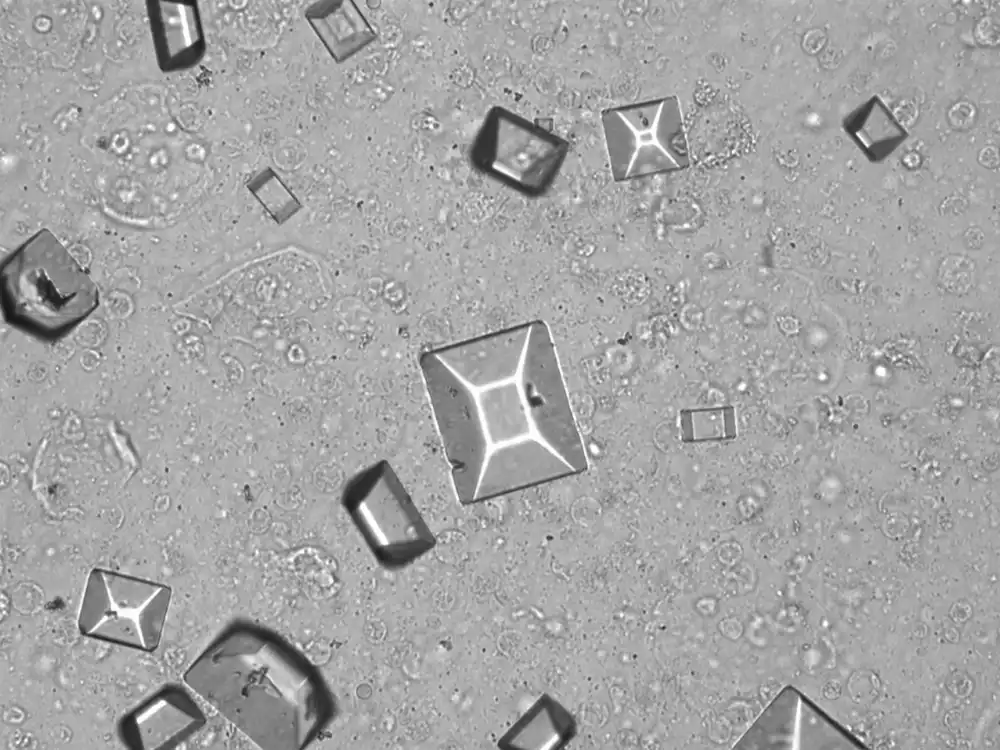
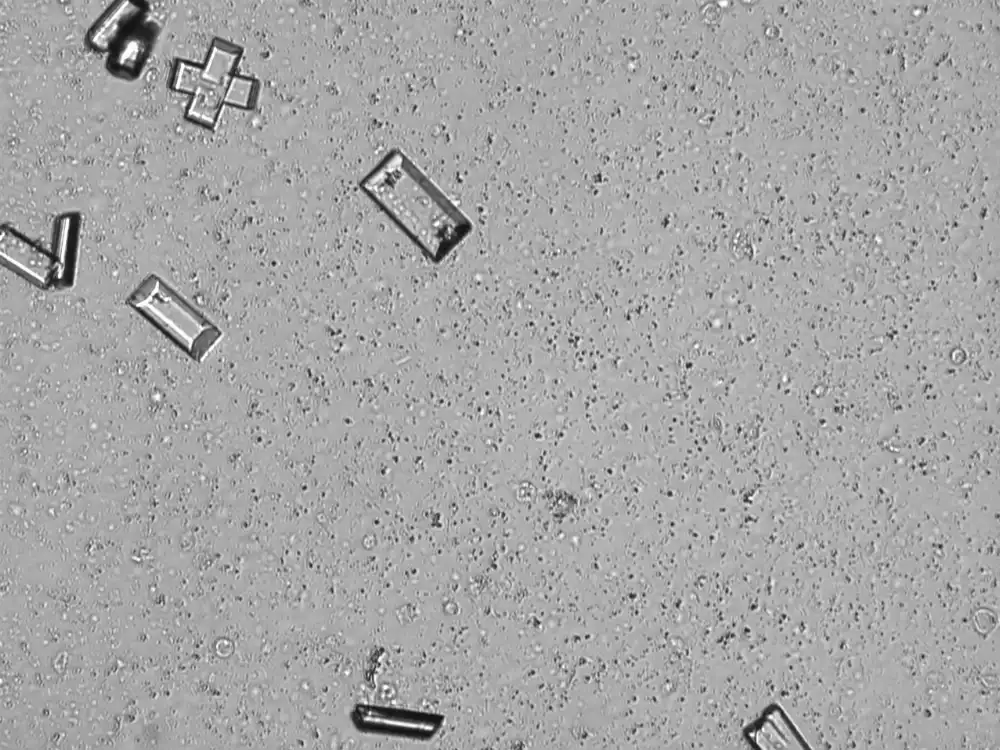
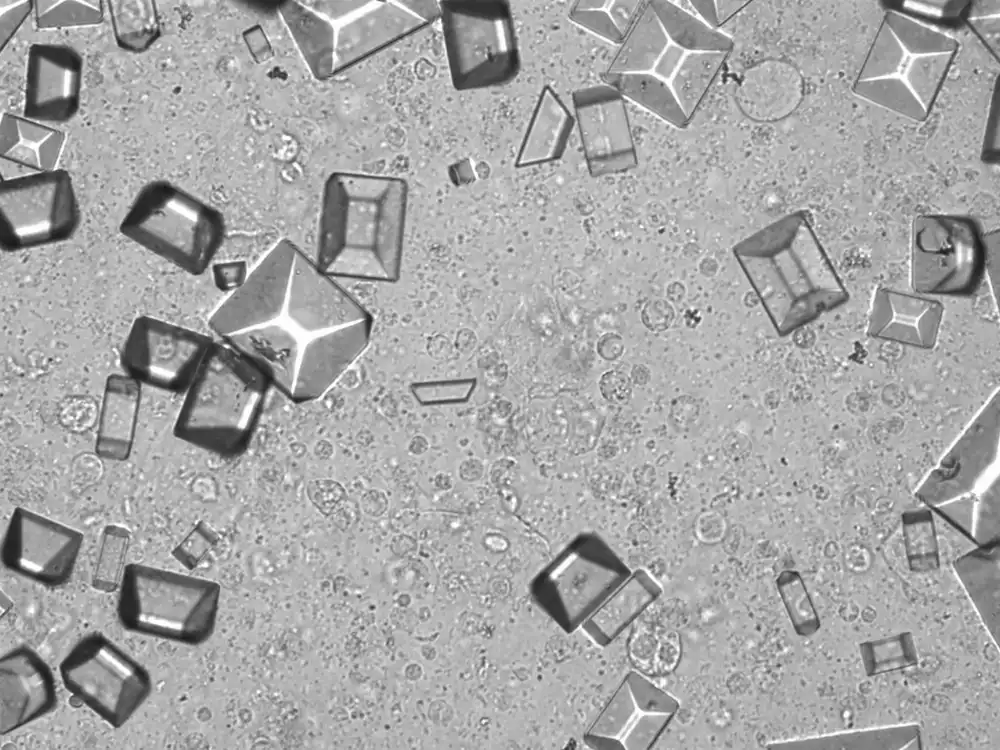
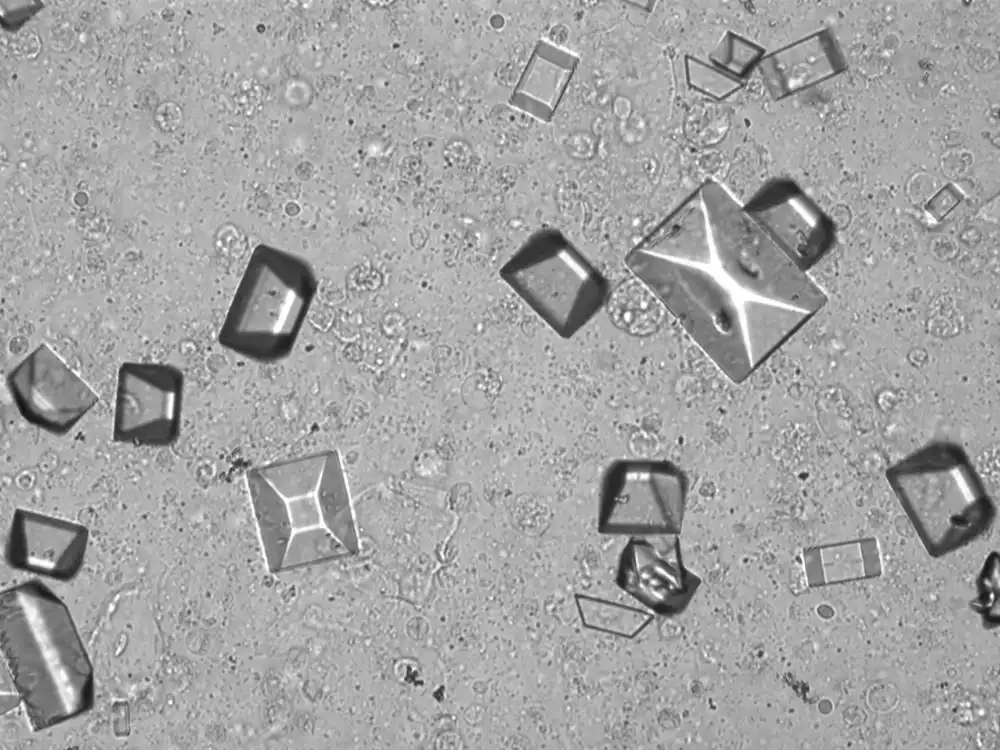
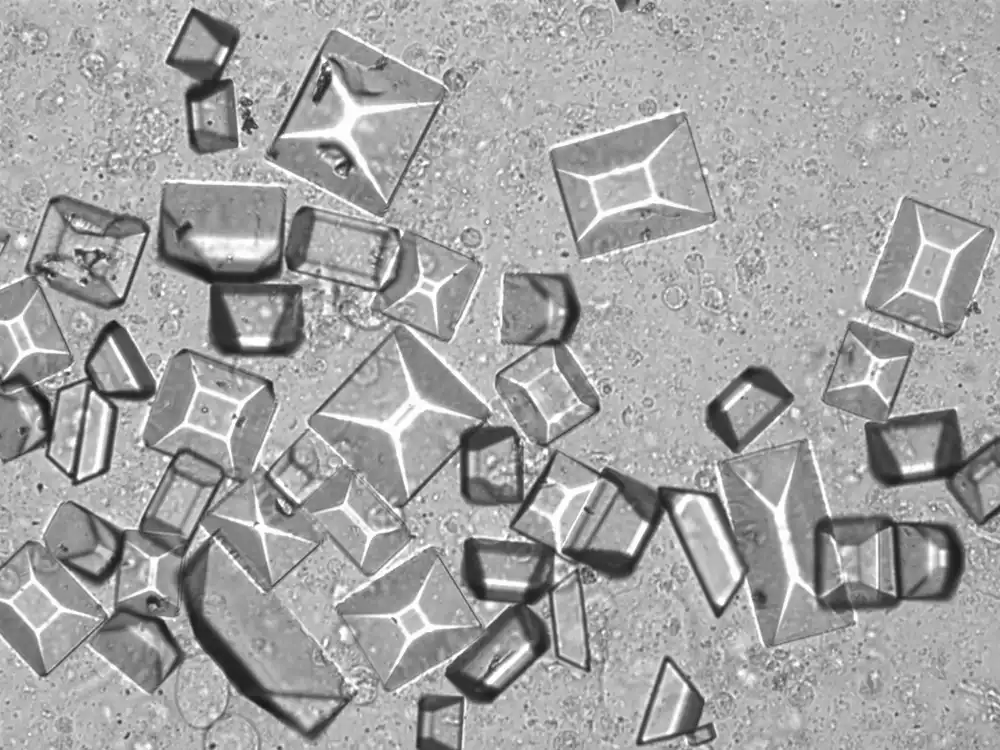
Triple phosphate - Coffin
Synonyms: Struvite, Magnesium ammonium phosphate, MgNH₄PO₄·6H₂O
