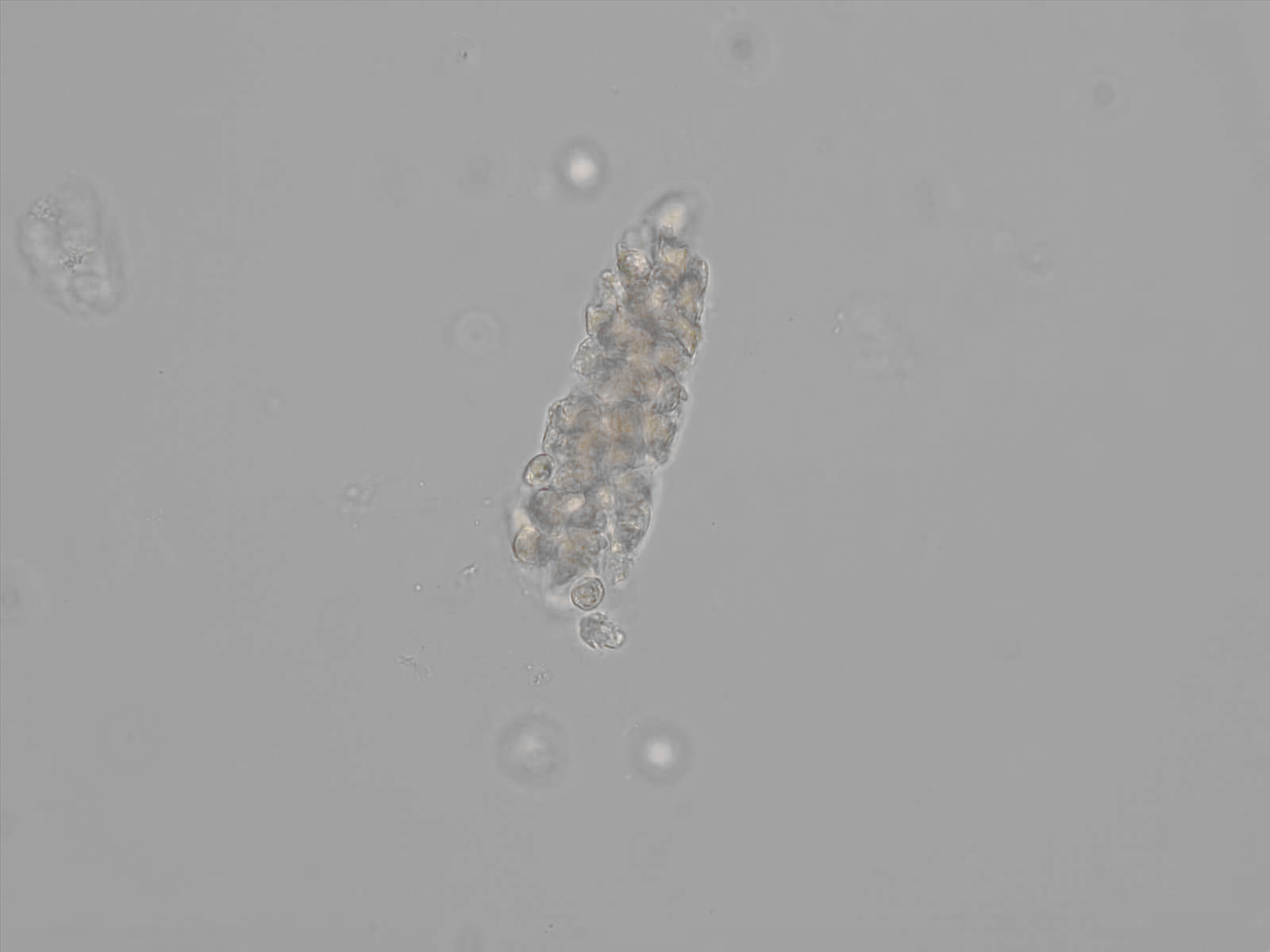
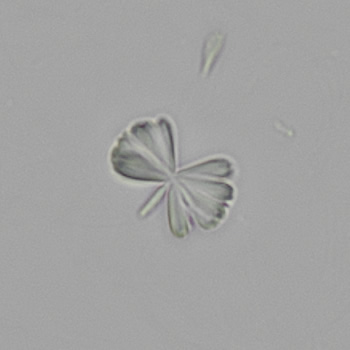
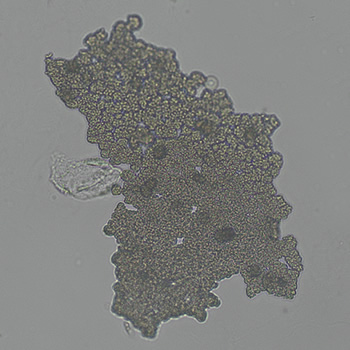
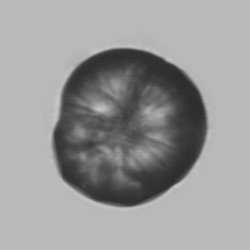
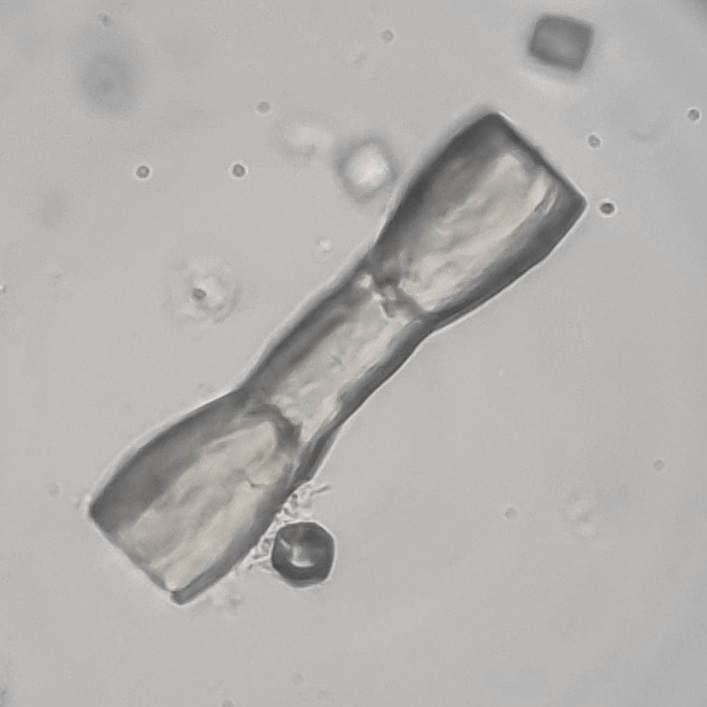
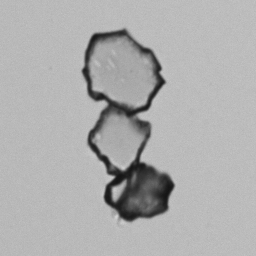
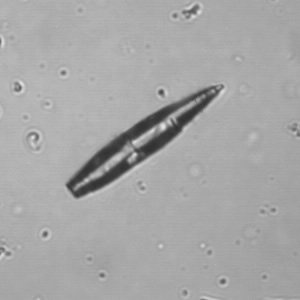
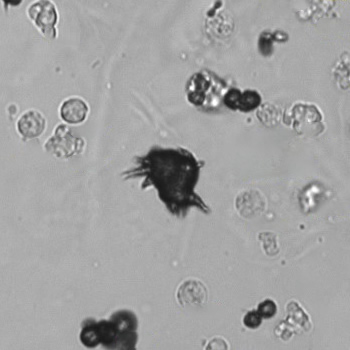
