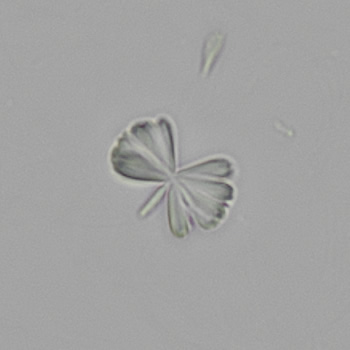
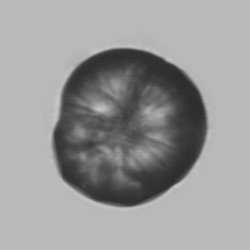
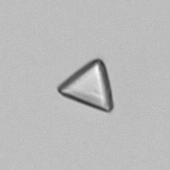
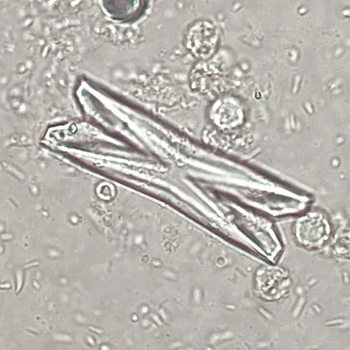
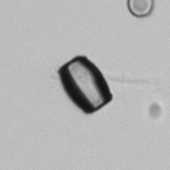
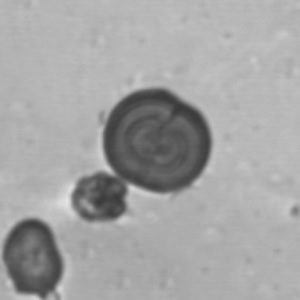
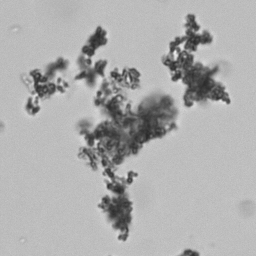
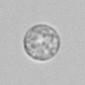
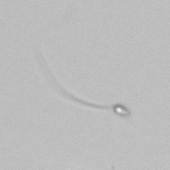
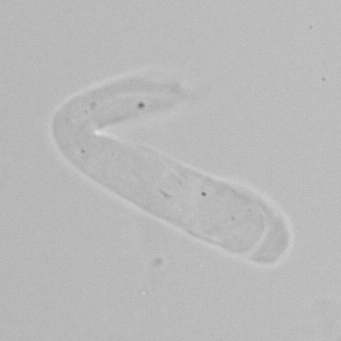
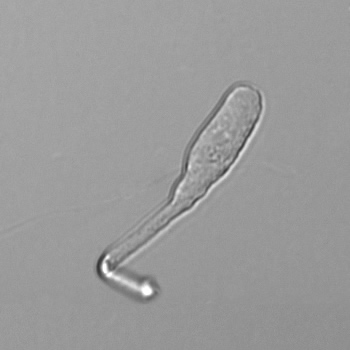
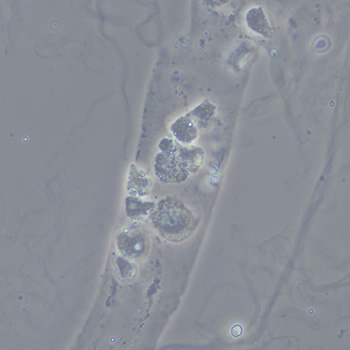
