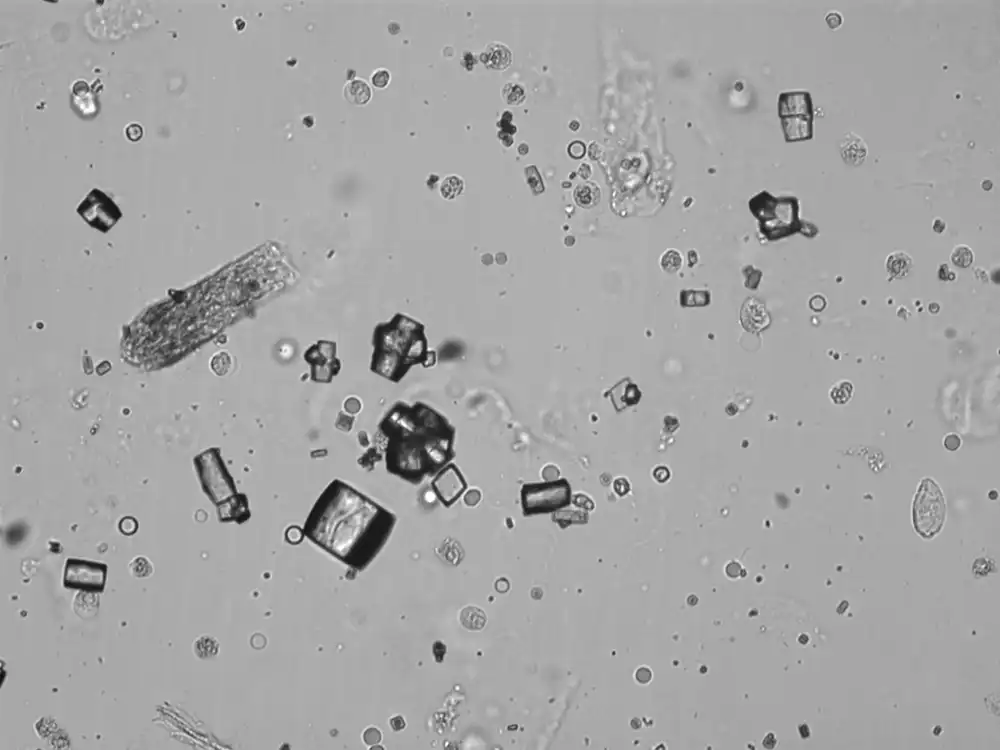
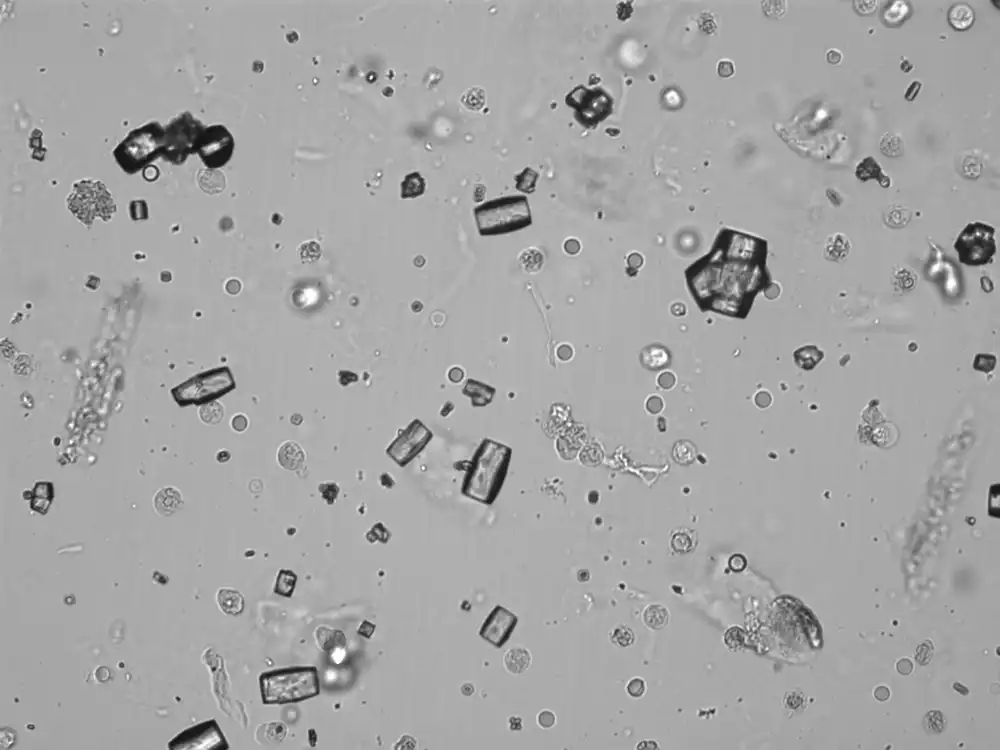
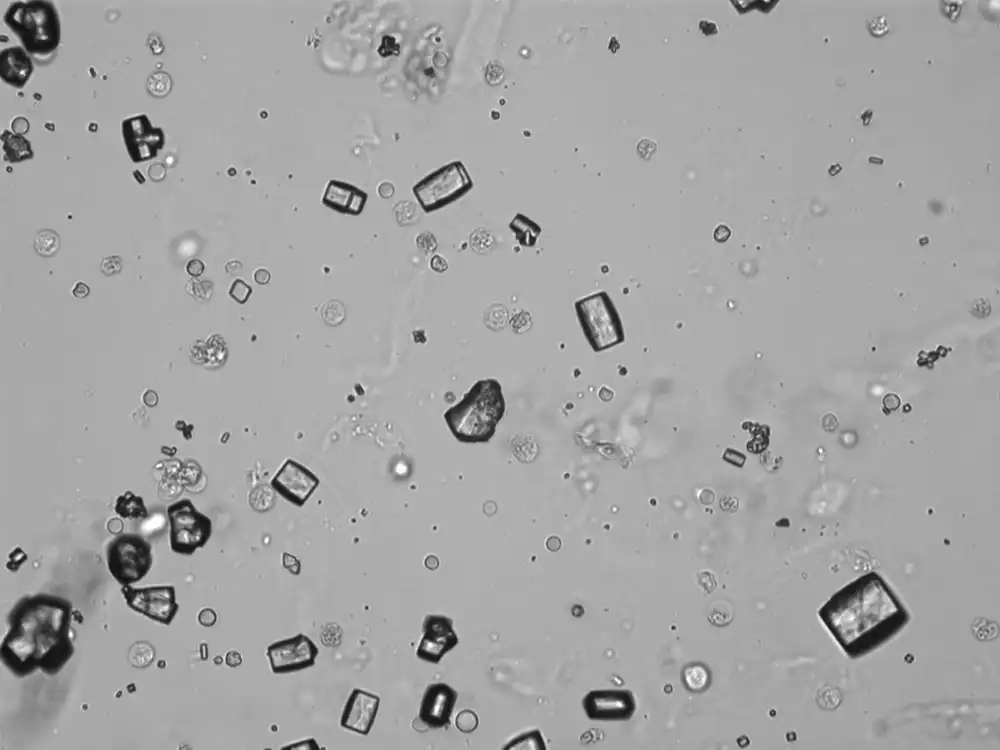
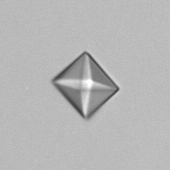
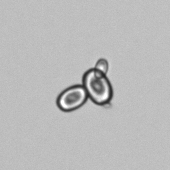
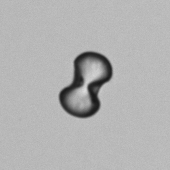
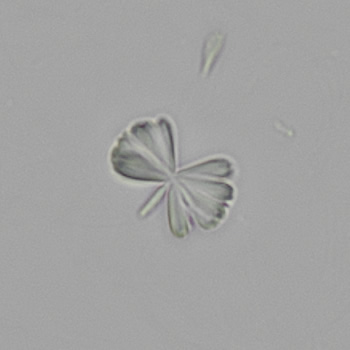
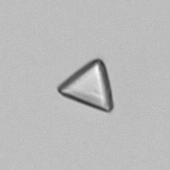
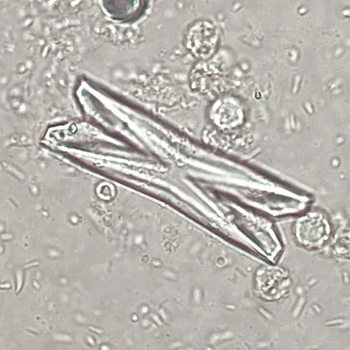
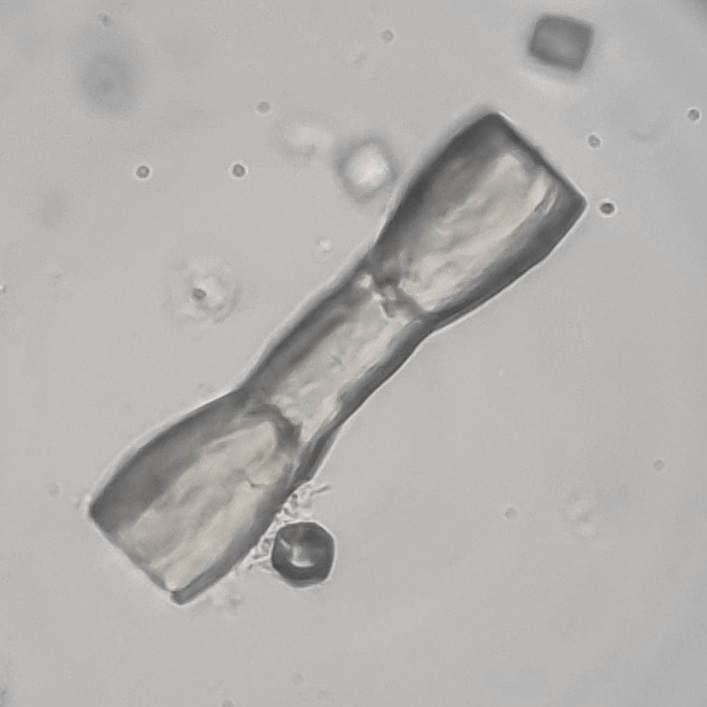
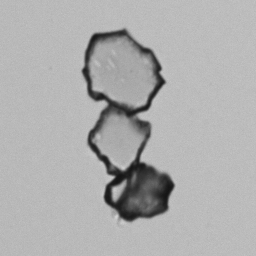
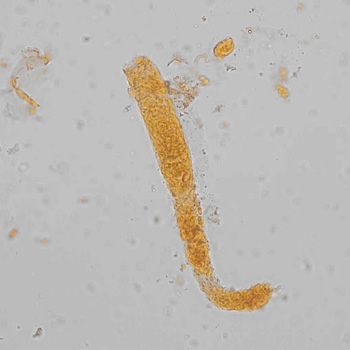