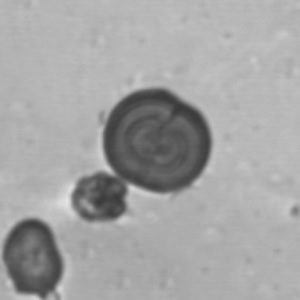
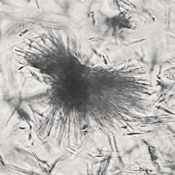
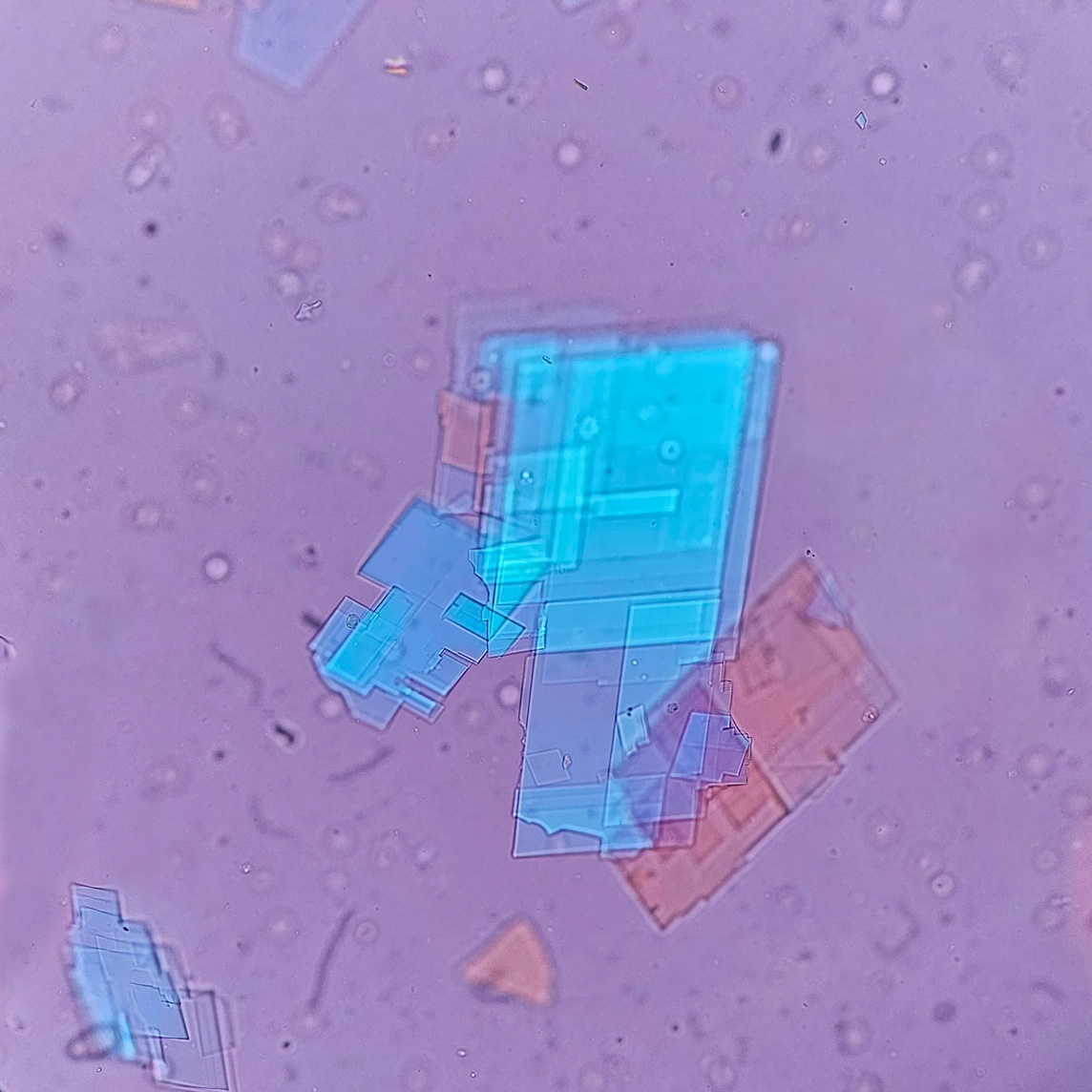
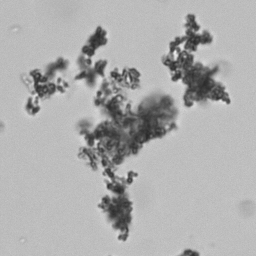
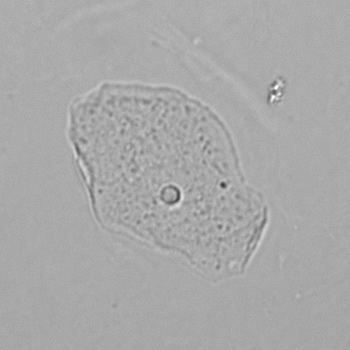
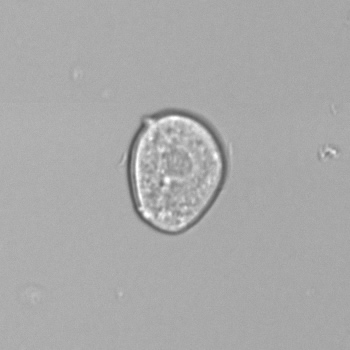
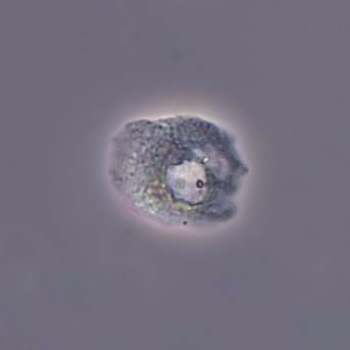
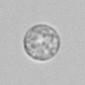