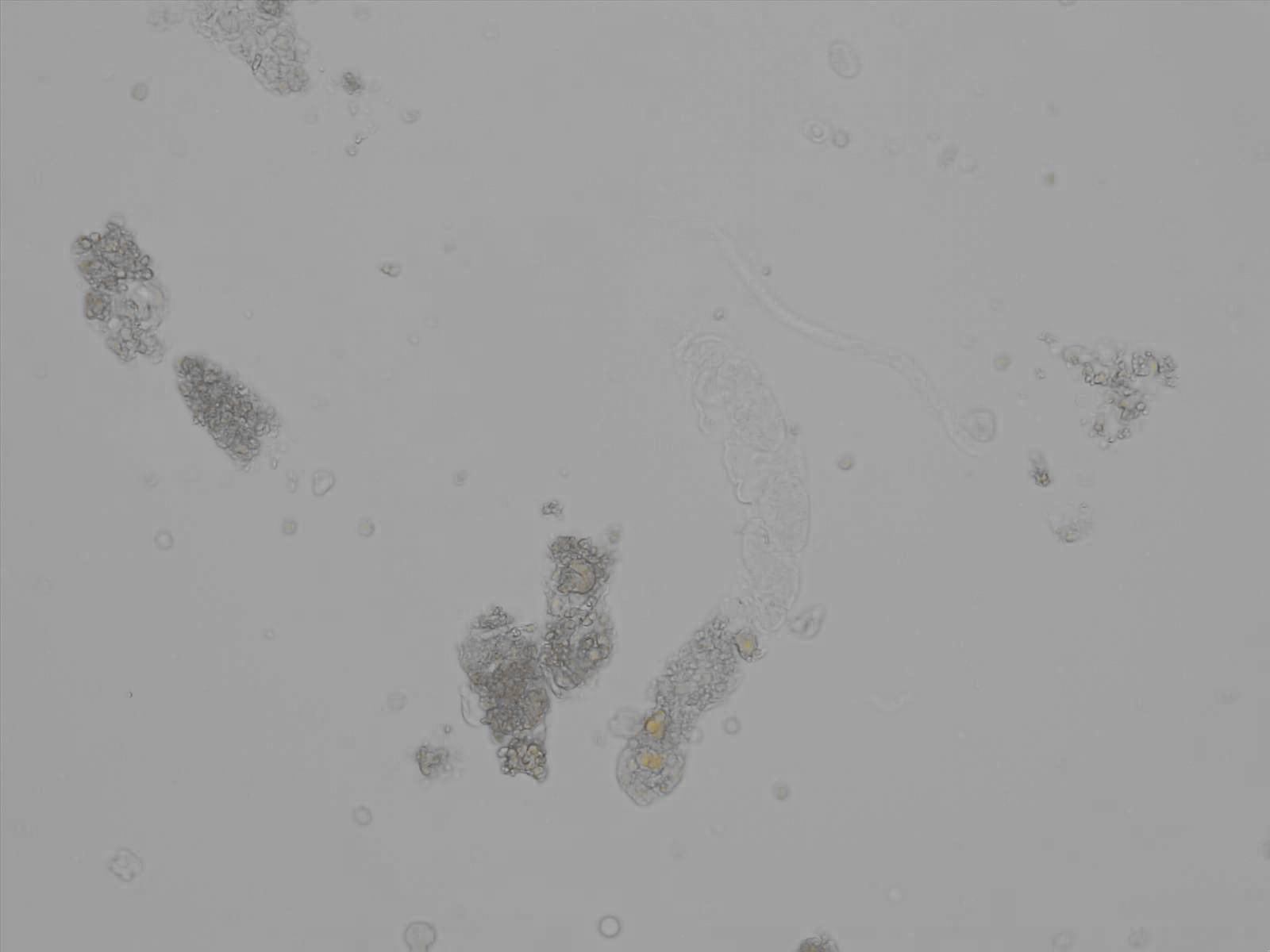
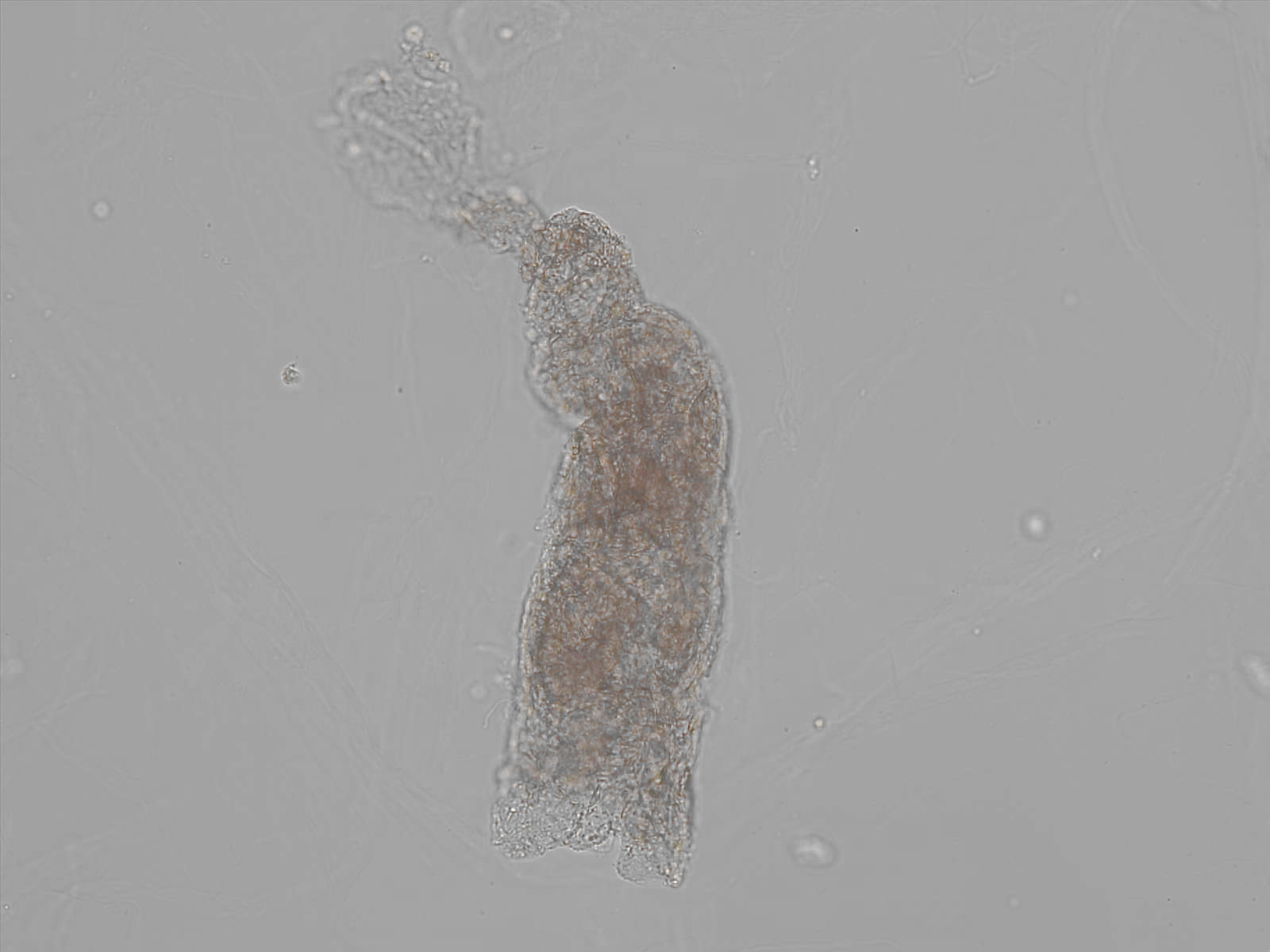
Granular cast
Synonyms: Granular cast
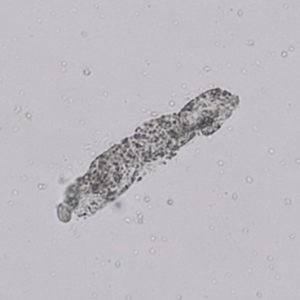
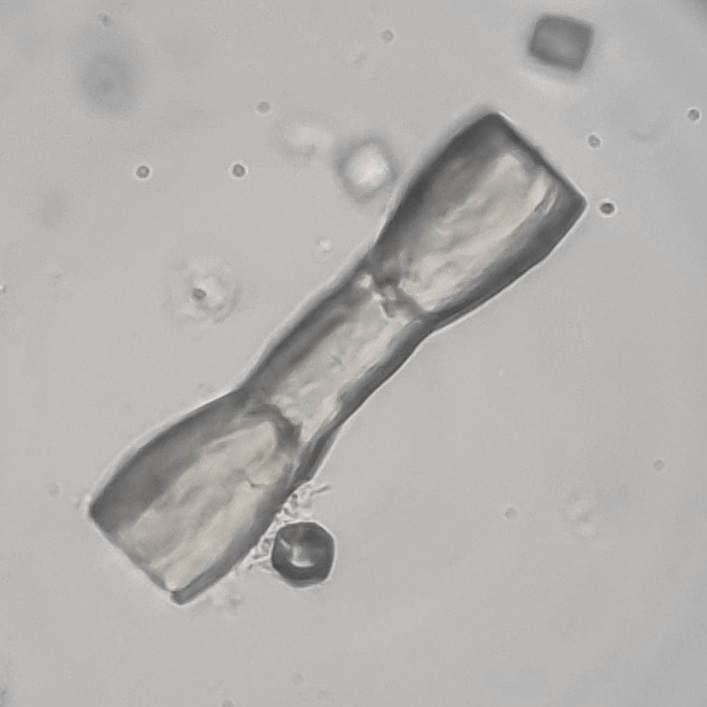
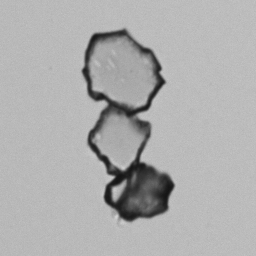
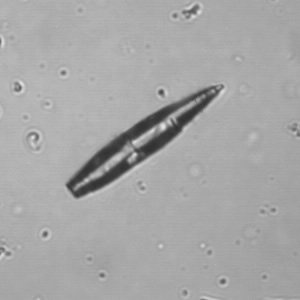
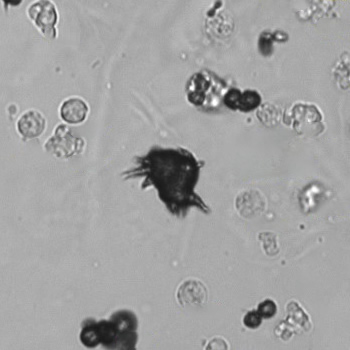
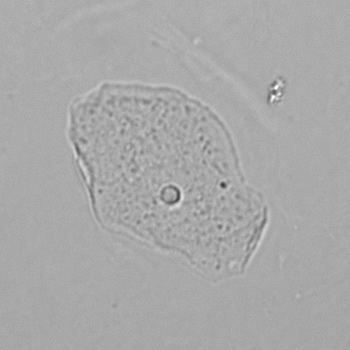
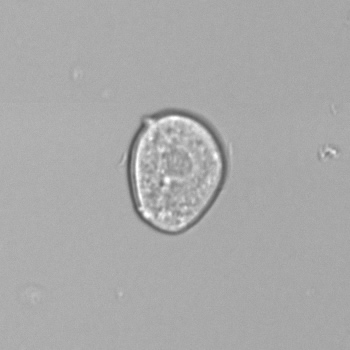
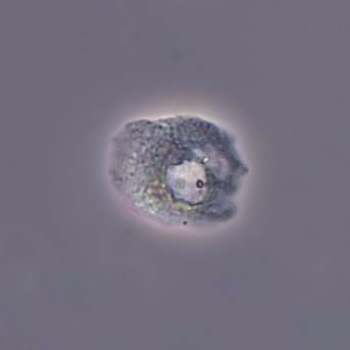
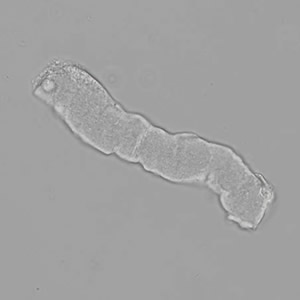
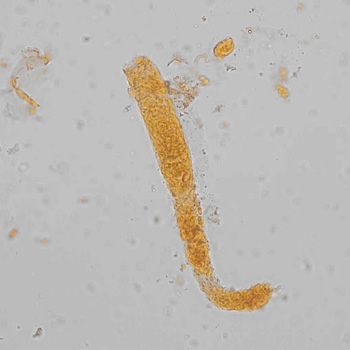