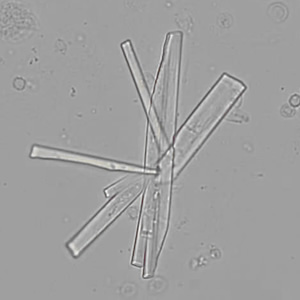
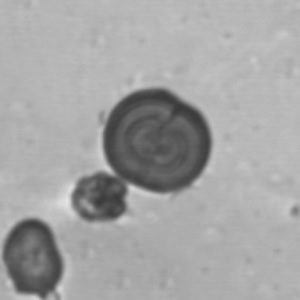
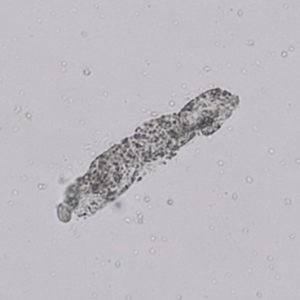
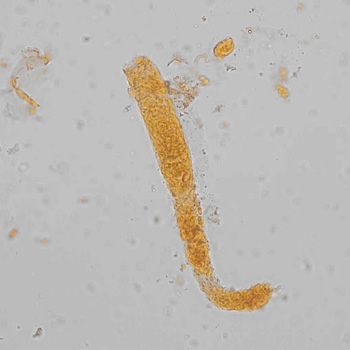
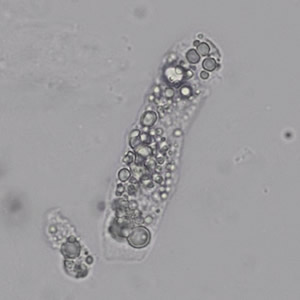
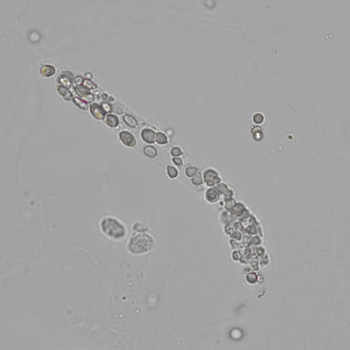