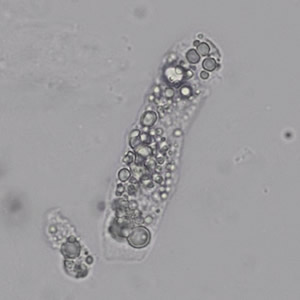
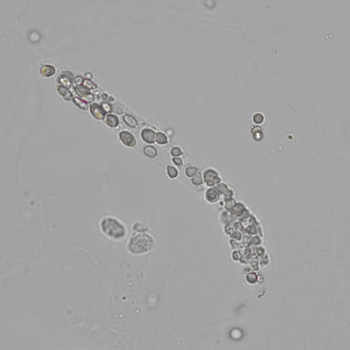
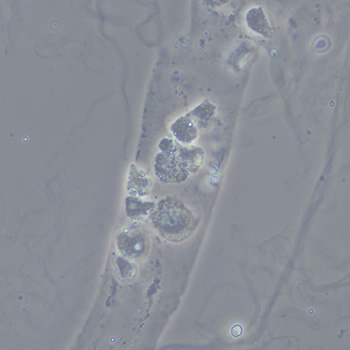
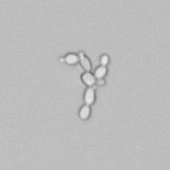
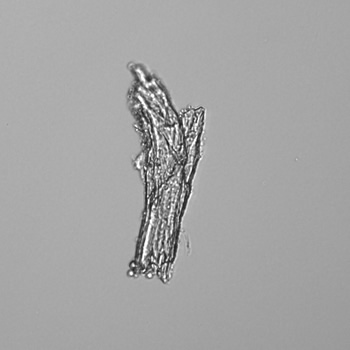
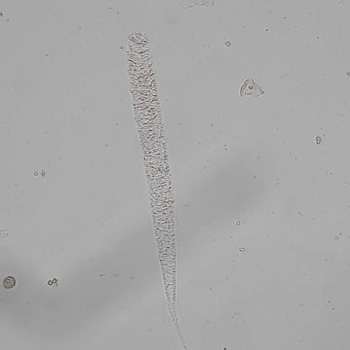
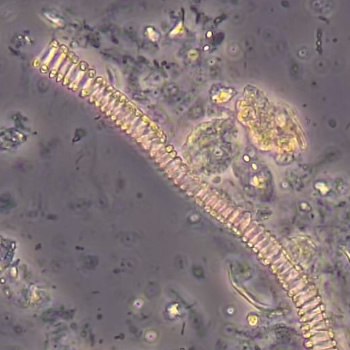
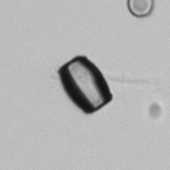
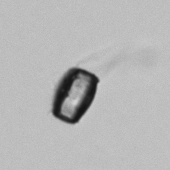
Uric acid - Cylinder
Synonyms: Urate, C₅H₄N₄O₃
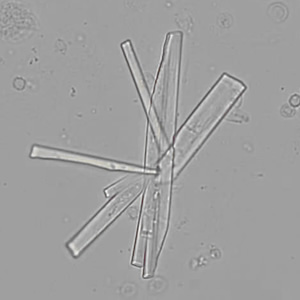