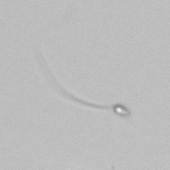
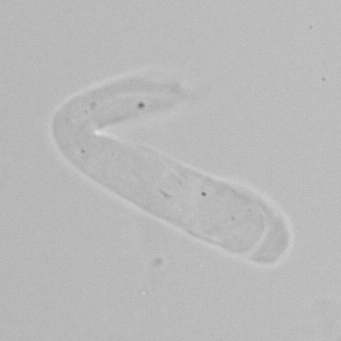
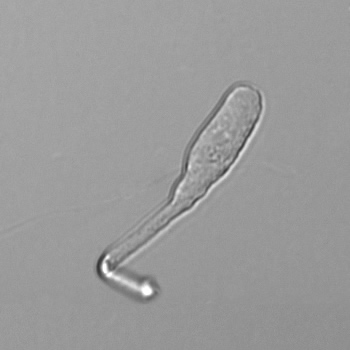
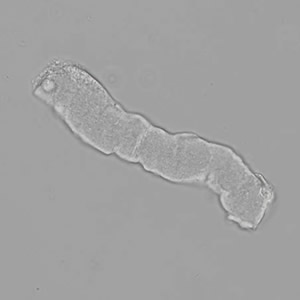
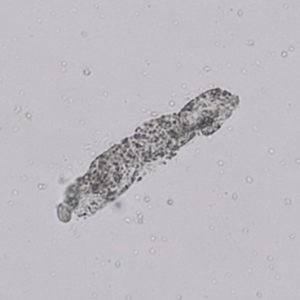
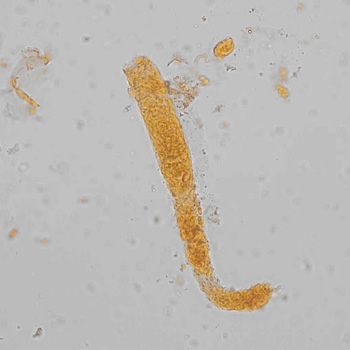
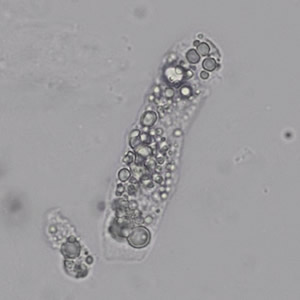
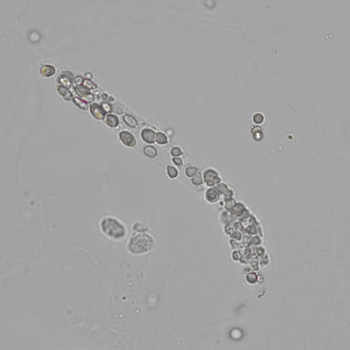