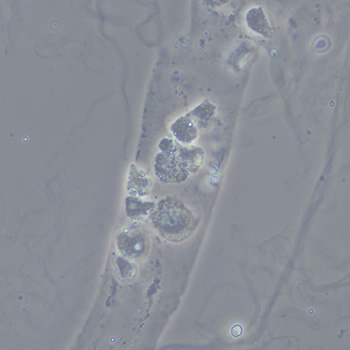
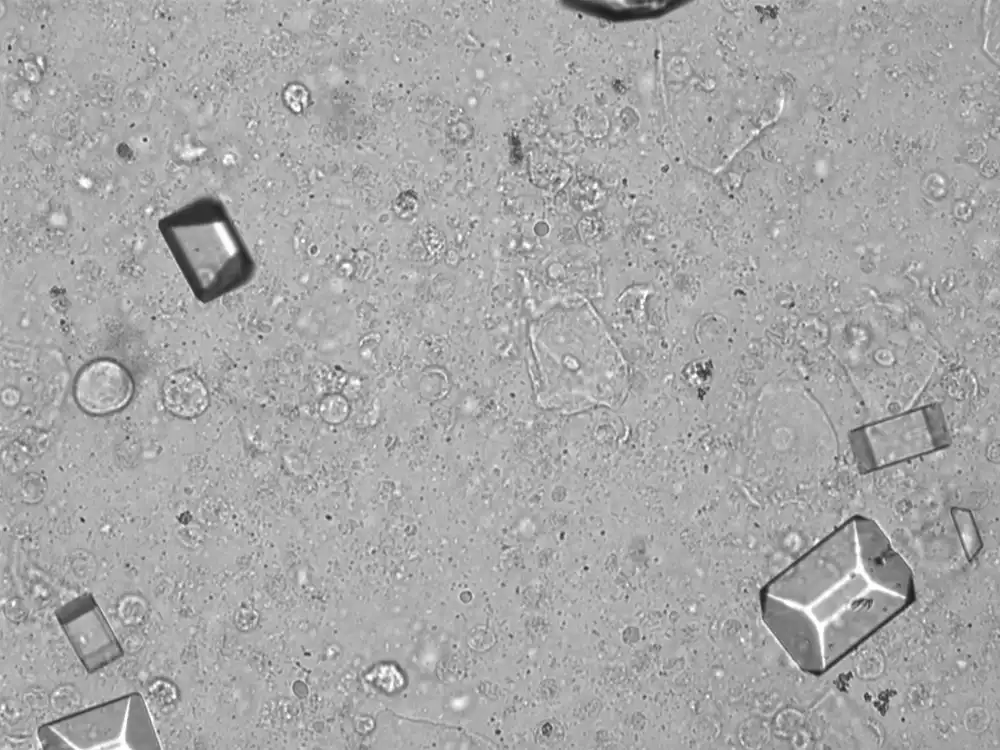
Tripel phosphate, also known as struvite or magnesium ammonium phosphate (MgNH₄PO₄·6H₂O), are frequently found in alkaline urine and are typically associated with urinary tract infections caused by urease-producing bacteria such as Proteus, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus and Ureaplasma urealyticum. These bacteria convert urea in the urine to ammonia, which raises the pH of the urine to neutral or alkaline values. The higher pH promotes the precipitation of struvite.
