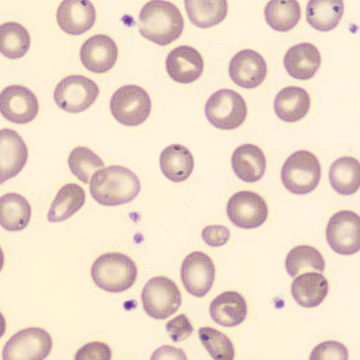
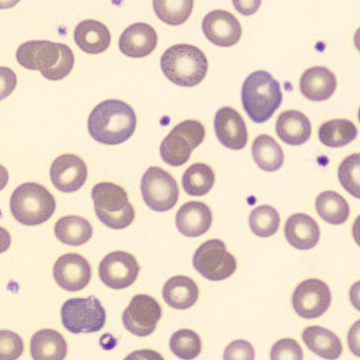
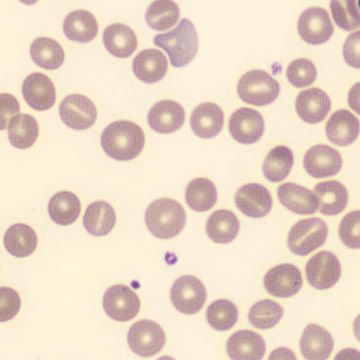
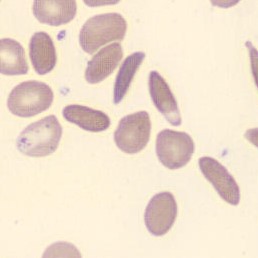
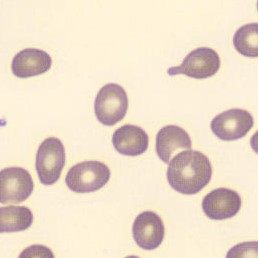
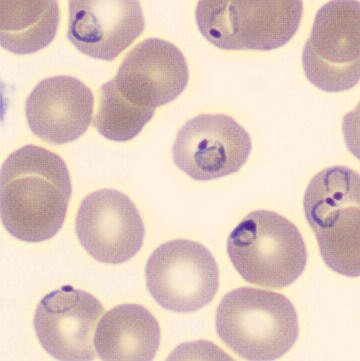
One speaks of dimorphism when two clearly distinguishable populations of erythrocytes are present. In the hemocytometer, this usually manifests as an increased RDW and sometimes even two separate peaks can be seen in the impedance channel.
The most common cause is transfusion of normocytic, normochromic donor erythrocytes to a patient with severe iron deficiency, where the patient's population is microcytic and hypochromic (see figure). Another cause is intravascular hemolysis (as in diffuse intravascular coagulation, TTP or severe burns), in which microcytic and/or hypochromic erythrocytes or fragmentocytes are generated.