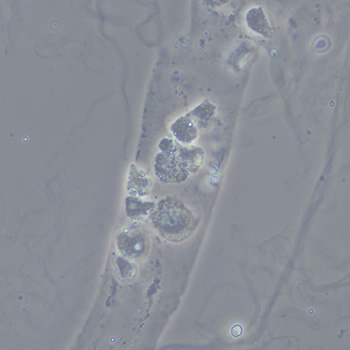
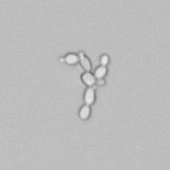
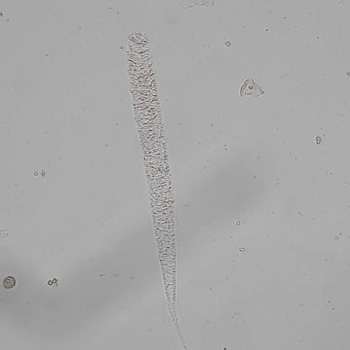
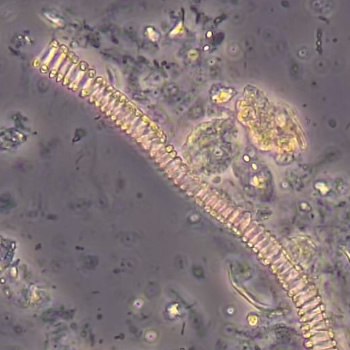
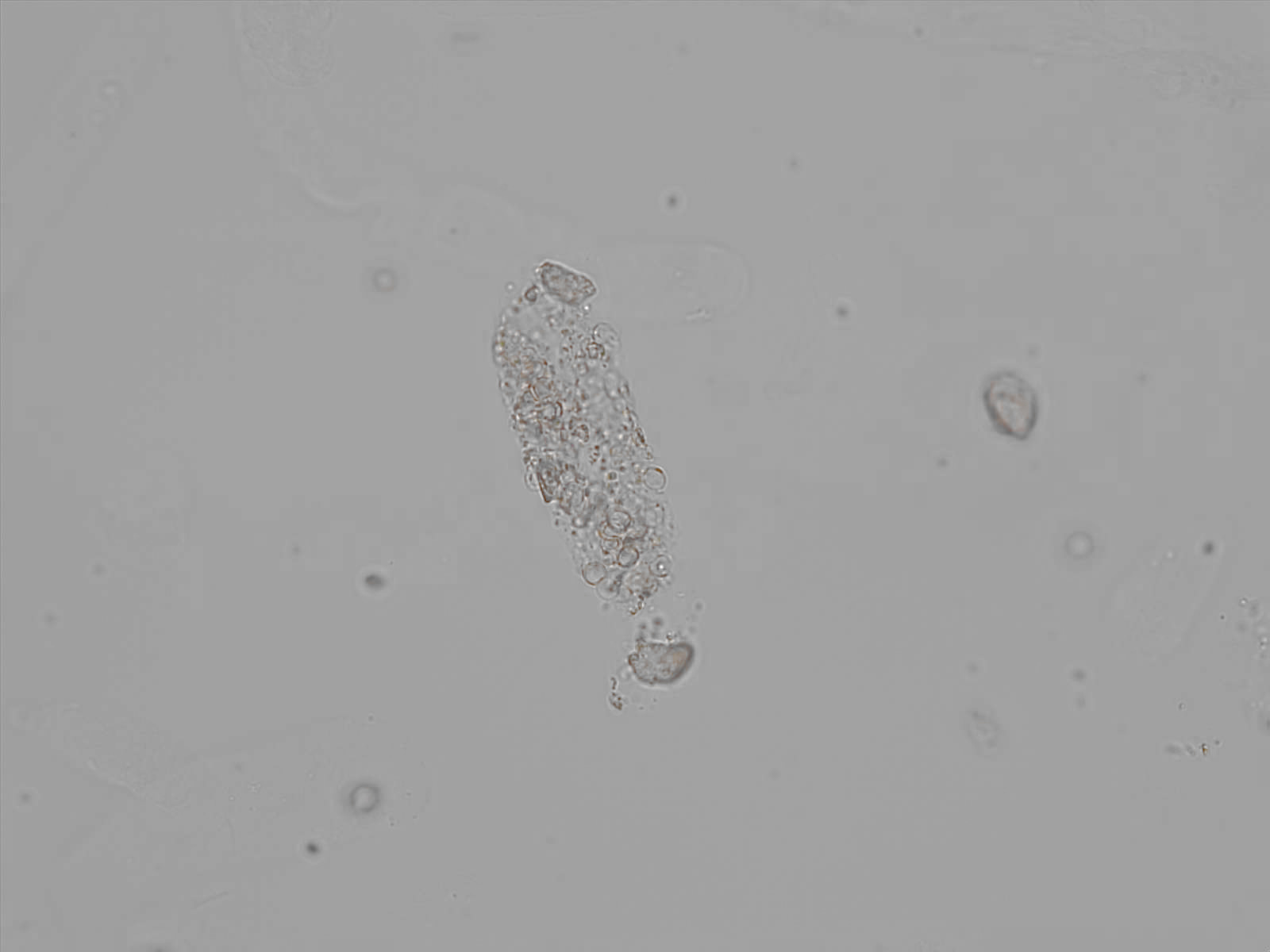
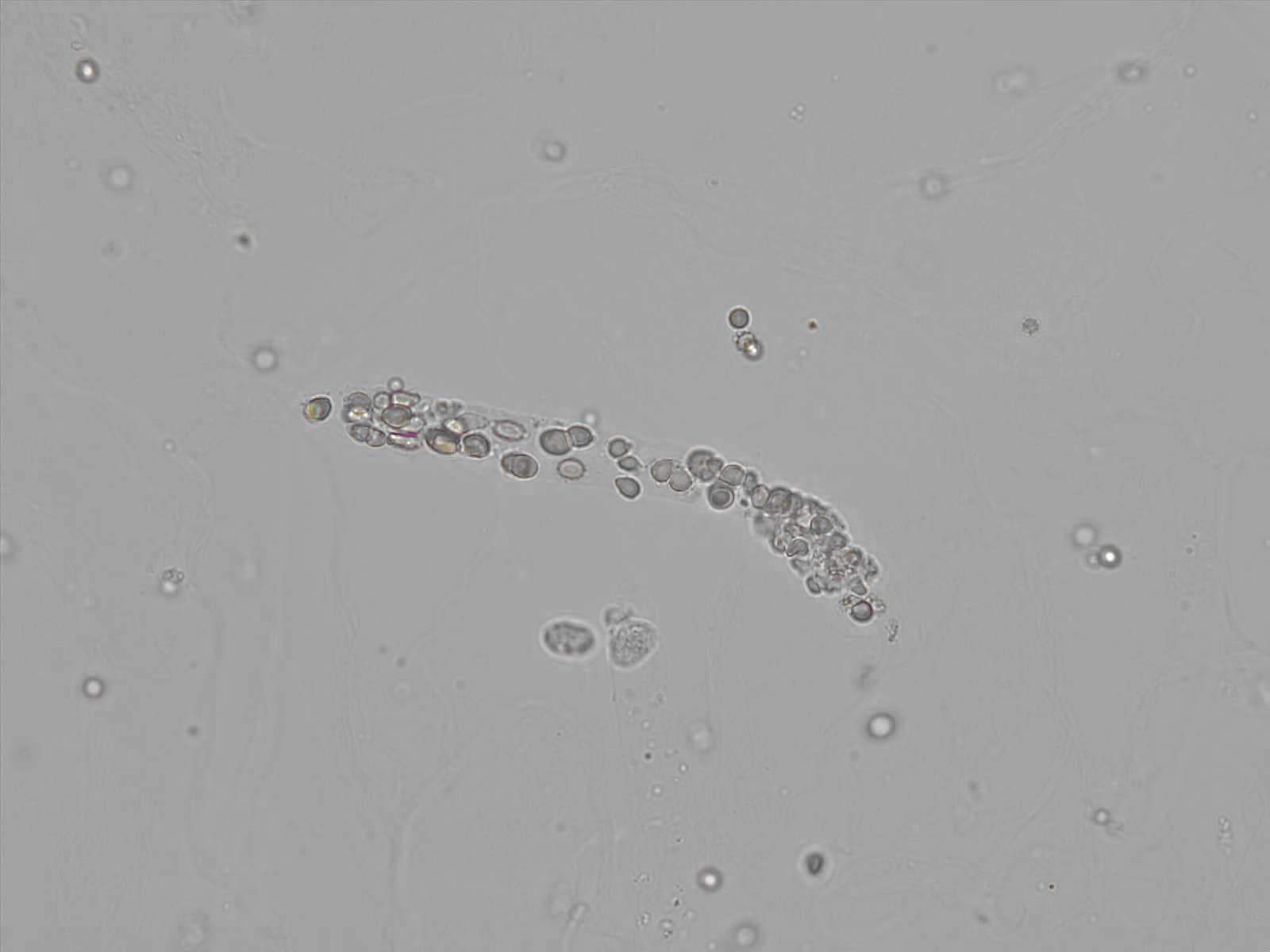
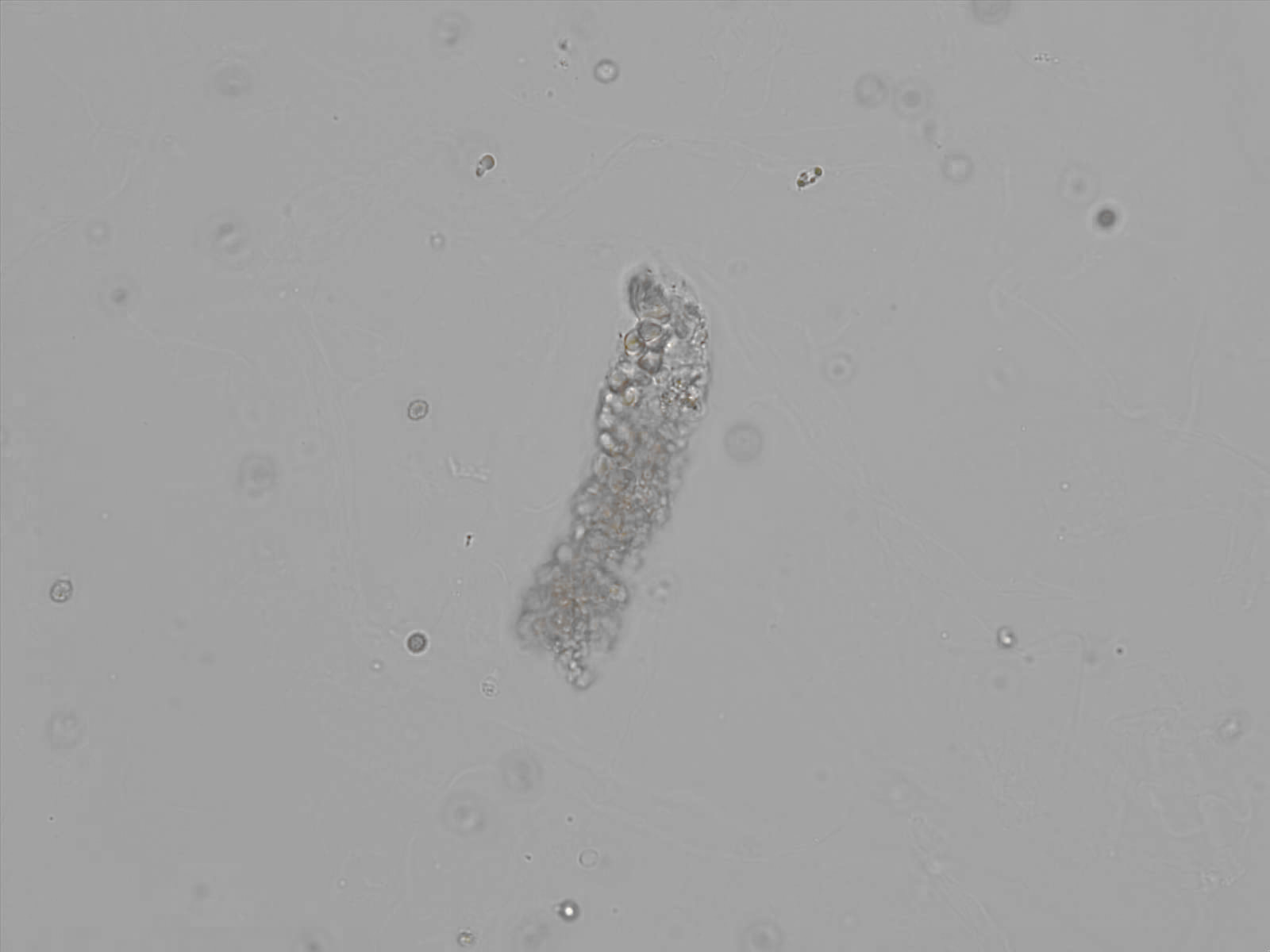
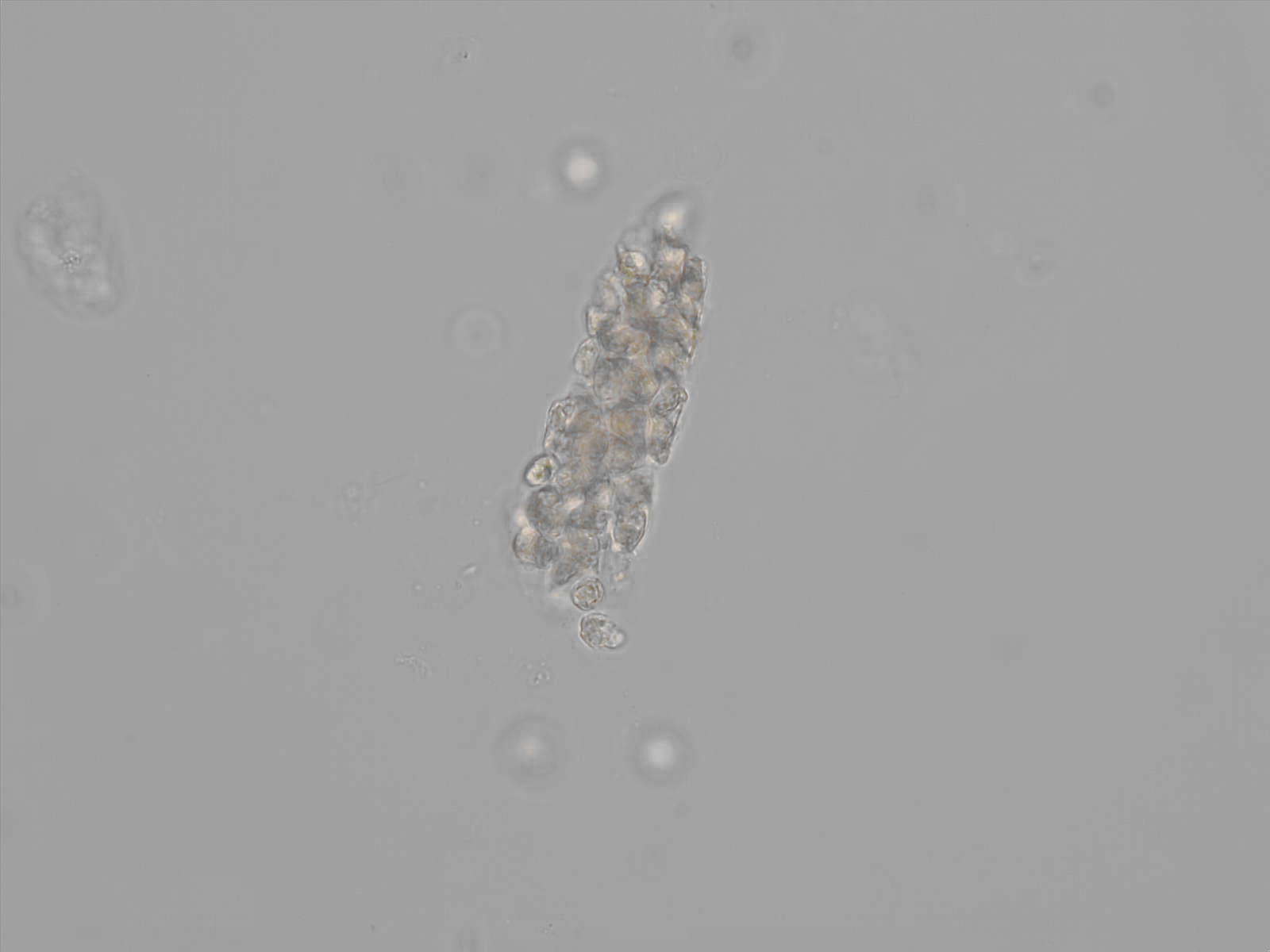