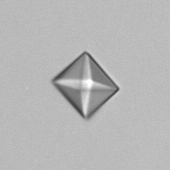
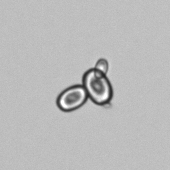
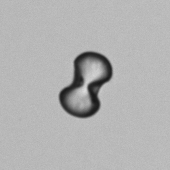
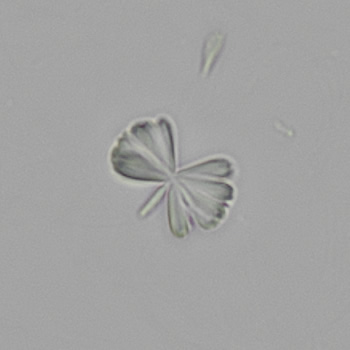
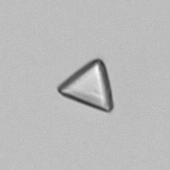
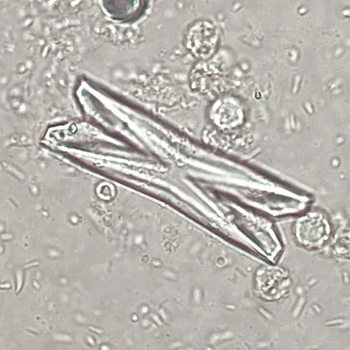
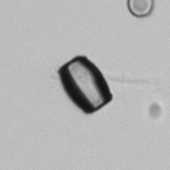
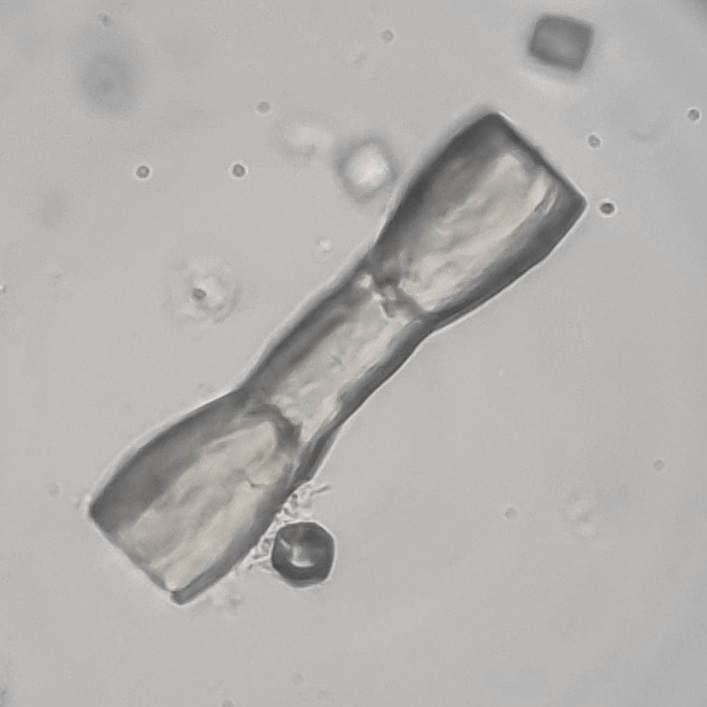
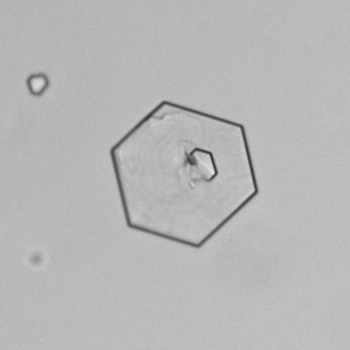