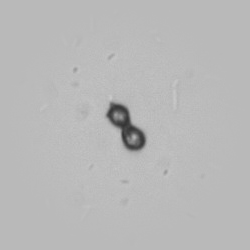
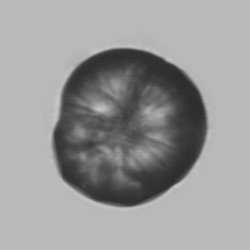
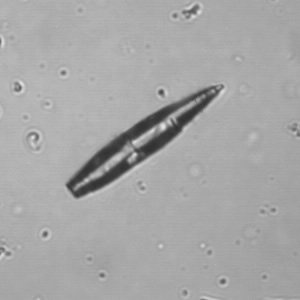
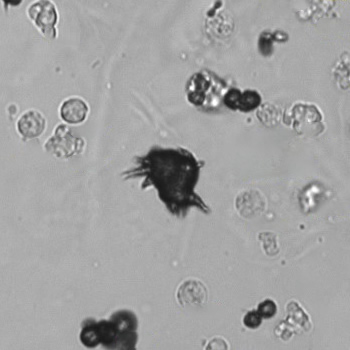
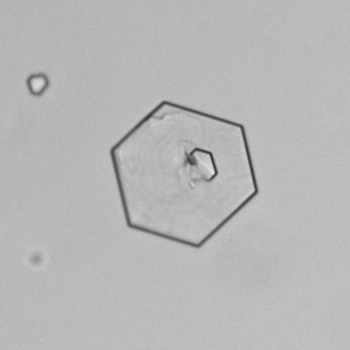
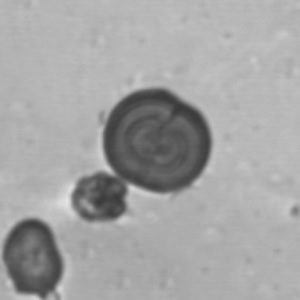
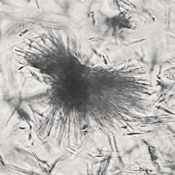
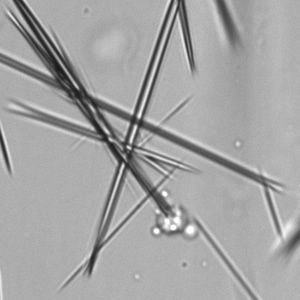
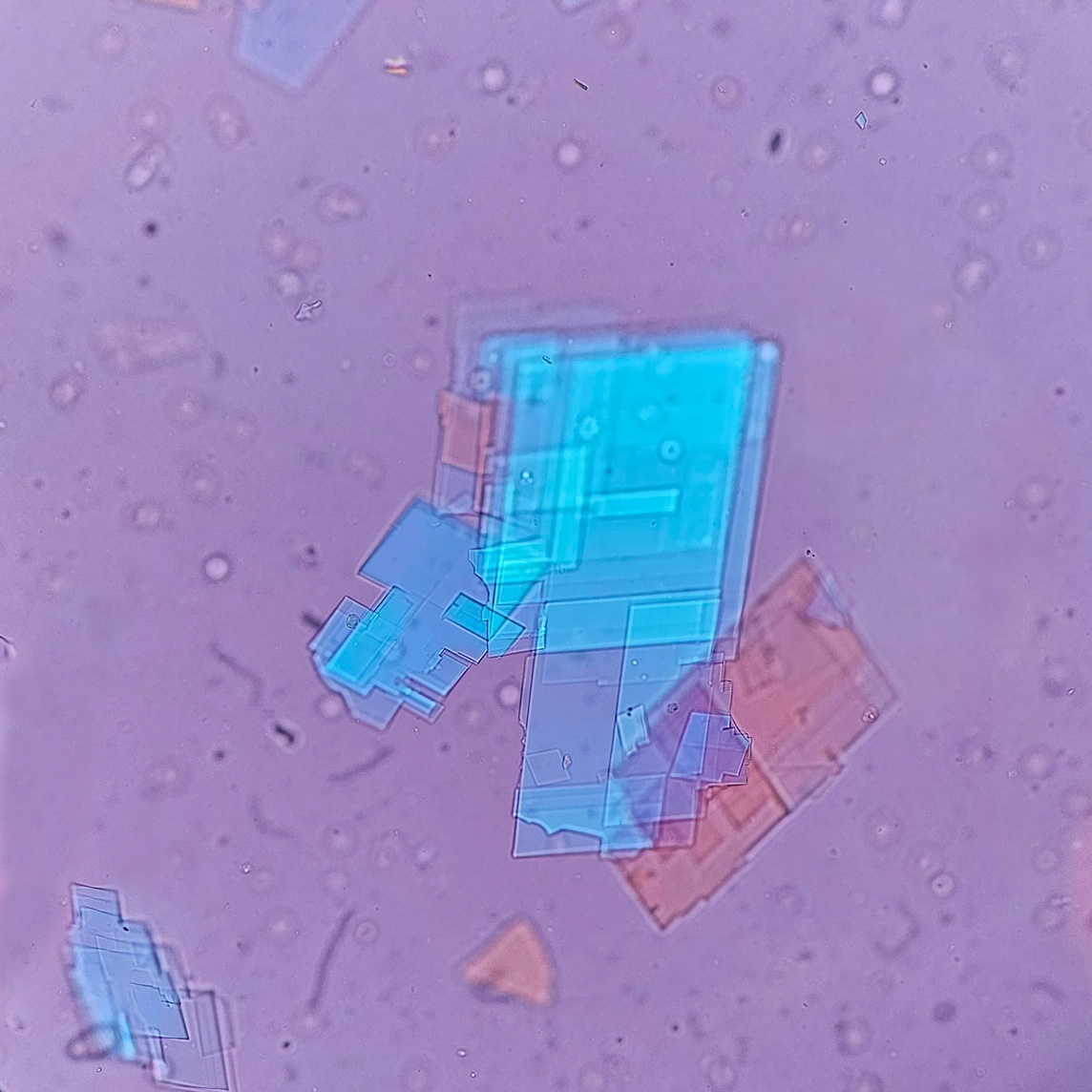
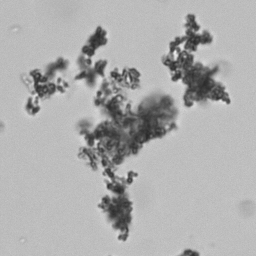
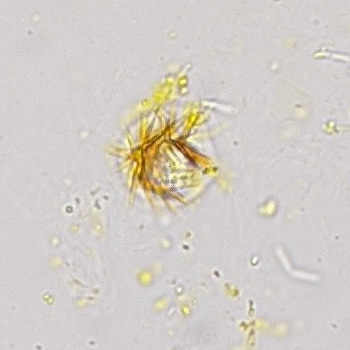
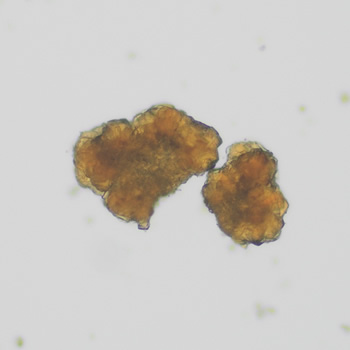