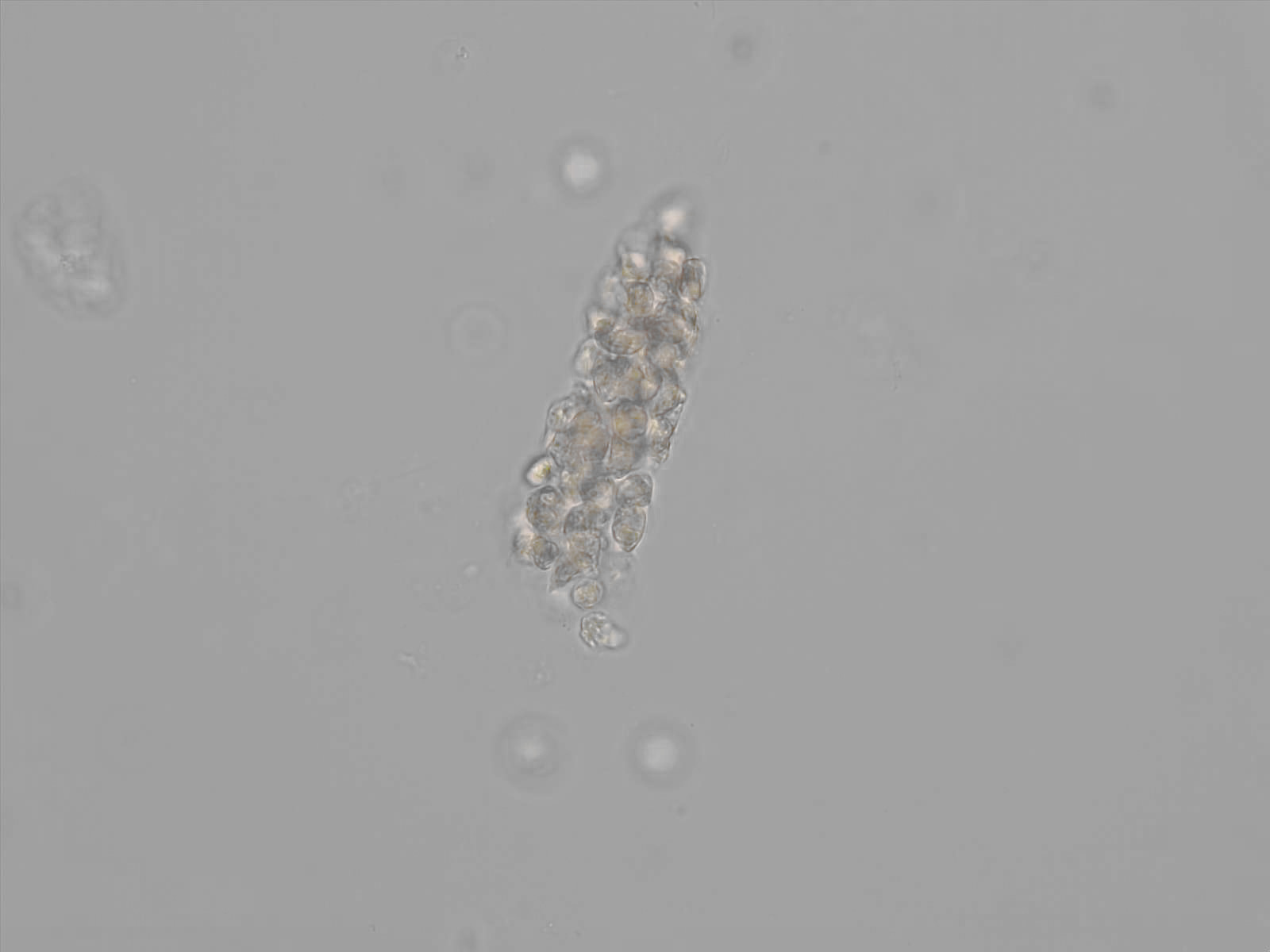
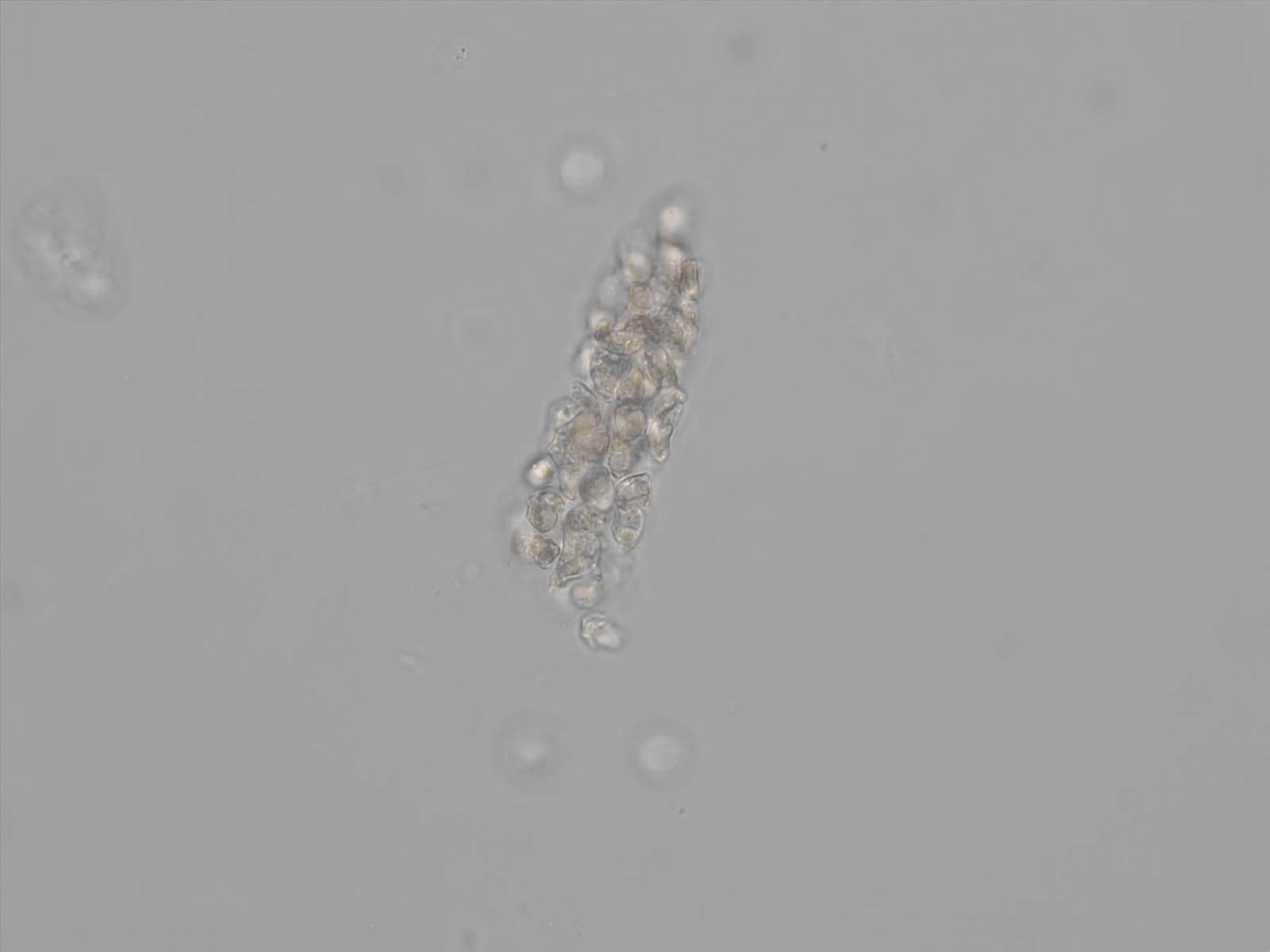
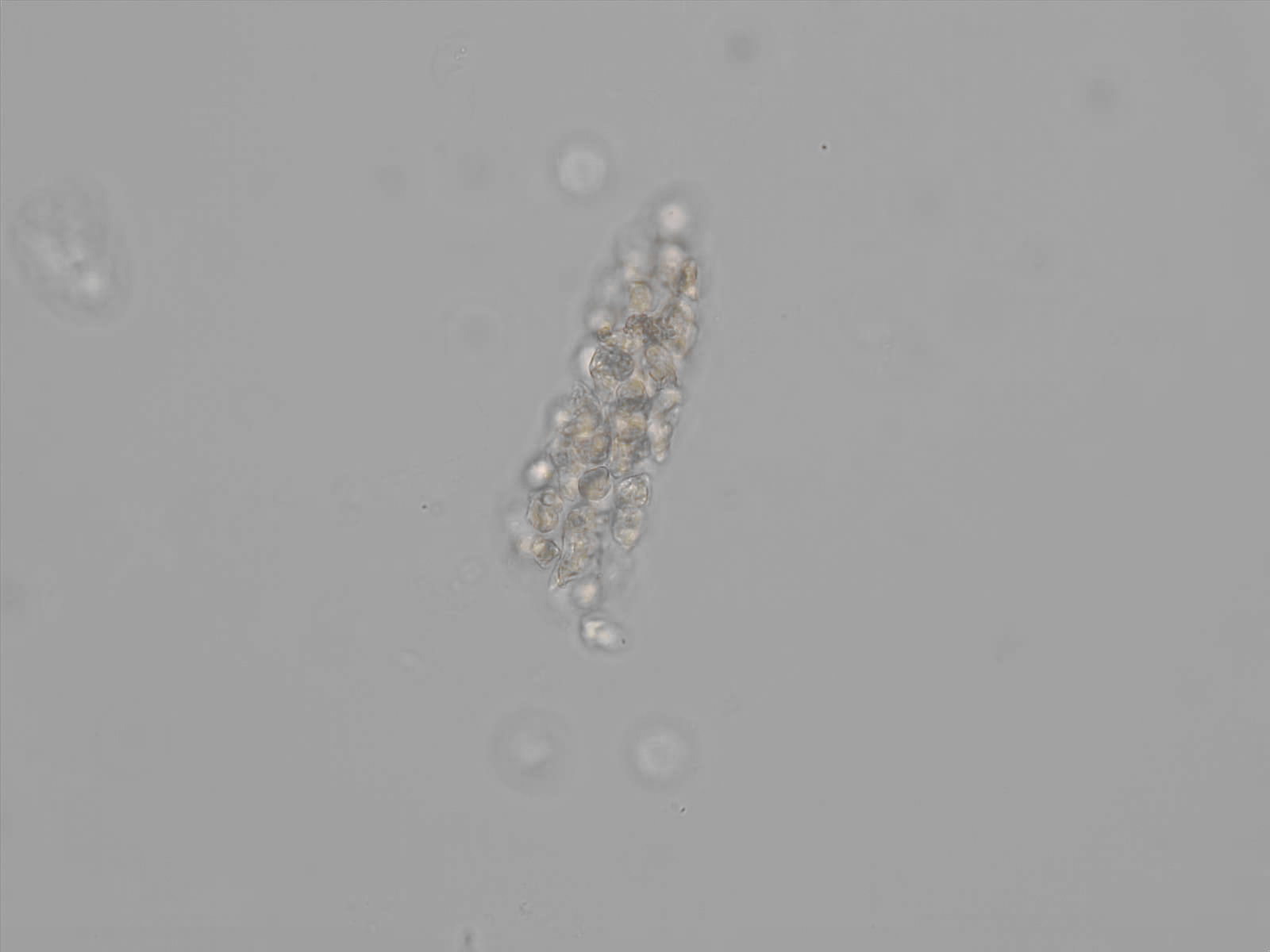
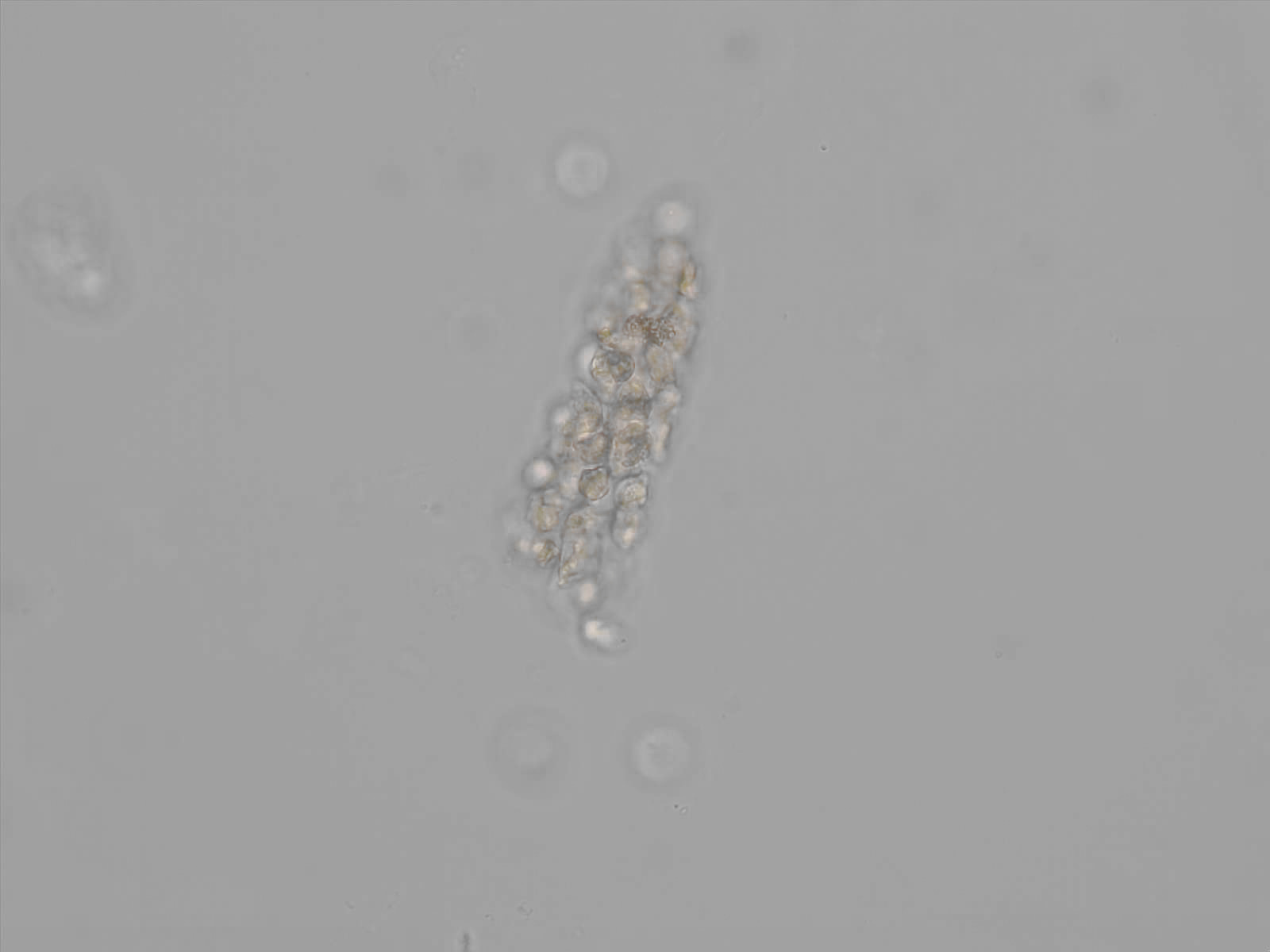
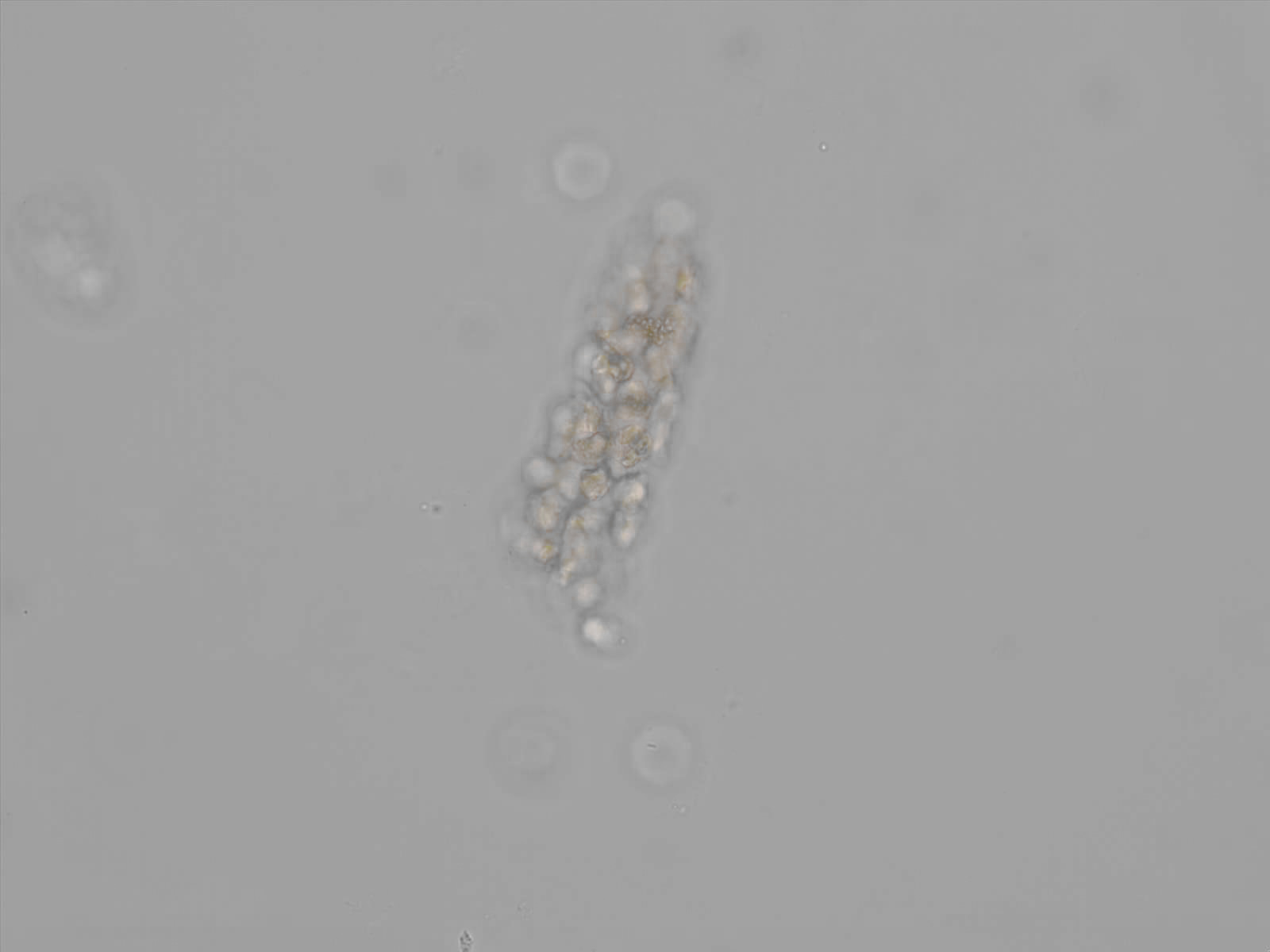
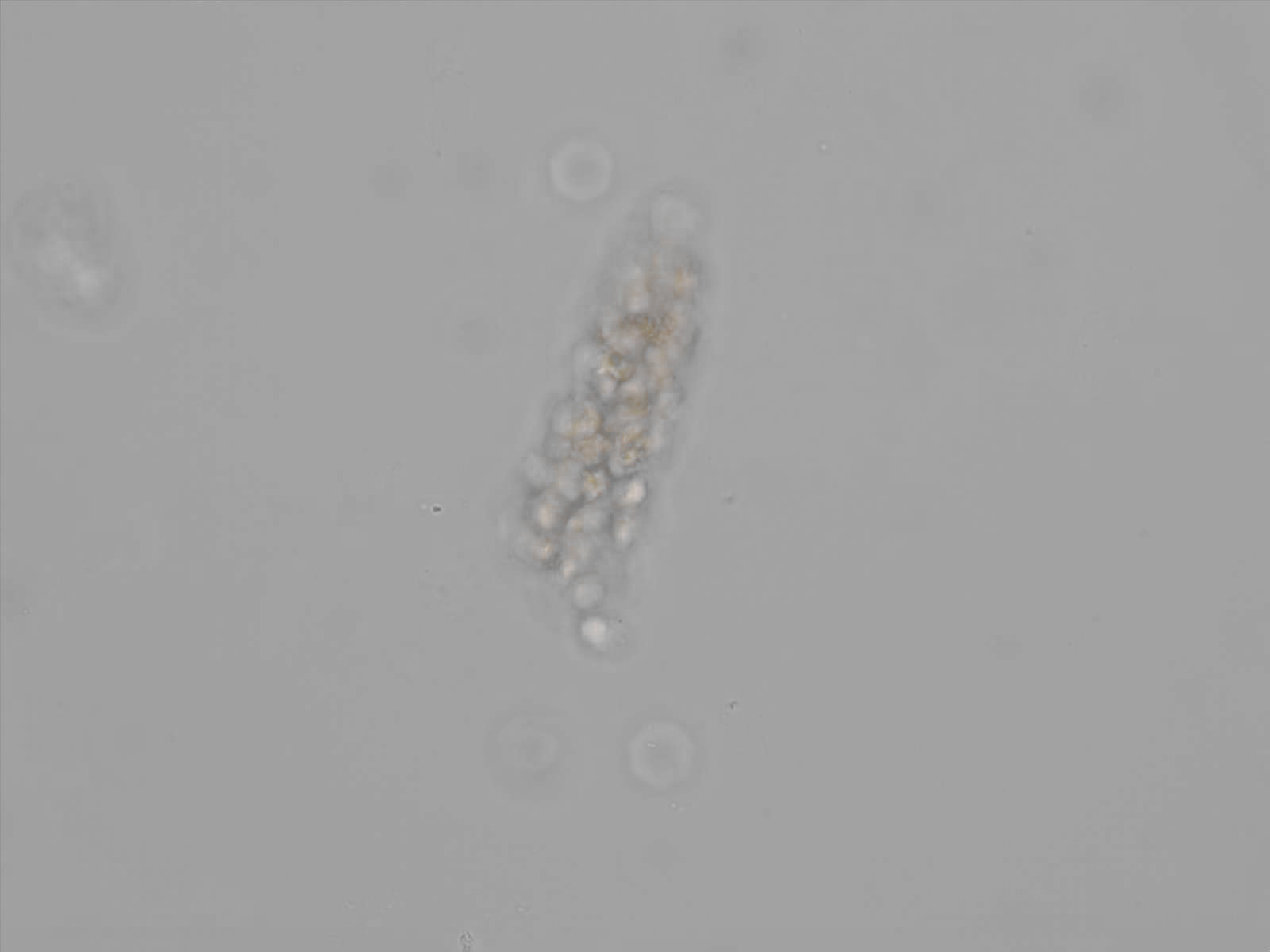
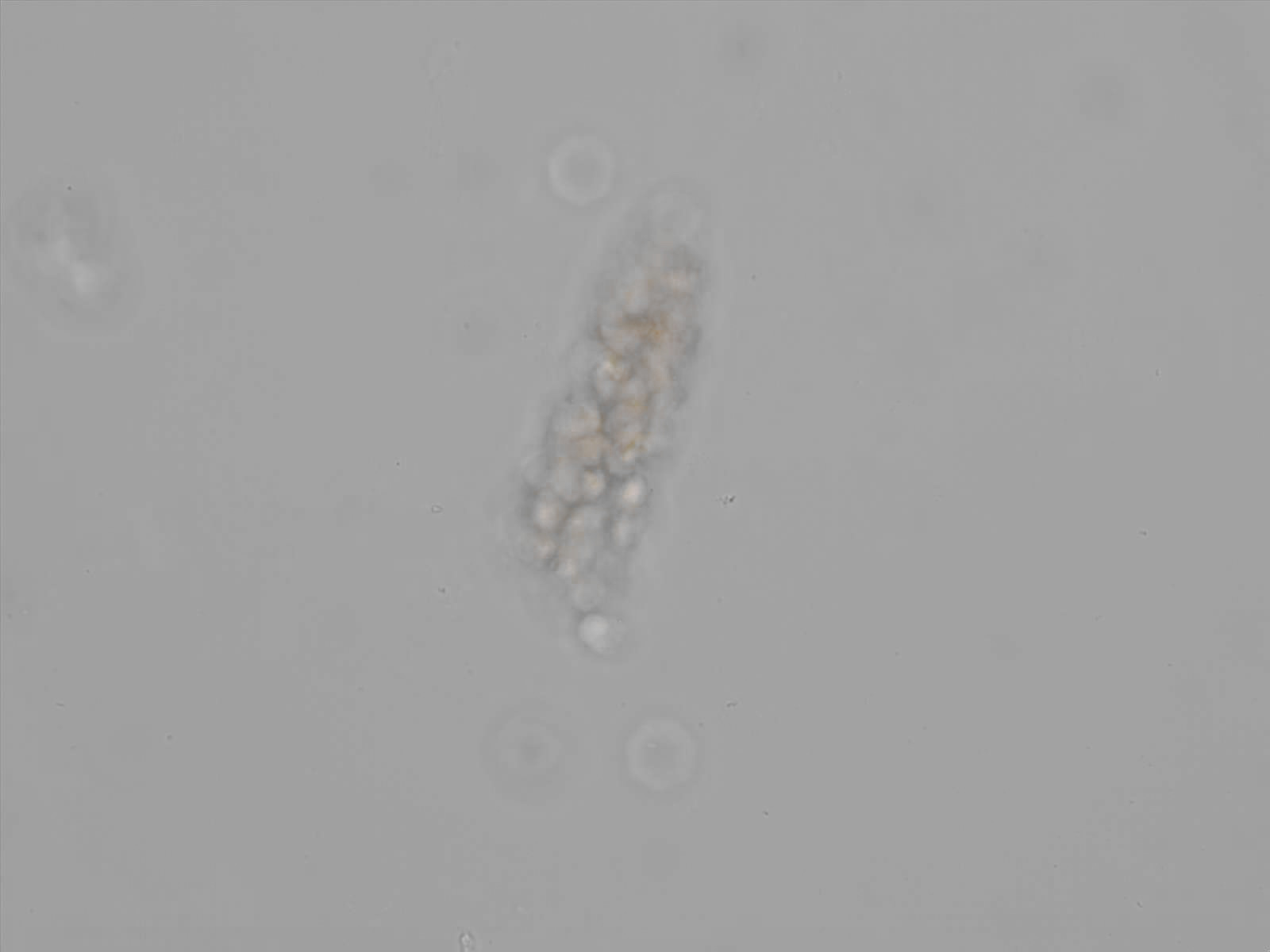
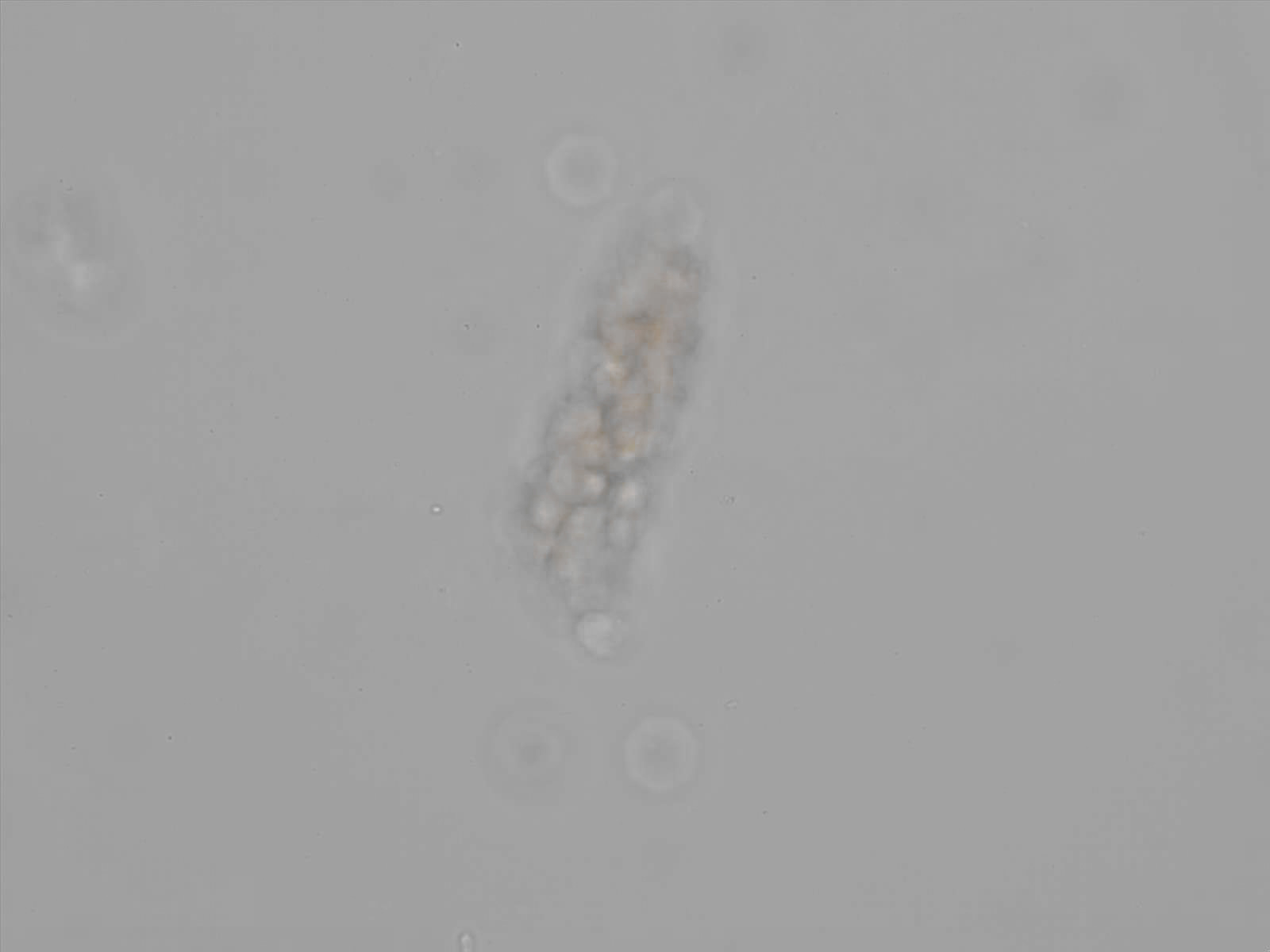