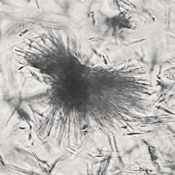
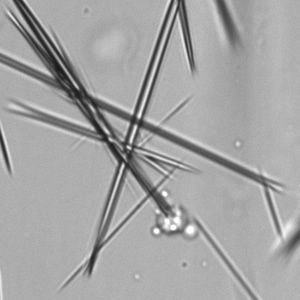
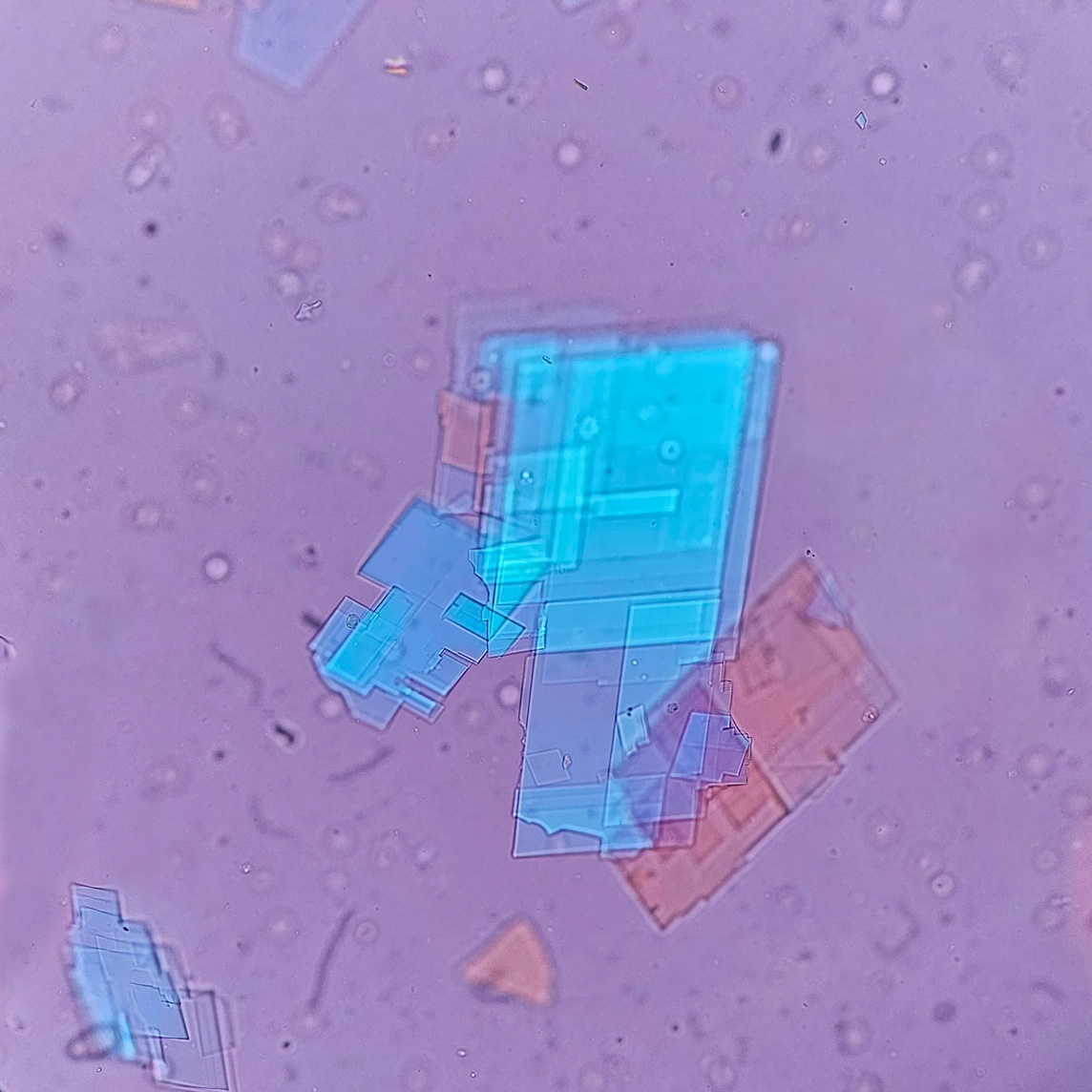
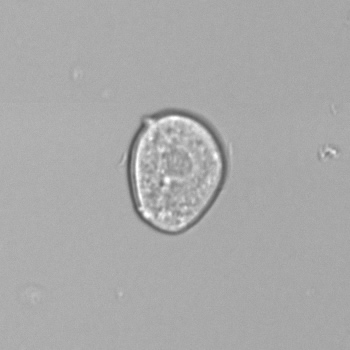
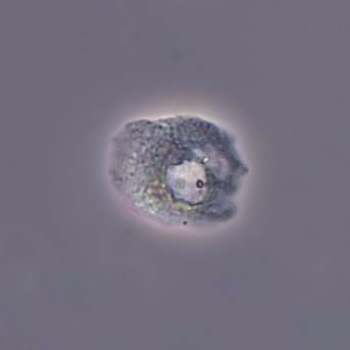
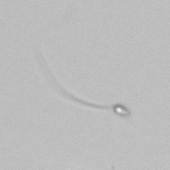
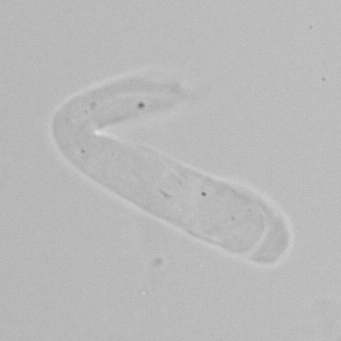
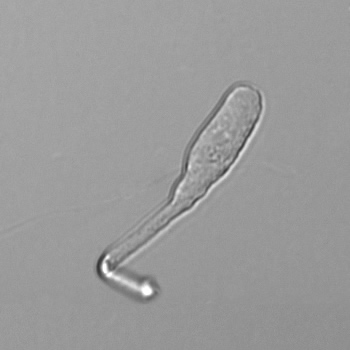
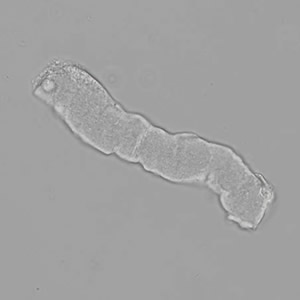