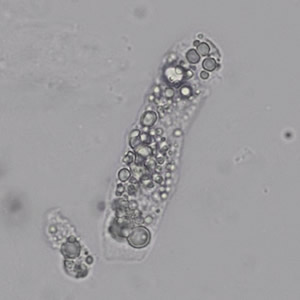
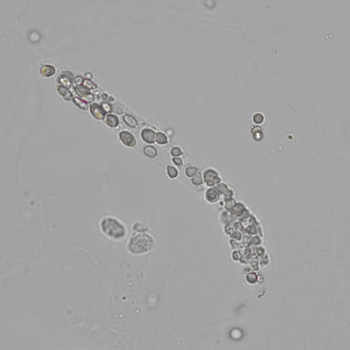
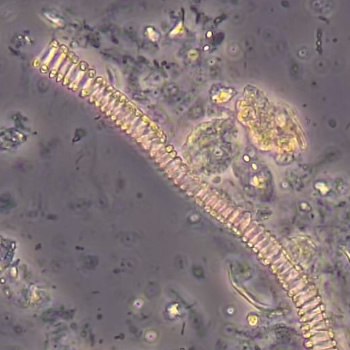
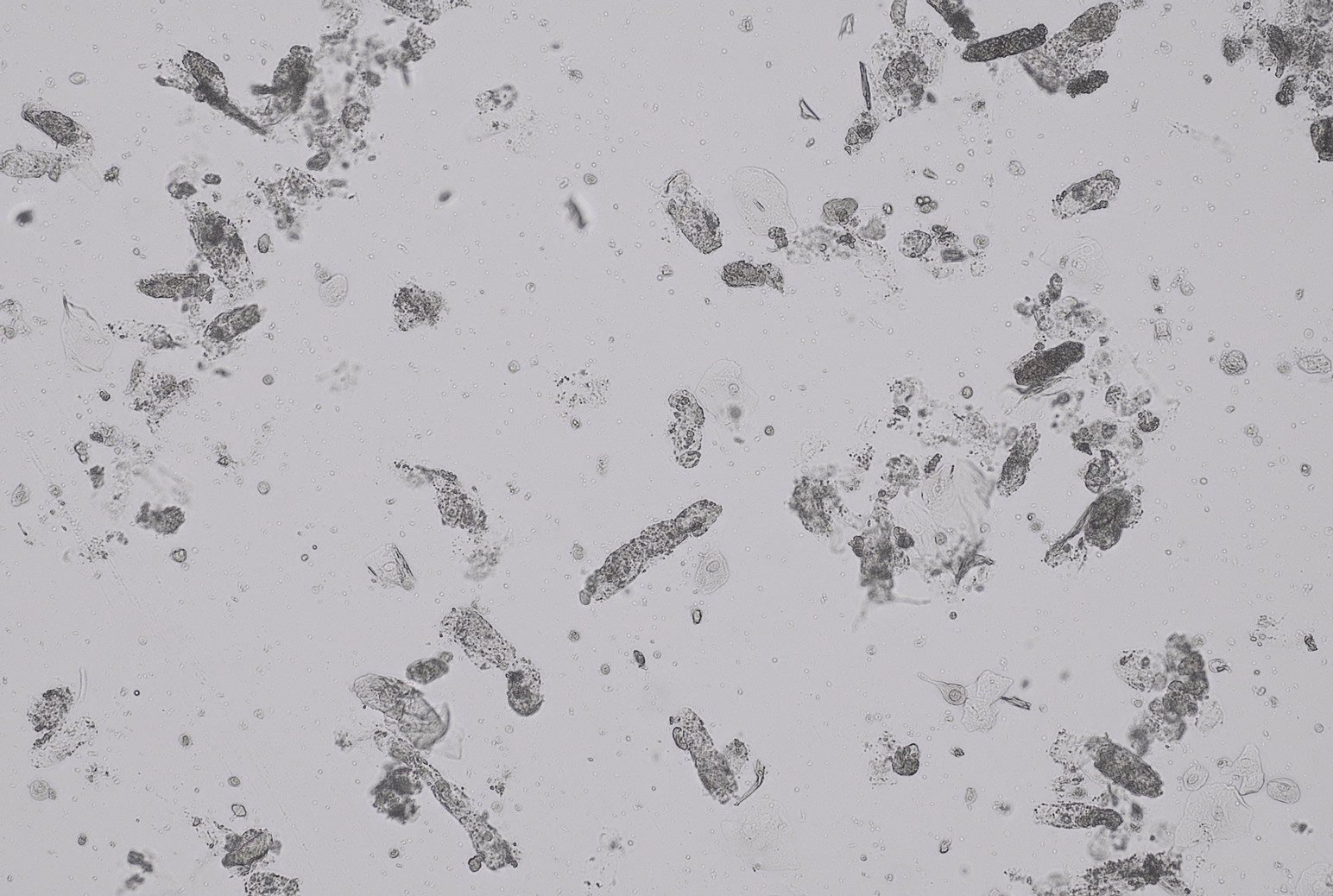
Casts are elongated structures formed in the renal tubules and composed mainly of uromodulin, also known as Tamm-Horsfall protein. This glycoprotein is secreted by cells in the ascending Lis of Henle and the distal tubule segment. The formation of casts is promoted by acidic pH and concentrated urine, conditions that allow the precipitation of uromodulin in a gel-like structure. During their formation, casts can enclose other components from the tubular fluid, such as cells, fat droplets or granular (granular) debris, creating different types of casts. In a sense, therefore, a cast can be considered a "biopsy" of the part of the tubule in which it is formed. Casts are visible microscopically, usually under bright-field microscopy, but their detection depends on their composition and transparency.
Grain casts are covered with granules that can be coarse or fine and vary in number and size. Fine granules usually consist of precipitated proteins, while coarse granules often arise from cellular degeneration of cells such as renal tubular epithelial cells, leukocytes or erythrocytes. They are seen almost exclusively in patients with renal disease, such as acute tubular necrosis, with or without renal tubular epithelial cell casts, or in glomerulonephritis. The demonstration of granule casts is therefore always pathologic.