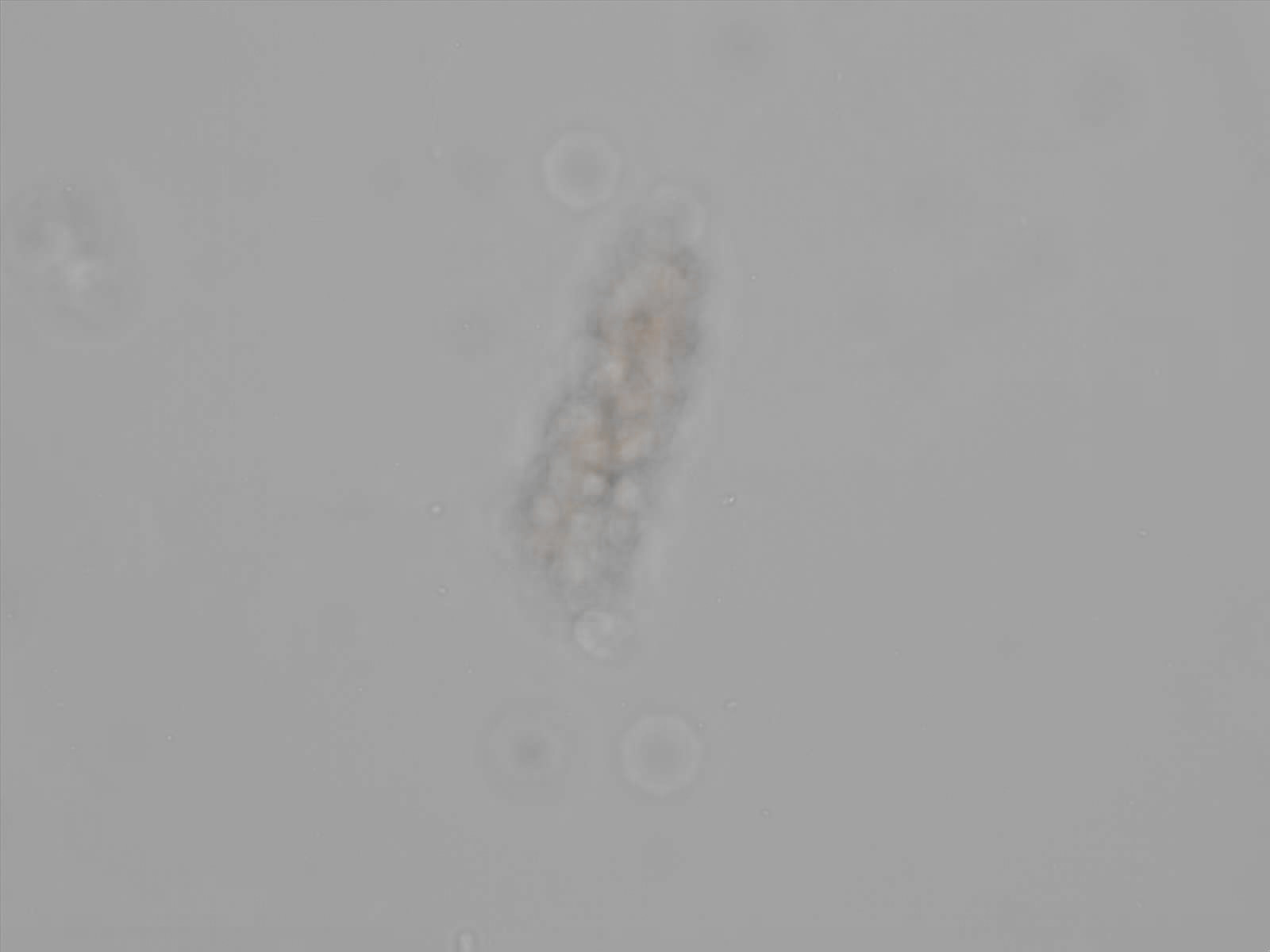
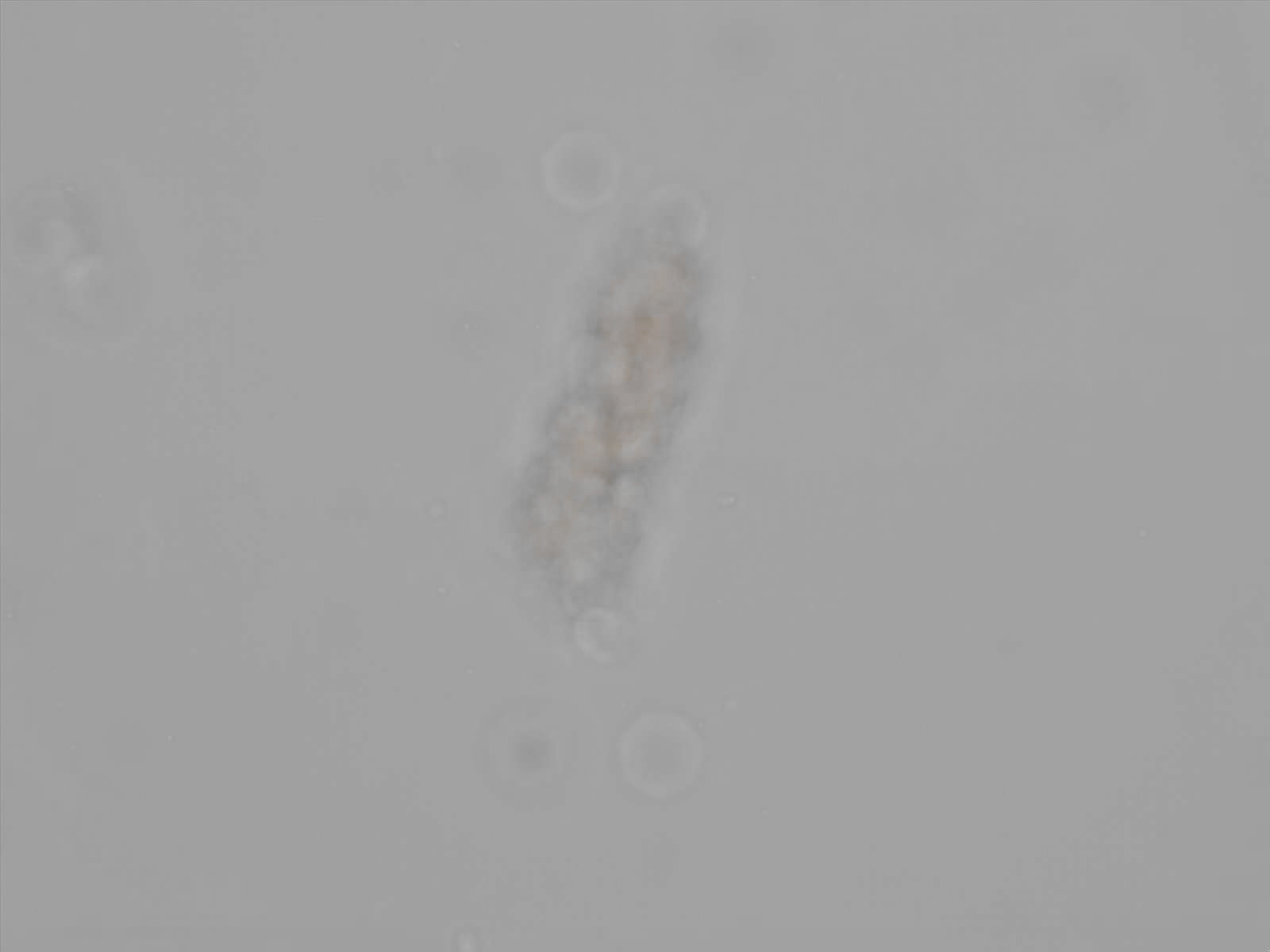
Erythrocyte cast
Pathological
Erythrocyte casts form when red blood cells in the tubule become trapped in a matrix of uromodulin. The erythrocytes may be compactly trapped or loosely embedded in the hyaline cast. The erythrocytes in the cast may contain normal and/or reduced levels of hemoglobin. The detection of erythrocyte cast is probative of hemorrhage of glomerular origin and is considered a strong indicator of active glomerular damage, such as in glomerulonephritis. It is important to pay attention to this in patients with isolated microscopic hematuria of unknown cause. Along with dysmorphic erythrocytes, erythrocyte casts are characteristic of a nephritic sediment. The decay of erythrocytes in the cast results in so-called hemoglobin casts, which have the same diagnostic value as erythrocyte casts. Although rare, erythrocyte casts can also occur in acute interstitial nephritis.
Technique


Cross section