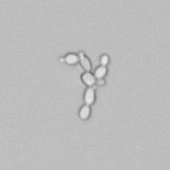
Microscopically, triple phosphate crystals usually have a recognizable coffin shape, but may also appear as trapezoids (triangle), elongated prisms, or rare fern and rosette-like structures. They are colorless, have moderate birefringence, and dissolve in dilute acetic acid.
Overview
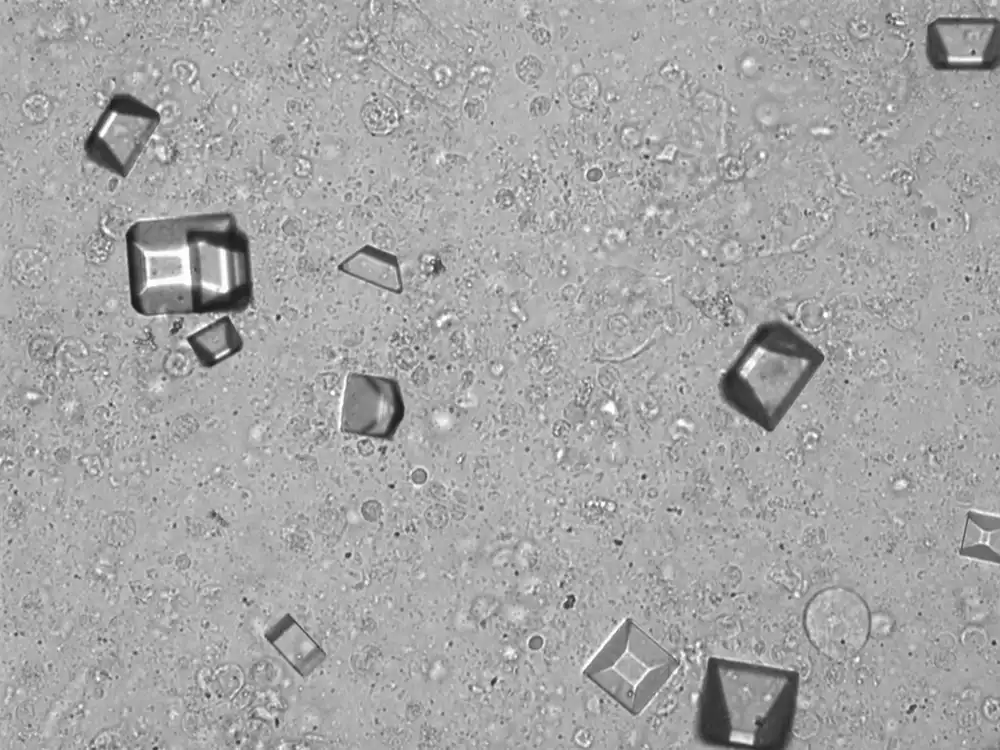

Technique