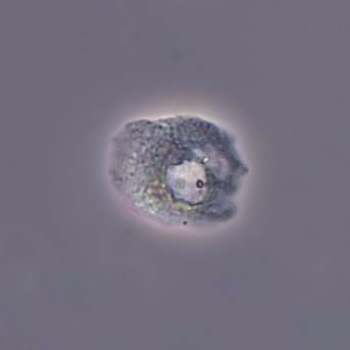
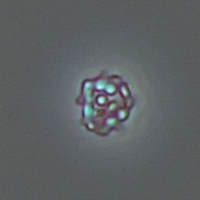
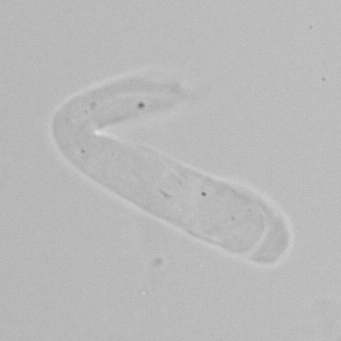
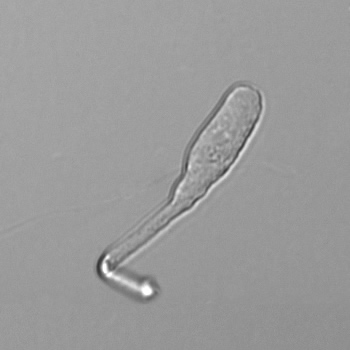
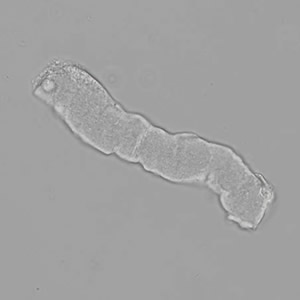
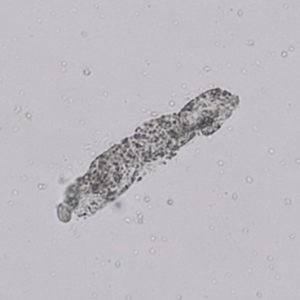
Uric acid crystals occur with increased uric acid excretion or in acidic urine (pH < 5.8). Uric acid is a waste product of purine metabolism; purines are chemical compounds such as adenine and guanine (DNA components), caffeine and xanthine, and are mainly found in meat (products). The crystals can take various forms: usually diamond- or diamond-shaped plates, hexagonal plates, cylindrical structures (barrels), elongated prisms, star-shaped, spherical, needle-shaped or dumbbell-shaped crystals. They are usually yellowish to brown in color and show strong, polychromatic birefringence. They may precipitate when the urine has been kept cold prior to analysis.
Clinically, these crystals are seen in conditions such as gout, uric acid stones, Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, and in situations with increased cell breakdown, for example, in leukemia or during chemotherapy. Drugs such as benzbromarone, probenecid, sulfinpyrazone, losartan and indometacin promote uric acid excretion. At very high concentrations, or when crystals are accompanied by erythrocytes or tubular epithelial cells, acute uric acid nephropathy or renal stone formation should be considered.
Individual
Overview